Batch processing in payments involves grouping multiple transactions to be processed together at scheduled intervals, optimizing efficiency and reducing processing costs for high-volume payments. Real-time processing enables immediate transaction authorization and settlement, enhancing customer experience with instant payment confirmation and faster fund availability. Choosing between batch and real-time payment processing depends on business needs for speed, cost, and operational complexity.
Table of Comparison
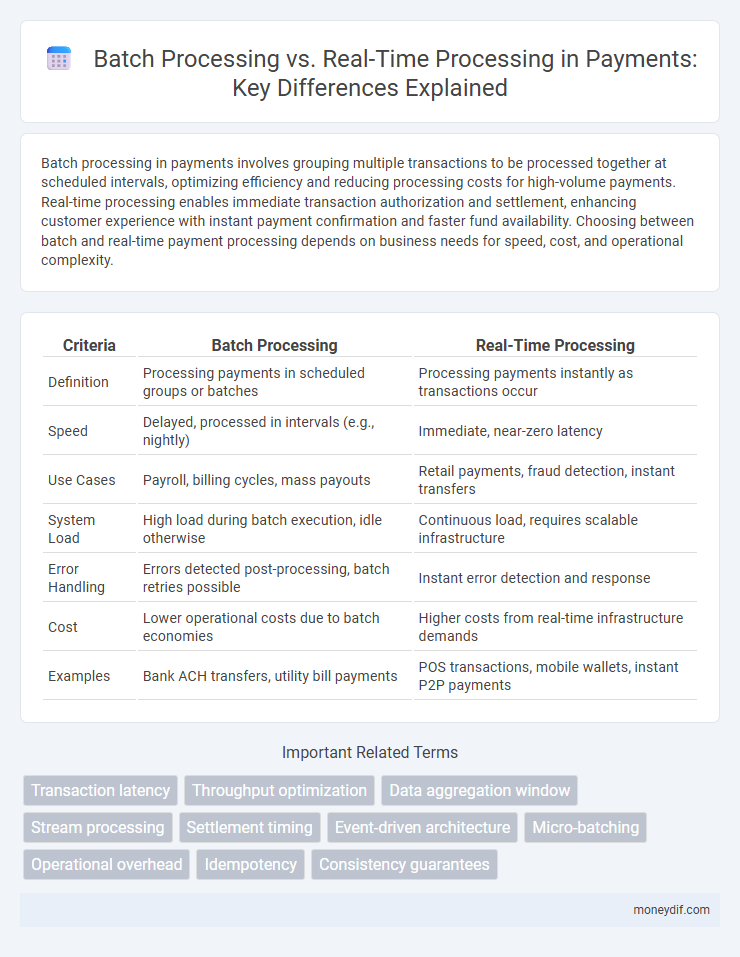
| Criteria | Batch Processing | Real-Time Processing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Processing payments in scheduled groups or batches | Processing payments instantly as transactions occur |
| Speed | Delayed, processed in intervals (e.g., nightly) | Immediate, near-zero latency |
| Use Cases | Payroll, billing cycles, mass payouts | Retail payments, fraud detection, instant transfers |
| System Load | High load during batch execution, idle otherwise | Continuous load, requires scalable infrastructure |
| Error Handling | Errors detected post-processing, batch retries possible | Instant error detection and response |
| Cost | Lower operational costs due to batch economies | Higher costs from real-time infrastructure demands |
| Examples | Bank ACH transfers, utility bill payments | POS transactions, mobile wallets, instant P2P payments |
Introduction to Payment Processing Methods
Batch processing in payment systems involves collecting and processing transactions in groups at scheduled intervals, optimizing efficiency for high-volume payments like payroll or utility bills. Real-time processing handles payments instantly, providing immediate authorization and confirmation, crucial for point-of-sale transactions and online purchases. Choosing between batch and real-time processing depends on business requirements for speed, transaction volume, and cost-effectiveness.
What is Batch Processing in Payments?
Batch processing in payments involves collecting and processing multiple transactions simultaneously at scheduled intervals, rather than individually in real-time. This method optimizes efficiency by reducing processing costs and resource usage, often used for payroll, bulk transfers, and settlement operations. Batch processing typically results in delayed settlement times compared to real-time payment systems but supports high-volume transaction handling with consolidated reporting.
What is Real-Time Payment Processing?
Real-time payment processing enables instant transfer of funds between sender and receiver, ensuring immediate transaction confirmation and settlement. This system leverages advanced payment gateways and APIs to process payments within seconds, enhancing cash flow and customer satisfaction. Unlike batch processing, which accumulates transactions for delayed processing, real-time payment processing supports continuous, on-demand financial interactions critical for modern e-commerce and banking operations.
Key Differences Between Batch and Real-Time Payments
Batch payments consolidate multiple transactions into a single processing cycle, reducing operational costs and enhancing efficiency for scheduled payments, while real-time payments process transactions instantly, offering immediate fund transfers and improved liquidity management. Batch processing typically involves delays ranging from hours to days, suitable for payroll or bulk disbursements, whereas real-time processing supports instant settlement and 24/7 availability, critical for urgent transfers and customer experience. Security protocols differ as batch systems emphasize batch-level validation and reconciliation, while real-time systems require continuous monitoring and fraud detection due to immediate transaction execution.
Advantages of Batch Payment Processing
Batch payment processing offers significant cost savings by handling large volumes of transactions simultaneously, reducing overhead and operational expenses. It enhances efficiency through automated scheduling and processing during off-peak hours, minimizing system strain and improving resource management. This method also provides improved error detection and reconciliation capabilities by consolidating payments into manageable groups, facilitating streamlined auditing and reporting.
Benefits of Real-Time Payment Processing
Real-time payment processing enables instant transaction confirmation, significantly reducing fraud risk and improving cash flow management for businesses. It enhances customer satisfaction by providing immediate payment verification and faster fund availability. This method supports seamless integration with digital wallets and mobile banking, driving efficiency in modern financial ecosystems.
Use Cases: When to Choose Batch vs Real-Time
Batch processing excels in scenarios involving large volumes of payments that do not require immediate confirmation, such as payroll disbursements or end-of-day bank settlements, where efficiency and cost savings are prioritized. Real-time processing is essential for time-sensitive transactions like retail POS payments, instant fund transfers, and fraud detection, ensuring immediate transaction validation and user notification. Choosing between batch and real-time processing depends on the business need for speed, transaction volume, and operational cost considerations.
Security Considerations in Payment Processing
Batch processing in payment systems groups transactions for periodic validation and settlement, reducing exposure to fraud during transmission through encrypted, secure batch uploads. Real-time processing demands robust, instantaneous fraud detection mechanisms and end-to-end encryption to protect sensitive cardholder data from interception or tampering. Implementing multi-factor authentication and tokenization enhances security posture in both methods, mitigating risks associated with unauthorized access and data breaches.
Impact on Customer Experience
Batch processing in payment systems often results in delayed transaction confirmations, which can lead to customer frustration due to uncertainty and lack of immediacy. Real-time processing enhances customer experience by providing instant payment verification, reducing wait times and increasing trust in the service. Faster transaction settlements also improve customer satisfaction and loyalty by enabling immediate access to purchased goods or services.
Future Trends in Payment Processing Systems
Future trends in payment processing systems emphasize a shift towards hybrid models combining batch processing's efficiency with real-time processing's immediacy. Advances in blockchain technology and AI-driven analytics enable seamless, secure, and instantaneous batch settlements while maintaining high throughput. The integration of ISO 20022 standards further enhances interoperability, supporting real-time data exchange and improved fraud detection in evolving payment ecosystems.
Important Terms
Transaction latency
Transaction latency in batch processing typically ranges from minutes to hours as data accumulates before processing, causing delayed insights and actions. Real-time processing reduces latency to milliseconds or seconds by handling transactions instantly, enabling immediate decision-making and enhanced system responsiveness.
Throughput optimization
Throughput optimization in data processing is achieved by balancing batch processing's high-volume, latency-tolerant workloads with real-time processing's low-latency, continuous data streams. Efficient resource allocation and parallelism maximize throughput in batch systems, while streamlining event-driven architectures enhances real-time data throughput, ensuring optimal system performance.
Data aggregation window
Data aggregation windows define the time intervals during which data is collected and summarized, crucial for distinguishing batch processing, which operates on fixed, often large time windows, from real-time processing that uses small or sliding windows to deliver near-instant insights. Optimizing aggregation windows enhances processing efficiency and accuracy, balancing latency and data completeness across big data analytics and streaming platforms like Apache Hadoop and Apache Kafka.
Stream processing
Stream processing handles continuous data flows by analyzing and processing events in real time, enabling immediate insights and rapid decision-making. Batch processing, in contrast, processes large volumes of data collected over time in scheduled intervals, focusing on throughput and completeness rather than low latency.
Settlement timing
Settlement timing in batch processing typically occurs at fixed intervals, causing delays in transaction finalization and impacting liquidity management. Real-time processing enables immediate settlement, improving cash flow accuracy and reducing counterparty risk by updating transaction records instantly.
Event-driven architecture
Event-driven architecture enables systems to respond instantly to data changes, optimizing real-time processing by triggering actions based on events instead of waiting for scheduled batches. This contrast with batch processing, which handles data in large, periodic chunks, highlights event-driven models' superiority in scenarios requiring low latency and continuous data flow.
Micro-batching
Micro-batching processes data in small, manageable batches to combine the throughput benefits of batch processing with the low-latency advantages of real-time processing. This approach enables near real-time analytics by minimizing processing delays while maintaining efficient resource utilization.
Operational overhead
Operational overhead in batch processing is typically higher due to scheduling complexities, data latency, and resource allocation bursts, whereas real-time processing demands continuous resource availability and low-latency infrastructure, leading to consistent but potentially increased operational costs. Efficient resource management and automation are crucial to minimizing overhead in both processing paradigms, with real-time systems emphasizing rapid data ingestion and immediate analytics capabilities.
Idempotency
Idempotency in batch processing ensures repeated executions of the same batch job produce consistent results without unintended side effects, critical for reliable data aggregation and analytics. In real-time processing, idempotency guarantees that event-driven transactions can be safely retried or replayed without causing duplicate data updates or system state inconsistencies.
Consistency guarantees
Consistency guarantees in batch processing typically provide strong consistency by processing large volumes of data in scheduled intervals, ensuring complete and accurate results at each batch completion. Real-time processing emphasizes low latency and continuous data updates, often using eventual consistency models to balance system responsiveness with manageable consistency levels.
batch processing vs real-time processing Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com