ISO 8583 is a messaging standard primarily used for card-based payment transactions, offering a fixed format that supports traditional point-of-sale systems and ATMs. ISO 20022 provides a more flexible and extensible XML-based framework designed to facilitate end-to-end financial messaging across various payment types and channels. Financial institutions are increasingly adopting ISO 20022 for its ability to enhance interoperability, data richness, and regulatory compliance in modern payment ecosystems.
Table of Comparison
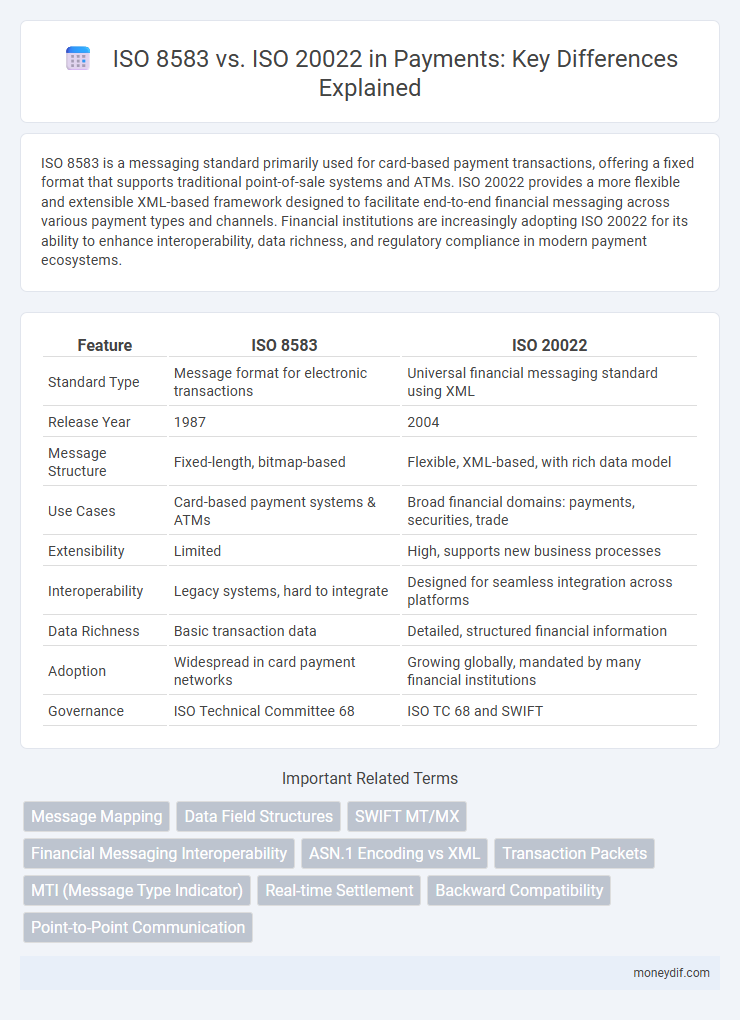
| Feature | ISO 8583 | ISO 20022 |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Type | Message format for electronic transactions | Universal financial messaging standard using XML |
| Release Year | 1987 | 2004 |
| Message Structure | Fixed-length, bitmap-based | Flexible, XML-based, with rich data model |
| Use Cases | Card-based payment systems & ATMs | Broad financial domains: payments, securities, trade |
| Extensibility | Limited | High, supports new business processes |
| Interoperability | Legacy systems, hard to integrate | Designed for seamless integration across platforms |
| Data Richness | Basic transaction data | Detailed, structured financial information |
| Adoption | Widespread in card payment networks | Growing globally, mandated by many financial institutions |
| Governance | ISO Technical Committee 68 | ISO TC 68 and SWIFT |
Introduction to ISO 8583 and ISO 20022
ISO 8583 serves as the global standard for financial transaction card-originated messages, facilitating real-time electronic payment systems through fixed message formats and bit-mapped data elements. ISO 20022 is a modern, XML-based messaging standard designed for enhanced interoperability and richer data exchange across various financial domains including payments, securities, and trade services. The transition from ISO 8583 to ISO 20022 aims to improve payment processing efficiency, data transparency, and regulatory compliance within financial institutions and payment networks.
Key Differences Between ISO 8583 and ISO 20022
ISO 8583 is a messaging standard primarily designed for card-based transactions with fixed message formats and limited data fields, whereas ISO 20022 provides a flexible, XML-based framework supporting richer, structured data and a wide range of financial services beyond payments, including securities and trade. ISO 8583 relies on predefined bitmaps and numeric fields optimizing speed for point-of-sale systems, while ISO 20022 enables extensibility and interoperability through standardized message definitions across various financial domains. The transition to ISO 20022 supports enhanced data quality, improved compliance with regulatory requirements, and facilitates innovation in payment processing through harmonized global messaging standards.
Structural Comparison: Message Formats
ISO 8583 utilizes a fixed, binary-based message format structured around data elements and bitmaps, facilitating efficient transaction processing in card payments. ISO 20022 employs an XML-based format with hierarchical, extensible data structures, enabling richer, more flexible payment information exchange across various financial services. The structural shift from ISO 8583 to ISO 20022 enhances interoperability and supports complex transaction data but may introduce processing overhead due to increased message size.
Data Richness and Flexibility
ISO 20022 offers greater data richness and flexibility compared to ISO 8583 by supporting complex and structured financial messages using XML, facilitating detailed transaction information and enhanced interoperability across diverse payment systems. ISO 8583, while widely used for card-based payment transactions, relies on fixed-length fields with limited data capacity, restricting the scope of data exchange. The adaptability of ISO 20022 enables seamless integration with modern payment infrastructures and supports evolving regulatory requirements more effectively.
Security Features in ISO 8583 and ISO 20022
ISO 8583 incorporates traditional security features such as message authentication codes (MACs) and encryption tailored for card-based transaction systems, ensuring data integrity and confidentiality within legacy payment networks. In contrast, ISO 20022 offers enhanced security capabilities by supporting XML-based extensible encryption, digital signatures, and comprehensive data validation, making it better suited for modern, interoperable financial ecosystems. Both standards prioritize transaction security, but ISO 20022's advanced cryptographic support provides stronger protection against fraud and cyber threats in complex payment environments.
Interoperability and Global Adoption
ISO 8583 remains a widely used standard for financial transaction messaging, particularly in traditional card-based payment systems, ensuring interoperability across legacy networks. ISO 20022 is rapidly gaining global adoption due to its flexible, XML-based structure, enabling richer data exchange and improved interoperability across diverse payment ecosystems like real-time payments and cross-border transactions. Major financial institutions and payment schemes are progressively transitioning to ISO 20022 to harmonize messaging standards, enhance interoperability, and support global payment system modernization.
Migration Challenges and Industry Impact
ISO 8583, a widely used messaging standard for payment transactions, faces migration challenges due to its rigid structure and limited data capacity compared to the more flexible, XML-based ISO 20022 standard. Transitioning to ISO 20022 involves significant industry impact, including the need for extensive system upgrades, staff retraining, and interoperability adjustments across global financial institutions. The enhanced data richness and standardization of ISO 20022 promise improved payment processing efficiency and compliance but require overcoming complex integration barriers and legacy system dependencies.
Use Cases in Modern Payment Systems
ISO 8583 remains the backbone of traditional card-based transaction processing, widely used in ATM withdrawals, point-of-sale purchases, and legacy payment networks due to its fast and reliable message format. ISO 20022 supports complex use cases in modern payment systems, including real-time fund transfers, cross-border payments, and rich data exchange, leveraging XML-based messaging for enhanced interoperability and compliance with regulatory requirements. Payment providers increasingly adopt ISO 20022 for future-proofing infrastructure, enabling seamless integration with blockchain, Open Banking APIs, and instant payment schemes.
Future Trends in Payment Messaging Standards
ISO 20022 is rapidly becoming the global standard for payment messaging due to its richer data capabilities and enhanced interoperability compared to the legacy ISO 8583. Future trends indicate a significant shift towards ISO 20022 adoption driven by increased regulatory support and the need for real-time payments, cross-border transactions, and improved fraud detection. Payment networks and financial institutions are prioritizing migration strategies to leverage ISO 20022's scalable, flexible framework for seamless integration with emerging technologies like blockchain and AI.
Choosing the Right Standard: ISO 8583 vs ISO 20022
Choosing the right payment messaging standard depends on transaction complexity and system compatibility, with ISO 8583 favored for traditional card-based transactions due to its widespread use in ATM and POS environments. ISO 20022 offers a more flexible and data-rich XML-based framework ideal for modern, multi-channel payment systems seeking enhanced interoperability and richer remittance information. Financial institutions aiming for future-proof solutions and regulatory compliance often prioritize ISO 20022 for its extensibility and global adoption momentum over the legacy ISO 8583.
Important Terms
Message Mapping
Message Mapping bridges ISO 8583, a standard focused on traditional card-based financial transactions, with ISO 20022, a comprehensive messaging system supporting diverse financial services through rich, structured XML syntax. This alignment enhances interoperability by translating ISO 8583's rigid, fixed-length data elements into ISO 20022's flexible, semantically detailed message formats for improved cross-platform communication.
Data Field Structures
ISO 8583 defines a fixed-length, hierarchical data field structure organized into primary and secondary bitmap fields enabling transaction messaging mainly for payment card systems, whereas ISO 20022 employs a flexible XML-based message structure with richly defined data elements supporting extensive financial services interoperability and enhanced semantic clarity. The transition from ISO 8583 to ISO 20022 facilitates improved data consistency, extensibility, and compliance with global financial messaging standards, particularly in payments, securities, and trade domains.
SWIFT MT/MX
SWIFT MT and MX message formats serve as primary communication standards in financial messaging, with MT aligned to legacy ISO 8583 transaction messaging and MX based on the modern ISO 20022 XML standard, enabling richer data and enhanced interoperability. ISO 20022 adoption through MX messages supports structured, extensible financial data exchange, improving cross-border payments, regulatory reporting, and real-time processing compared to the more rigid, fixed-format ISO 8583-linked MT messages.
Financial Messaging Interoperability
Financial messaging interoperability hinges on the transition from ISO 8583, a protocol primarily designed for card-based transaction messaging, to ISO 20022, which offers a richer, more flexible XML-based standard supporting a broad range of payment types and financial services. ISO 20022 enhances cross-system compatibility and data consistency across global payment networks, enabling more efficient processing, improved regulatory compliance, and enhanced real-time transaction monitoring compared to ISO 8583's limited format and capabilities.
ASN.1 Encoding vs XML
ASN.1 encoding offers compact, binary data serialization ideal for high-speed financial messaging in ISO 8583, whereas XML provides verbose, human-readable text formatting favored by ISO 20022 for comprehensive and interoperable financial data exchange. ISO 8583's ASN.1 emphasizes efficient processing in card-based transactions, while ISO 20022 leverages XML to support rich data structures and enhanced semantic clarity in modern payment systems.
Transaction Packets
Transaction packets in ISO 8583 are designed primarily for card-based payment systems, using fixed-length fields and a binary bitmap to indicate data elements, optimizing speed and simplicity for ATM and POS transactions. In contrast, ISO 20022 uses XML or JSON formats for transaction packets, enabling richer data content, extensibility, and interoperability across diverse financial services beyond card payments, supporting real-time processing and compliance with global regulatory standards.
MTI (Message Type Indicator)
MTI (Message Type Indicator) in ISO 8583 serves as a 4-digit numeric code defining the message class, function, and origin used primarily in card-based electronic transactions, enabling precise routing and processing of financial messages. Unlike ISO 8583, ISO 20022 adopts an XML-based, message-driven approach without MTI, focusing on rich, structured data models for broader financial communication standardization beyond card payments.
Real-time Settlement
Real-time settlement systems leverage ISO 20022 for enhanced data richness and interoperability across financial institutions, surpassing the limitations of ISO 8583's transaction-focused messaging structure. ISO 20022's XML-based framework supports more comprehensive payment information and facilitates seamless real-time reconciliation, improving transaction speed and accuracy in modern payment ecosystems.
Backward Compatibility
ISO 8583 maintains backward compatibility by supporting legacy financial transaction systems widely used in ATMs and card-based payments, whereas ISO 20022 offers a more comprehensive, XML-based messaging standard designed for richer data and improved interoperability across modern payment ecosystems. Transitioning from ISO 8583 to ISO 20022 involves mapping legacy transaction formats to ISO 20022's structured messages to ensure seamless integration without disrupting existing infrastructure.
Point-to-Point Communication
Point-to-Point Communication in ISO 8583 focuses on direct transaction message exchange between two systems, often used in traditional card payment networks, ensuring fast and secure data transfer. In contrast, ISO 20022 supports more complex, flexible, and standardized message structures, enabling richer data exchange and interoperability across multiple financial services within global payment ecosystems.
ISO 8583 vs ISO 20022 Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com