The acquirer is the financial institution that processes credit or debit card payments on behalf of a merchant, facilitating the transaction approval and settlement. The issuer, on the other hand, is the bank or entity that provides the consumer's payment card and authorizes the transaction by verifying available funds or credit. Understanding the roles of acquirer and issuer is crucial for seamless payment processing and fraud prevention.
Table of Comparison
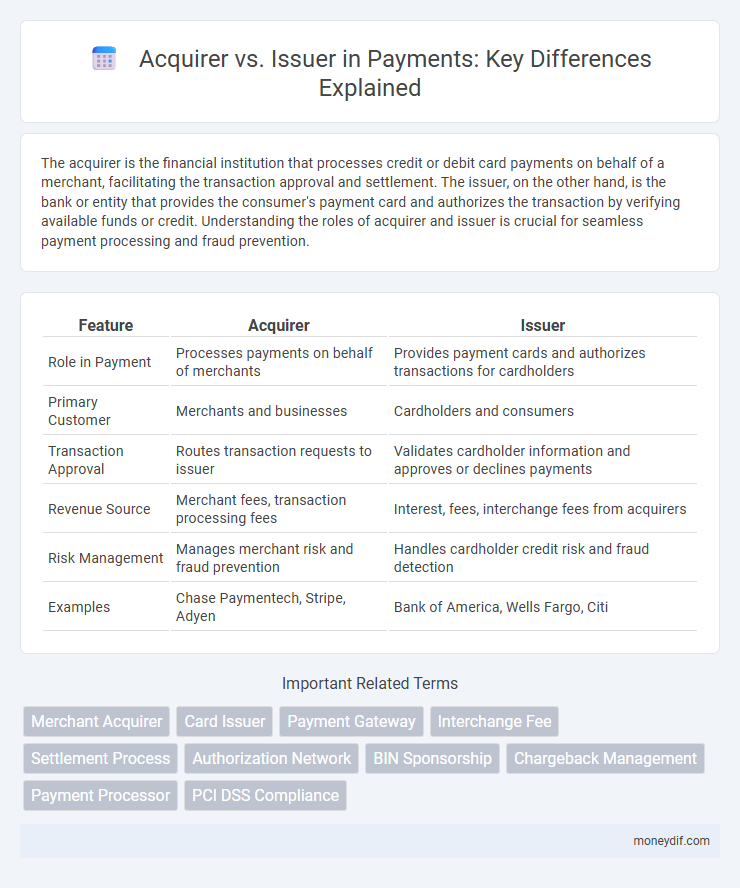
| Feature | Acquirer | Issuer |
|---|---|---|
| Role in Payment | Processes payments on behalf of merchants | Provides payment cards and authorizes transactions for cardholders |
| Primary Customer | Merchants and businesses | Cardholders and consumers |
| Transaction Approval | Routes transaction requests to issuer | Validates cardholder information and approves or declines payments |
| Revenue Source | Merchant fees, transaction processing fees | Interest, fees, interchange fees from acquirers |
| Risk Management | Manages merchant risk and fraud prevention | Handles cardholder credit risk and fraud detection |
| Examples | Chase Paymentech, Stripe, Adyen | Bank of America, Wells Fargo, Citi |
Understanding Acquirer and Issuer in Payment Systems
Acquirers are financial institutions that process credit and debit card payments on behalf of merchants, ensuring funds are captured and settled from the cardholder's bank. Issuers, on the other hand, are banks or entities that provide payment cards to consumers and manage cardholder accounts, authorizing and approving transactions during purchases. Understanding the distinct roles of acquirers and issuers is crucial for grasping the flow of funds and security measures in electronic payment systems.
Key Differences Between Acquirer and Issuer
The acquirer is a financial institution that processes credit and debit card payments on behalf of a merchant, while the issuer is the bank or entity that provides the cardholder with the payment card. Acquirers manage merchant accounts and facilitate transaction settlement, whereas issuers verify and authorize transactions, extending credit or debiting funds from the cardholder's account. Key differences include their roles in the payment ecosystem, with acquirers focusing on merchant relationships and issuers on cardholder accounts and risk management.
Roles of Acquirer and Issuer in Card Transactions
The acquirer plays a crucial role by processing card payment transactions on behalf of the merchant, ensuring funds are received securely from the cardholder's bank. The issuer, typically the cardholder's bank, authorizes the transaction by verifying the cardholder's account details, confirming sufficient funds or credit availability. Both entities work together within the payment ecosystem to facilitate seamless and secure financial exchanges between merchants and consumers.
How Acquirers Facilitate Merchant Payments
Acquirers process payment transactions by connecting merchants to payment networks, enabling the acceptance of credit and debit card payments. They verify transaction details, ensure funds are available, and facilitate the transfer of payment from the issuer bank to the merchant's account. This seamless communication between acquirers and issuers is critical for efficient merchant payment settlements and reducing fraud risks.
The Issuer’s Role in Cardholder Transactions
The issuer plays a crucial role in cardholder transactions by authorizing payments and managing the cardholder's account, ensuring available credit or funds before approving the transaction. It also handles billing, fraud detection, and customer disputes, safeguarding cardholders throughout the payment process. This control helps maintain transaction security and trust between the cardholder and the payment network.
Payment Settlement: Acquirer vs Issuer Responsibilities
The acquirer is responsible for processing merchant payments, capturing transaction data, and submitting it to the payment network for authorization. The issuer verifies the cardholder's credentials, authorizes or declines the transaction, and ensures funds are available for settlement. During payment settlement, the acquirer credits the merchant's account while the issuer debits the cardholder's account, completing the transfer of funds.
Common Challenges for Acquirers and Issuers
Acquirers and issuers both face significant challenges such as fraud detection, ensuring transaction security, and complying with evolving regulatory standards like PCI DSS and PSD2. Acquirers struggle with managing chargebacks and maintaining merchant relationships, while issuers contend with cardholder authentication and mitigating credit risk. The constant need to balance seamless payment experiences with stringent security measures remains a critical issue for both entities in the payment ecosystem.
Acquirer and Issuer Fees Explained
Acquirer fees are charges paid by merchants to the acquiring bank for processing payment transactions, typically including a percentage of the transaction amount and a fixed fee per transaction. Issuer fees are levied by the cardholder's issuing bank and may include interchange fees, which compensate the issuer for handling cardholder services and fraud risk. Understanding the distinction between acquirer and issuer fees is crucial for optimizing payment processing costs and improving merchant profitability.
Security Measures: Acquirer vs Issuer
Acquirers implement robust fraud detection systems and secure payment gateways to protect merchant transactions, leveraging encryption and tokenization to minimize data breaches. Issuers enhance cardholder security through multi-factor authentication, real-time transaction monitoring, and EMV chip technology to prevent unauthorized use. Both parties collaborate via secure communication protocols and compliance with PCI DSS standards to ensure end-to-end payment security.
Future Trends for Acquirers and Issuers in Payments
Future trends for acquirers in payments emphasize the adoption of advanced security protocols such as tokenization and biometric authentication to reduce fraud and enhance transaction safety. Issuers are increasingly leveraging AI-driven analytics to personalize customer experiences and streamline risk management processes. Both acquirers and issuers are expected to integrate blockchain technology to improve payment transparency and enable faster, cross-border settlements.
Important Terms
Merchant Acquirer
A merchant acquirer processes payment transactions on behalf of merchants, distinct from issuers who provide payment cards to consumers.
Card Issuer
The card issuer is a financial institution that provides payment cards to consumers, while the acquirer is the merchant's bank that processes card transactions and facilitates funds transfer from the issuer.
Payment Gateway
A payment gateway securely facilitates transaction data transmission between the acquirer, representing the merchant's bank, and the issuer, the cardholder's bank, ensuring seamless authorization and payment processing.
Interchange Fee
Interchange fees are transaction charges paid by the acquirer to the issuer to compensate for the costs and risks associated with processing card payments.
Settlement Process
The settlement process involves the acquirer transferring transaction funds to the issuer through the payment network to complete the cardholder's purchase securely and efficiently.
Authorization Network
The Authorization Network processes transaction requests by facilitating communication between the Acquirer, which initiates the payment, and the Issuer, which validates and approves or declines the cardholder's payment authorization.
BIN Sponsorship
BIN sponsorship allows an acquirer to enable merchants to accept payments by leasing a bank identification number (BIN) from an issuer, facilitating transaction processing without the acquirer obtaining its own BIN.
Chargeback Management
Chargeback management involves the acquirer verifying disputed transactions with the issuer to resolve payment conflicts and prevent fraud.
Payment Processor
An acquirer processes merchant payments while an issuer provides customers with payment cards and manages cardholder accounts in the payment processor ecosystem.
PCI DSS Compliance
PCI DSS compliance ensures both acquirers and issuers implement robust security measures to protect cardholder data and prevent fraud during payment processing.
Acquirer vs Issuer Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com