BIN sponsorship enables smaller merchants to process card payments by partnering with a larger bank that owns the Bank Identification Number, reducing entry barriers and compliance burdens. Direct acquiring involves merchants working directly with an acquiring bank to handle transactions, offering greater control and potentially lower fees but requiring full regulatory compliance and higher setup costs. Selecting between BIN sponsorship and direct acquiring depends on business scale, risk tolerance, and desire for operational independence.
Table of Comparison
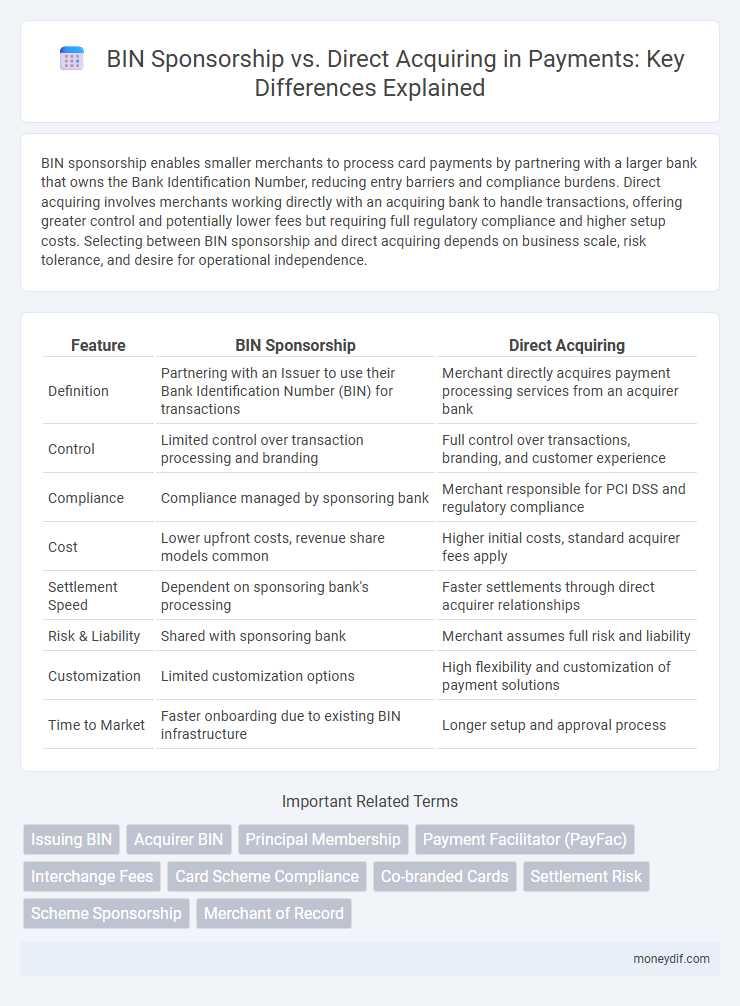
| Feature | BIN Sponsorship | Direct Acquiring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Partnering with an Issuer to use their Bank Identification Number (BIN) for transactions | Merchant directly acquires payment processing services from an acquirer bank |
| Control | Limited control over transaction processing and branding | Full control over transactions, branding, and customer experience |
| Compliance | Compliance managed by sponsoring bank | Merchant responsible for PCI DSS and regulatory compliance |
| Cost | Lower upfront costs, revenue share models common | Higher initial costs, standard acquirer fees apply |
| Settlement Speed | Dependent on sponsoring bank's processing | Faster settlements through direct acquirer relationships |
| Risk & Liability | Shared with sponsoring bank | Merchant assumes full risk and liability |
| Customization | Limited customization options | High flexibility and customization of payment solutions |
| Time to Market | Faster onboarding due to existing BIN infrastructure | Longer setup and approval process |
Understanding BIN Sponsorship vs Direct Acquiring
BIN sponsorship allows smaller payment processors to use a bank identification number (BIN) owned by a larger financial institution, enabling them to facilitate transactions without holding a banking license. Direct acquiring involves a payment processor obtaining its own BIN, granting full control over transaction processing, settlement, and compliance responsibilities. Understanding the differences clarifies operational scope, regulatory obligations, and partnership dependencies in payment ecosystems.
Key Differences Between BIN Sponsorship and Direct Acquiring
BIN sponsorship allows merchants to access payment networks through a third-party institution's Bank Identification Number, enabling faster market entry with lower regulatory burdens and operational costs. Direct acquiring involves a merchant establishing a direct relationship with an acquirer bank, providing more control over transaction processes, pricing, and data management but requiring rigorous compliance and higher upfront investment. The primary differences lie in control, compliance responsibility, and financial commitment, where BIN sponsorship offers convenience and scalability, whereas direct acquiring prioritizes autonomy and long-term profitability.
Pros and Cons of BIN Sponsorship in Payment Processing
BIN sponsorship allows smaller payment processors or fintech companies to access established payment networks without acquiring a full banking license, offering faster market entry and reduced regulatory burden. However, reliance on a BIN sponsor limits control over transaction management, potentially increases costs due to revenue sharing, and may introduce dependency risks if the sponsor changes terms or withdraws support. While BIN sponsorship simplifies compliance and lowers upfront investment, it can restrict scalability and flexibility compared to direct acquiring models.
Advantages and Challenges of Direct Acquiring
Direct acquiring enables merchants to process transactions directly with card networks, reducing dependency on intermediaries and lowering fees, which enhances transaction speed and control over payment data. This approach offers improved risk management and compliance capabilities by allowing acquirers to directly handle authorization and settlement processes. However, direct acquiring requires significant investment in infrastructure, regulatory compliance, and ongoing maintenance, presenting challenges for smaller businesses or new market entrants.
Regulatory Requirements: BIN Sponsorship vs Direct Acquiring
BIN sponsorship involves a third-party sponsor bank that holds the necessary regulatory licenses, allowing payment facilitators to operate under their BIN without obtaining a separate license. Direct acquiring requires the payment provider to meet stringent regulatory requirements independently, including obtaining acquiring licenses, adhering to anti-money laundering (AML) policies, and maintaining risk management protocols. Regulatory compliance in BIN sponsorship relies heavily on the sponsor bank's oversight, while direct acquirers bear full responsibility for regulatory adherence and reporting to financial authorities.
Cost Implications: BIN Sponsorship Compared to Direct Acquiring
BIN sponsorship often reduces upfront costs by leveraging the sponsor bank's existing infrastructure, minimizing investment in technology and compliance. Direct acquiring incurs higher operational expenses due to the need for separate licensing, fraud management, and regulatory compliance. The cost savings associated with BIN sponsorship can enhance margins for smaller merchants or fintech startups unable to bear the overhead of direct acquiring.
Risk Management: BIN Sponsorship vs Direct Acquiring
Risk management in BIN sponsorship involves the acquirer relying on the sponsor bank's compliance and underwriting frameworks, which can introduce third-party risk and less direct control over fraud detection. Direct acquiring allows merchants to implement tailored risk assessment protocols and real-time transaction monitoring, enhancing fraud prevention and regulatory adherence. Effective risk mitigation requires balancing the security strengths of direct acquiring with the scalability and resource sharing benefits of BIN sponsorship.
When to Choose BIN Sponsorship Over Direct Acquiring
Choose BIN sponsorship over direct acquiring when launching a payment solution with limited resources or without acquiring licenses, as BIN sponsorship enables rapid market entry under an established bank's infrastructure. It suits fintech startups and non-bank businesses seeking to leverage existing regulatory frameworks and reduce compliance burdens. Opt for BIN sponsorship to access payment networks quickly while minimizing capital expenditure and operational complexities.
Case Studies: BIN Sponsorship vs Direct Acquiring in Practice
Case studies in payment processing reveal that BIN sponsorship enables smaller merchants to leverage established banks' infrastructure, reducing entry barriers and operational costs while benefiting from faster market access. Direct acquiring, employed by larger enterprises, offers greater control over transaction routing, data security, and profitability but demands significant compliance and technological investment. Analysis of real-world implementations shows BIN sponsorship excels in scalability and speed, whereas direct acquiring suits high-volume merchants optimizing long-term financial margins.
Future Trends in BIN Sponsorship and Direct Acquiring
Future trends in BIN sponsorship and direct acquiring emphasize increased collaboration between fintech companies and traditional banks to streamline payment processing. Advances in tokenization and real-time transaction data analytics are driving enhanced security and faster settlement times. The rise of embedded finance solutions also fosters greater adoption of BIN sponsorship models, enabling non-banks to offer card issuance and payment services without direct acquiring licenses.
Important Terms
Issuing BIN
Issuing BIN refers to the process where financial institutions obtain a Bank Identification Number to issue payment cards directly or sponsor others to issue cards under their BIN. BIN sponsorship enables smaller issuers to leverage an established entity's BIN for card issuance without acquiring direct BIN ownership, facilitating faster market entry and regulatory compliance.
Acquirer BIN
Acquirer BIN (Bank Identification Number) enables merchants to process card payments by identifying the acquiring bank involved in transactions. BIN sponsorship allows smaller or non-bank entities to access acquiring networks through a sponsor bank's BIN, while direct acquiring means the merchant works directly with an acquirer that owns the BIN, providing more control and potentially lower costs.
Principal Membership
Principal Membership enables merchants to directly acquire card transactions and manage payment processing without intermediary involvement, enhancing control over data and transaction flow. BIN sponsorship, conversely, involves a third-party financial institution providing access to a Bank Identification Number, allowing sub-merchants to process payments under the sponsor's license but limiting direct access to acquiring services and merchant data.
Payment Facilitator (PayFac)
Payment Facilitators (PayFacs) accelerate onboarding for merchants by leveraging BIN sponsorship from established acquiring banks, enabling faster transaction processing without requiring direct acquiring relationships. Direct acquiring involves merchant accounts acquired by banks themselves, which can offer more control but demands rigorous underwriting and longer setup times compared to the streamlined BIN sponsorship model used by PayFacs.
Interchange Fees
Interchange fees vary significantly between BIN sponsorship and direct acquiring models, with direct acquiring often enabling merchants to access lower fees by eliminating intermediaries and negotiating rates directly with card networks. BIN sponsorship involves a sponsor bank providing access to payment processing infrastructure, typically resulting in higher interchange fees due to additional layers and shared revenue splits.
Card Scheme Compliance
Card scheme compliance ensures adherence to payment network rules governing transaction processing, fraud prevention, and security standards, critical in both BIN sponsorship and direct acquiring models. BIN sponsorship allows smaller merchants to access card schemes through a licensed institution's BIN, while direct acquiring requires the merchant to obtain their own BIN license, impacting regulatory responsibilities and operational control.
Co-branded Cards
Co-branded cards leverage BIN sponsorship to enable partnerships between banks and merchants, allowing non-bank entities to issue cards under a sponsor's banking license and BIN. Direct acquiring involves the merchant's bank directly managing card transactions, offering greater control but requiring full compliance with payment network regulations and risk management.
Settlement Risk
Settlement risk in BIN sponsorship arises when a third-party sponsor facilitates transaction processing for a merchant, increasing dependency on the sponsor's financial stability and compliance controls, which can delay fund settlement or cause losses. Direct acquiring reduces settlement risk by enabling merchants to establish their own acquiring bank relationships, ensuring more transparent transaction settlement and enhanced control over payment flows.
Scheme Sponsorship
Scheme sponsorship allows non-acquiring entities to gain payment scheme access by partnering with an acquiring bank, enabling BIN sponsorship where the sponsor bank provides a Bank Identification Number for card issuing and transaction processing. This contrasts with direct acquiring, where merchants or issuers connect directly to card networks, granting greater control but requiring compliance with all scheme regulations independently.
Merchant of Record
Merchant of Record (MoR) models often involve BIN sponsorship to enable payment processing under a sponsor bank's BIN, facilitating merchant onboarding without needing a direct acquiring license. Direct acquiring requires the merchant or MoR to hold a banking license for BIN ownership, allowing more control over transaction processing and settlement but involving higher regulatory and operational complexities.
BIN sponsorship vs direct acquiring Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com