Batch settlement processes multiple transactions together at scheduled intervals, reducing processing costs but delaying funds availability. Real-time settlement completes each transaction instantly, offering immediate fund transfer and enhanced cash flow management. Choosing between batch and real-time settlement depends on business needs for speed, cost efficiency, and liquidity control.
Table of Comparison
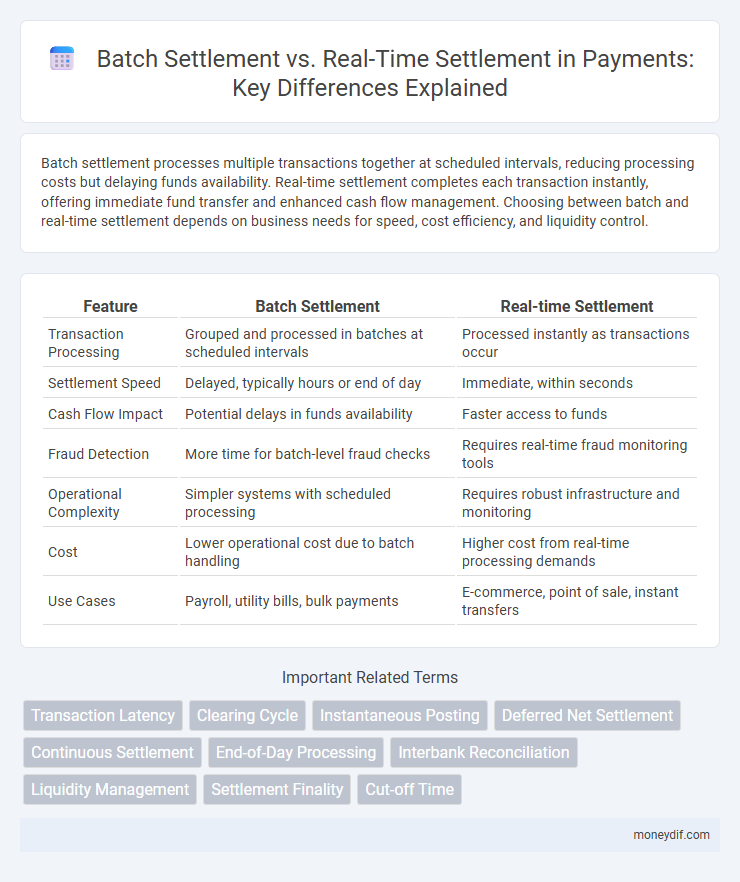
| Feature | Batch Settlement | Real-time Settlement |
|---|---|---|
| Transaction Processing | Grouped and processed in batches at scheduled intervals | Processed instantly as transactions occur |
| Settlement Speed | Delayed, typically hours or end of day | Immediate, within seconds |
| Cash Flow Impact | Potential delays in funds availability | Faster access to funds |
| Fraud Detection | More time for batch-level fraud checks | Requires real-time fraud monitoring tools |
| Operational Complexity | Simpler systems with scheduled processing | Requires robust infrastructure and monitoring |
| Cost | Lower operational cost due to batch handling | Higher cost from real-time processing demands |
| Use Cases | Payroll, utility bills, bulk payments | E-commerce, point of sale, instant transfers |
Introduction to Payment Settlement Methods
Batch settlement processes multiple payment transactions collectively at scheduled intervals, reducing processing costs and simplifying reconciliation for merchants. Real-time settlement enables immediate transfer of funds upon transaction approval, enhancing cash flow and providing faster confirmation to customers. Payment settlement methods vary based on business needs, transaction volume, and the requirement for speed or cost efficiency in financial operations.
Defining Batch Settlement
Batch settlement is a payment processing method where multiple transactions are accumulated and processed collectively at scheduled intervals, typically at the end of the business day. This approach reduces transaction fees and operational overhead by consolidating payments into a single batch, enhancing efficiency for merchants and financial institutions. Batch settlement contrasts with real-time settlement by delaying fund transfers, which may impact cash flow and transaction finality.
Understanding Real-time Settlement
Real-time settlement processes financial transactions instantly, reducing credit risk by ensuring immediate fund transfers between parties. Unlike batch settlement, which accumulates and processes payments in bulk at scheduled intervals, real-time settlement enhances cash flow management and operational efficiency for businesses and banks. This method supports faster transaction confirmation, critical for industries requiring immediate payment finality such as retail and e-commerce.
Key Differences Between Batch and Real-time Settlement
Batch settlement processes multiple transactions simultaneously at scheduled intervals, reducing transaction fees but delaying fund availability. Real-time settlement finalizes transactions instantly, providing immediate fund access and improved cash flow, essential for time-sensitive payments. The choice impacts liquidity management, operational efficiency, and customer experience in payment processing systems.
Advantages of Batch Settlement
Batch settlement reduces transaction processing costs by consolidating multiple payments into a single transaction, improving operational efficiency for businesses. It enables easier reconciliation and fewer settlement errors due to the aggregation of payment data, which streamlines accounting processes. Batch settlement also offers predictable cash flow management by allowing scheduled processing times, enhancing financial planning accuracy.
Benefits of Real-time Settlement for Businesses
Real-time settlement offers businesses immediate fund transfer, enhancing cash flow management and reducing credit risk compared to batch settlement. It enables instant transaction confirmation, improving customer satisfaction and operational efficiency. Access to real-time data supports accurate financial reporting and quicker decision-making.
Challenges of Batch and Real-time Settlement
Batch settlement faces challenges including delayed fund availability, increased risk of failed transactions due to processing large volumes simultaneously, and limited transparency for merchants and consumers. Real-time settlement struggles with high operational costs, the need for robust infrastructure to handle continuous transactions, and potential security vulnerabilities from instant processing. Both methods must balance trade-offs between speed, cost, and reliability to optimize payment system performance.
Use Cases for Batch Settlement
Batch settlement is ideal for high-volume retail merchants and utility companies processing numerous transactions daily, where consolidating settlements reduces operational costs and simplifies reconciliation. It suits environments with predictable transaction patterns, such as payroll disbursements or subscription services, enabling scheduled processing at specific intervals. This approach optimizes cash flow management and lowers the risk of settlement errors by aggregating multiple transactions into a single settlement event.
When to Choose Real-time Settlement
Real-time settlement is ideal for high-value transactions requiring immediate fund transfers and instant confirmation, such as online retail and emergency payments. It enhances cash flow management by reducing settlement delays and minimizing credit risk for merchants. Businesses prioritizing customer trust and rapid transaction finality benefit significantly from real-time settlement systems.
Future Trends in Payment Settlement Methods
Future trends in payment settlement methods emphasize increasing adoption of real-time settlement systems, driven by the demand for instant fund transfers and enhanced liquidity management. Batch settlement remains relevant for processing large volumes of transactions efficiently but is gradually supplemented by real-time platforms leveraging blockchain and distributed ledger technologies to ensure transparency and reduce settlement risks. The proliferation of open banking APIs and regulatory frameworks like PSD2 are accelerating innovation toward seamless, faster payment experiences across global markets.
Important Terms
Transaction Latency
Batch settlement increases transaction latency by processing payments in grouped intervals, while real-time settlement minimizes latency by confirming transactions instantly.
Clearing Cycle
Clearing cycle duration significantly differs between batch settlement, which processes transactions in scheduled intervals, and real-time settlement, which completes transactions instantly to reduce settlement risk.
Instantaneous Posting
Instantaneous posting enables real-time settlement by immediately updating transactions, contrasting with batch settlement that processes multiple transactions collectively at scheduled intervals.
Deferred Net Settlement
Deferred Net Settlement processes multiple transactions in batches, reducing liquidity demands compared to Real-time Settlement, which settles each transaction individually and instantly.
Continuous Settlement
Continuous settlement processes transactions immediately upon execution, contrasting with batch settlement that accumulates transactions for periodic processing and real-time settlement that finalizes transactions instantly to enhance liquidity and reduce counterparty risk.
End-of-Day Processing
End-of-Day Processing consolidates Batch Settlement by grouping transactions for overnight verification, contrasting with Real-time Settlement that processes payments instantly to enhance liquidity and reduce counterparty risk.
Interbank Reconciliation
Interbank reconciliation ensures accurate matching of transactions by comparing batch settlement, which processes payments in scheduled intervals, with real-time settlement that instantaneously clears transactions to reduce settlement risk.
Liquidity Management
Liquidity management improves cash flow efficiency by comparing batch settlement's delayed fund availability with real-time settlement's immediate transaction finality.
Settlement Finality
Batch settlement processes multiple transactions collectively at scheduled intervals, enhancing operational efficiency but increasing settlement risk, while real-time settlement executes transactions immediately, reducing counterparty risk and improving liquidity management.
Cut-off Time
Cut-off time determines the latest moment for processing transactions in batch settlement, while real-time settlement processes transactions instantly without waiting for any cut-off.
Batch Settlement vs Real-time Settlement Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com