EMV technology offers enhanced security by using chip-based encryption that significantly reduces fraud compared to the traditional magstripe method, which stores static data easily copied by skimmers. The dynamic authentication in EMV cards makes transaction data unique for each purchase, preventing counterfeit cards and unauthorized use. Merchants adopting EMV benefit from lower chargeback risk and improved customer trust due to advanced fraud protection.
Table of Comparison
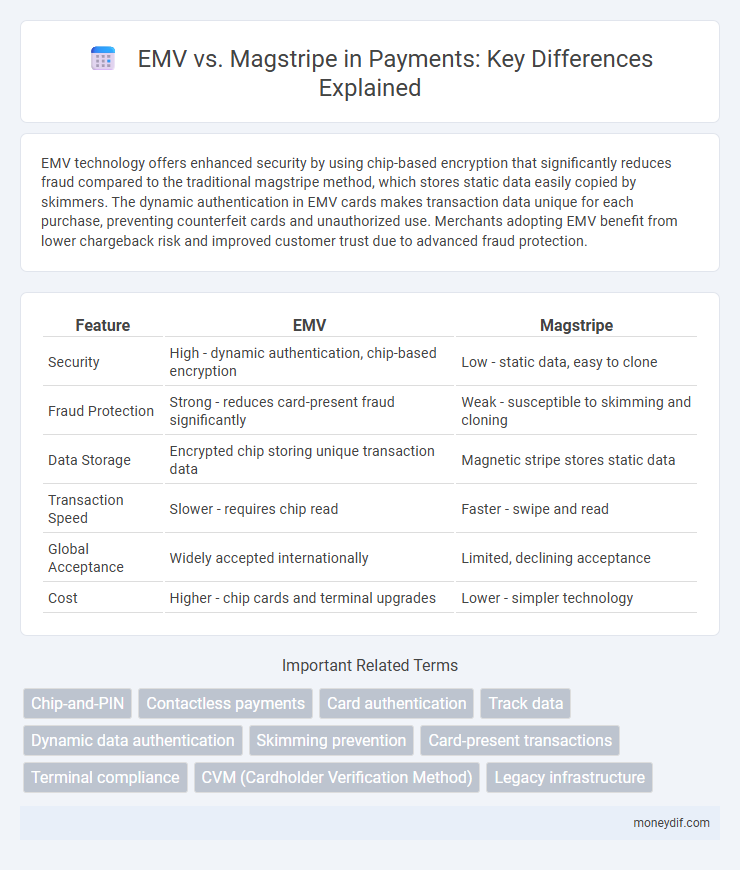
| Feature | EMV | Magstripe |
|---|---|---|
| Security | High - dynamic authentication, chip-based encryption | Low - static data, easy to clone |
| Fraud Protection | Strong - reduces card-present fraud significantly | Weak - susceptible to skimming and cloning |
| Data Storage | Encrypted chip storing unique transaction data | Magnetic stripe stores static data |
| Transaction Speed | Slower - requires chip read | Faster - swipe and read |
| Global Acceptance | Widely accepted internationally | Limited, declining acceptance |
| Cost | Higher - chip cards and terminal upgrades | Lower - simpler technology |
EMV vs Magstripe: Understanding the Basics
EMV technology uses microprocessor chips to securely process payments, significantly reducing the risk of fraud compared to traditional magstripe cards, which store static data easily cloned by criminals. Merchants and consumers benefit from EMV's dynamic authentication, enabling unique transaction codes for each purchase and enhancing overall payment security. As global adoption of EMV increases, chip card transactions have become the standard for safeguarding sensitive payment information against skimming and counterfeit fraud.
How EMV Chip Technology Works
EMV chip technology uses a microprocessor chip embedded in credit and debit cards to generate a unique transaction code for each payment, enhancing security and reducing fraud compared to magnetic stripe cards. When inserted into a chip-enabled terminal, the card communicates with the payment system through dynamic data authentication, making it difficult for criminals to clone or reuse transaction information. Unlike magstripe cards that transmit static data, EMV chips create encrypted and transaction-specific data, providing higher protection against counterfeit fraud.
Magstripe Cards: Traditional Payment Explained
Magstripe cards rely on a magnetic stripe encoding payment information, making them vulnerable to skimming and cloning due to unencrypted data transmission. Despite widespread use in traditional payment systems, magstripe technology lacks the enhanced security features of EMV chip cards, such as dynamic authentication and encryption. Merchants and consumers face higher risks of fraud, leading to a global shift toward EMV adoption for safer transactions.
Security Comparison: EMV vs Magstripe
EMV chip cards offer enhanced security by generating a unique transaction code for each purchase, significantly reducing fraud compared to magstripe cards that store static data vulnerable to skimming and cloning. Magstripe transactions rely on static card information, making them more susceptible to data breaches and unauthorized use. The cryptographic features of EMV technology provide stronger protection against counterfeit fraud, making it the preferred standard for secure payment processing worldwide.
Transaction Speed: Chip vs Swipe
EMV chip transactions typically take 10 to 30 seconds due to encryption and authentication steps, offering enhanced security but slower processing compared to magstripe swipes. Magnetic stripe transactions complete within 1 to 3 seconds, providing faster checkout experiences but with increased risk of data breaches and card cloning. Merchants must balance transaction speed with fraud prevention when choosing between EMV chip and magstripe payment methods.
Global Adoption of EMV vs Magstripe
EMV chip technology has achieved widespread global adoption, with over 80 countries implementing EMV standards to enhance payment security and reduce fraud compared to magnetic stripe cards. Magstripe cards remain prevalent in regions with limited infrastructure, but their global share is rapidly declining as merchants and issuers prioritize EMV for its superior encryption and authentication features. The migration to EMV is supported by international payment networks such as Visa and Mastercard, driving interoperability and consumer trust in contact and contactless chip payments worldwide.
Fraud Prevention: Which is More Secure?
EMV chip cards provide enhanced fraud prevention by generating a unique transaction code for each purchase, making it significantly harder for criminals to clone cards compared to magstripe technology, which stores static data easily copied by fraudsters. EMV's dynamic authentication reduces counterfeit card fraud and card-present fraud incidents, contributing to a decrease in payment fraud globally. While magstripe remains vulnerable to skimming attacks, EMV chip cards support stronger encryption and verification, making them the preferred choice for secure payment transactions.
Costs and Implementation for Merchants
EMV payment terminals involve higher upfront costs and more complex installation compared to magstripe systems but significantly reduce fraud-related expenses for merchants. Magstripe card readers are cheaper and easier to implement but expose merchants to greater chargeback liabilities and fraud risks. Investing in EMV technology ultimately leads to lower operational costs and enhanced security for businesses.
Future Trends: Moving Beyond Magstripe
EMV technology offers enhanced security through chip authentication, significantly reducing card-present fraud compared to traditional magstripe cards, which remain vulnerable to skimming and cloning. Future payment trends emphasize contactless EMV and mobile wallets leveraging tokenization, aiming to replace magstripe as the standard for secure transactions. Banks and retailers are rapidly adopting EMV-compatible terminals and NFC-enabled devices, signaling a shift toward more secure and convenient payment ecosystems.
Consumer Experience: EMV Chip vs Magstripe
EMV chip technology enhances consumer payment security by generating unique transaction codes, reducing fraud risks compared to magnetic stripe cards that rely on static data. Consumers experience faster checkout times and increased trust with EMV-enabled terminals supporting contactless and chip insert payments. Although magstripe cards offer broader acceptance, EMV adoption significantly elevates protection and payment reliability for cardholders worldwide.
Important Terms
Chip-and-PIN
Chip-and-PIN technology enhances payment security by utilizing EMV chips, which generate unique transaction codes, unlike magstripe cards that store static data vulnerable to cloning. EMV chip cards significantly reduce fraud compared to magstripe cards by requiring a personal identification number (PIN) for transaction authorization.
Contactless payments
Contactless payments leveraging EMV technology offer enhanced security through dynamic data encryption and tokenization, significantly reducing fraud risks compared to traditional magstripe cards that store static, easily copied information. EMV contactless facilitates faster transaction times and widespread global acceptance, making it the preferred method over magstripe in modern payment systems.
Card authentication
Card authentication using EMV technology employs dynamic cryptographic data, significantly enhancing security against fraud compared to static data stored on magstripe cards. EMV chips generate unique transaction codes for each payment, reducing risks of card cloning and unauthorized use prevalent in traditional magstripe card transactions.
Track data
EMV chip technology significantly reduces fraud by generating unique transaction codes, while magstripe cards store static data vulnerable to cloning and skimming. Track data on magstripe cards contains sensitive information like cardholder name, account number, and expiration date, making it a prime target for cybercriminals compared to the dynamic authentication process utilized by EMV chips.
Dynamic data authentication
Dynamic Data Authentication (DDA) enhances payment security in EMV chip cards by generating unique cryptographic codes for each transaction, preventing card cloning and counterfeiting common in magstripe technology. Unlike static data stored on magstripe cards, EMV's DDA ensures real-time authentication, significantly reducing fraud risks in point-of-sale and ATM transactions.
Skimming prevention
EMV chip technology significantly enhances skimming prevention by generating unique transaction codes for each purchase, making copied card data from magstripe cards vulnerable to fraud. Magstripe cards store static data that skimmers can easily capture and clone, while EMV reduces counterfeit fraud by relying on dynamic authentication methods.
Card-present transactions
Card-present transactions using EMV technology offer enhanced security through dynamic authentication, significantly reducing fraud compared to traditional magstripe transactions that rely on static data vulnerable to skimming attacks. EMV chip cards generate unique transaction codes, making unauthorized duplication nearly impossible, whereas magstripe cards store fixed information that can be easily copied and exploited.
Terminal compliance
Terminal compliance ensures payment devices meet EMV standards for chip card transactions, offering enhanced security through dynamic data authentication compared to magnetic stripe technology. EMV-enabled terminals reduce fraud risk by verifying card authenticity and transaction integrity, whereas magstripe terminals remain more vulnerable to skimming and counterfeit attacks.
CVM (Cardholder Verification Method)
Cardholder Verification Method (CVM) in EMV transactions relies on dynamic authentication techniques such as PIN entry and biometric verification, enhancing security compared to static and easily replicated magstripe signatures. EMV cards utilize cryptographic processing to validate CVM, significantly reducing fraud risks associated with magnetic stripe cards that primarily depend on physically replicable signature verification.
Legacy infrastructure
Legacy infrastructure relying on magstripe technology poses significant security risks due to its vulnerability to skimming and cloning, whereas EMV chip technology enhances transaction security through dynamic authentication and encryption. Transitioning from magstripe to EMV infrastructure reduces fraud, complies with payment industry standards, and supports contactless and mobile payment innovations.
EMV vs magstripe Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com