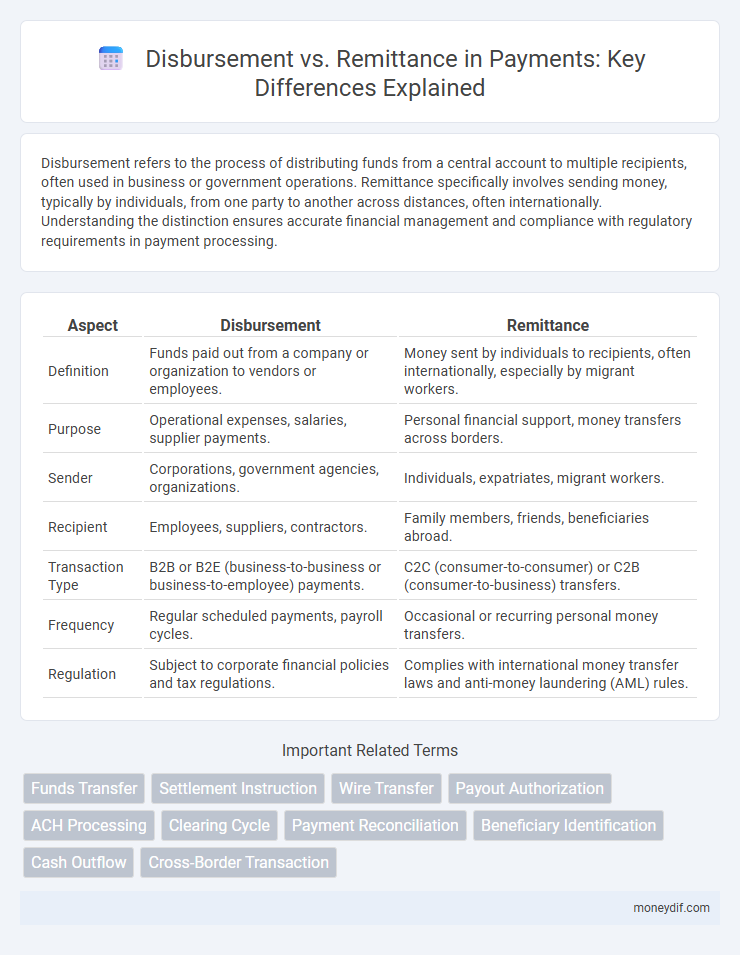
Disbursement refers to the process of distributing funds from a central account to multiple recipients, often used in business or government operations. Remittance specifically involves sending money, typically by individuals, from one party to another across distances, often internationally. Understanding the distinction ensures accurate financial management and compliance with regulatory requirements in payment processing.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Disbursement | Remittance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Funds paid out from a company or organization to vendors or employees. | Money sent by individuals to recipients, often internationally, especially by migrant workers. |
| Purpose | Operational expenses, salaries, supplier payments. | Personal financial support, money transfers across borders. |
| Sender | Corporations, government agencies, organizations. | Individuals, expatriates, migrant workers. |
| Recipient | Employees, suppliers, contractors. | Family members, friends, beneficiaries abroad. |
| Transaction Type | B2B or B2E (business-to-business or business-to-employee) payments. | C2C (consumer-to-consumer) or C2B (consumer-to-business) transfers. |
| Frequency | Regular scheduled payments, payroll cycles. | Occasional or recurring personal money transfers. |
| Regulation | Subject to corporate financial policies and tax regulations. | Complies with international money transfer laws and anti-money laundering (AML) rules. |
Disbursement vs Remittance: Key Definitions
Disbursement refers to the actual distribution of funds from an organization or individual to payees, including employees, vendors, or beneficiaries. Remittance involves the transfer of money, often by a foreign worker to their home country, or as a payment against an invoice or bill. Understanding the distinction is crucial for accurate financial reporting and compliance in payment processing systems.
How Disbursement Works in Payment Systems
Disbursement in payment systems refers to the process of distributing funds from a central account to multiple recipients, typically involving businesses, government agencies, or financial institutions. This process relies on automated clearing houses (ACH), wire transfers, or electronic funds transfers (EFT) to ensure timely and accurate delivery of payments for salaries, supplier invoices, or social benefits. Disbursement systems prioritize security protocols and transaction tracking to minimize errors and fraud during fund allocation.
Understanding Remittance in Financial Transactions
Remittance in financial transactions refers to the transfer of funds from one party to another, often across international borders, typically involving individual payments such as salaries or personal funds sent by migrants to family members. Unlike disbursement, which generally involves the distribution of payments from an organization or institution for operational expenses, remittance emphasizes personal or business-to-business money transfers. Understanding remittance includes recognizing its role in global financial flows, transaction tracking through remittance advice, and compliance with regulatory standards to prevent money laundering.
Major Differences Between Disbursement and Remittance
Disbursement refers to the outflow of funds from a business or organization to settle obligations such as expenses, salaries, or vendor payments, while remittance specifically involves sending money, often internationally, from one party to another, usually for personal or business transactions. The major difference lies in scope: disbursement encompasses a broader range of payments made by an entity, whereas remittance typically focuses on transferring money across locations. Tracking disbursements is crucial for company financial management, whereas remittances are closely monitored for compliance with international payment regulations.
Disbursement Use Cases in Business Payments
Disbursement refers to the process of distributing funds from a central source to various recipients, commonly used for payroll, vendor payments, and expense reimbursements in business operations. Unlike remittance, which primarily involves sending payments to fulfill invoices or debts, disbursement encompasses broader financial outflows, including grants, dividends, and loan proceeds. Effective disbursement systems enhance cash flow management, ensure regulatory compliance, and improve transparency in corporate financial transactions.
The Role of Remittance in Cross-Border Payments
Remittance plays a crucial role in cross-border payments by facilitating the direct transfer of funds from individuals working abroad to their families or beneficiaries in home countries, often via digital platforms or money transfer operators. Unlike disbursement, which typically involves payments made by organizations for salaries, grants, or supplier transactions, remittance primarily supports personal financial flows that contribute significantly to developing economies. Efficient remittance systems reduce transaction costs and transfer times, enhancing financial inclusion and economic stability in recipient countries.
Disbursement Methods: Bank Transfer, Check, and Digital Wallet
Disbursement methods include bank transfers, checks, and digital wallets, each offering distinct benefits for payment distribution. Bank transfers provide secure, direct fund delivery to recipients' accounts, ideal for large or recurring payments. Checks offer a traditional, tangible payment option, while digital wallets enable fast, convenient transactions through mobile devices or online platforms.
Remittance Channels: Traditional and Digital Solutions
Remittance channels encompass traditional methods such as bank transfers, money orders, and cash pickups, alongside digital solutions including mobile wallets, online payment platforms, and blockchain-based remittances. Digital remittance channels offer faster transaction speeds, lower fees, and enhanced accessibility, especially in developing regions. Efficient remittance processing depends on selecting appropriate channels to balance cost, speed, and security for cross-border payments.
Compliance and Regulatory Considerations
Disbursement involves the authorized release of funds from an organization to recipients, requiring strict adherence to anti-money laundering (AML) laws and accurate reporting under the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) guidelines. Remittance, referring to the transfer of funds typically by individuals across borders, is subject to compliance with the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) and Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act (FATCA) to prevent illicit financial flows. Both processes demand rigorous Know Your Customer (KYC) protocols and continuous monitoring by regulatory bodies like the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) to ensure lawful and transparent transactions.
Choosing the Right Payment Process: Disbursement or Remittance
Choosing the right payment process depends on the nature of the transaction and the parties involved. Disbursement refers to the distribution of funds by an organization to multiple recipients, often for expenses, salaries, or reimbursements, while remittance is the transfer of money from an individual or business to a specific recipient, typically across borders. Evaluating factors such as transaction volume, regulatory requirements, and speed helps determine whether disbursement or remittance best suits your payment needs.
Important Terms
Funds Transfer
Funds transfer in disbursement involves allocating payments from an organization's account to multiple recipients for expenses or payroll, while remittance focuses on sending money, often cross-border, from individuals or businesses to beneficiaries, emphasizing accuracy and compliance with transfer regulations. Both processes require secure channels to ensure timely delivery, with remittance typically including currency exchange and additional verification steps.
Settlement Instruction
Settlement instructions specify the precise procedures and account details for transferring funds during a disbursement, ensuring accurate payment delivery to beneficiaries. Remittance involves sending payment information along with funds, focusing on communication of transaction details for proper reconciliation by recipients.
Wire Transfer
Wire transfer refers to the electronic movement of funds between banks or financial institutions, commonly used for large disbursements such as payroll or vendor payments. In contrast, remittance involves sending smaller amounts of money, often for personal purposes like family support, typically crossing international borders.
Payout Authorization
Payout authorization ensures secure approval for releasing funds, distinguishing disbursement as the business-driven distribution of payments, while remittance focuses on the transfer of money sent as settlement or payment between parties. Accurate authorization processes optimize financial control and compliance within both disbursement and remittance workflows.
ACH Processing
ACH processing enables efficient electronic transfer of funds, streamlining disbursements by automating payments to vendors, employees, and suppliers. In contrast, remittance focuses on providing detailed payment information to recipients, ensuring accurate reconciliation of invoices and accounts payable records.
Clearing Cycle
The clearing cycle in financial transactions represents the period during which disbursed funds are processed and reconciled against remittances, ensuring accurate settlement between payer and payee accounts. Efficient synchronization of the clearing cycle minimizes delays by aligning disbursement schedules with remittance verification protocols, reducing fund float and improving cash flow management.
Payment Reconciliation
Payment reconciliation involves matching disbursement records with remittance advices to ensure financial accuracy and transparency. Efficient reconciliation reduces discrepancies by verifying that disbursed amounts align exactly with remitted payments documented in transaction records.
Beneficiary Identification
Beneficiary identification ensures accurate verification of recipients in both disbursement and remittance processes, minimizing fraud and compliance risks. Distinguishing between disbursement, which involves allocating funds to beneficiaries, and remittance, which refers to sending money internationally, requires precise beneficiary data to guarantee secure and efficient fund transfers.
Cash Outflow
Cash outflow involves the disbursement of funds from a company's accounts to pay for expenses, suppliers, or operational costs, while remittance specifically refers to the transfer of money to a distant party, often across borders, for settlement of transactions or personal transfers. Disbursement is a broader term encompassing all outgoing payments, whereas remittance focuses on sending money, commonly in contexts of international finance or payroll.
Cross-Border Transaction
Cross-border transactions involve disbursement, where funds are paid out to beneficiaries in different countries, and remittance, which refers to transferring money, often by individuals, to family members abroad. Efficient management of disbursement versus remittance processes is crucial for minimizing fees, exchange rate losses, and ensuring regulatory compliance in international financial transfers.
Disbursement vs Remittance Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com