NACHA files and BACS files are essential formats used in electronic payment processing in the United States and the United Kingdom, respectively. NACHA files facilitate ACH payments by organizing transaction data for direct deposits and withdrawals, while BACS files handle automated clearing house payments primarily for bank transfers in the UK banking system. Understanding the differences in format and regulatory requirements ensures seamless cross-border payment integration and compliance.
Table of Comparison
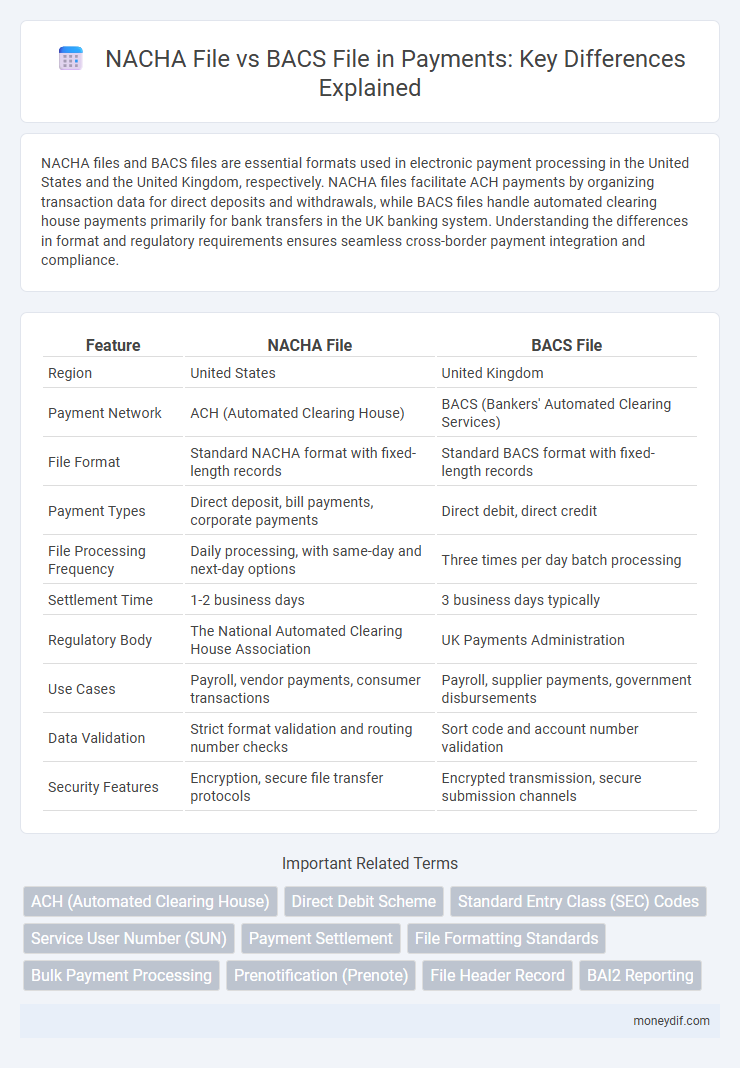
| Feature | NACHA File | BACS File |
|---|---|---|
| Region | United States | United Kingdom |
| Payment Network | ACH (Automated Clearing House) | BACS (Bankers' Automated Clearing Services) |
| File Format | Standard NACHA format with fixed-length records | Standard BACS format with fixed-length records |
| Payment Types | Direct deposit, bill payments, corporate payments | Direct debit, direct credit |
| File Processing Frequency | Daily processing, with same-day and next-day options | Three times per day batch processing |
| Settlement Time | 1-2 business days | 3 business days typically |
| Regulatory Body | The National Automated Clearing House Association | UK Payments Administration |
| Use Cases | Payroll, vendor payments, consumer transactions | Payroll, supplier payments, government disbursements |
| Data Validation | Strict format validation and routing number checks | Sort code and account number validation |
| Security Features | Encryption, secure file transfer protocols | Encrypted transmission, secure submission channels |
Understanding NACHA and BACS: Key Differences
NACHA files are widely used in the United States for Automated Clearing House (ACH) payments, enabling secure and standardized electronic fund transfers between banks. BACS files, primarily used in the United Kingdom, facilitate direct debit and credit transactions through the BACS payment system, adhering to UK banking regulations. Key differences include geographical usage, file format specifications, and processing timelines, with NACHA offering same-day payment options while BACS typically processes payments over three business days.
What is a NACHA File?
A NACHA file is a standardized electronic payment format used in the United States to facilitate Automated Clearing House (ACH) transactions, including direct deposits and bill payments. It contains detailed payment instructions such as account numbers, routing numbers, and transaction types, enabling financial institutions to process bulk electronic payments efficiently. NACHA files adhere to strict formatting and compliance rules set by the National Automated Clearing House Association, ensuring secure and accurate fund transfers.
What is a BACS File?
A BACS file is a standardized electronic payment file used in the United Kingdom for processing direct debit and direct credit transactions through the BACS payment system. It contains detailed payment instructions, including account numbers, sort codes, and payment amounts, formatted according to BACS specifications to ensure secure and accurate fund transfers. BACS files facilitate bulk payments between businesses and banks, enabling efficient end-to-end automation of payroll, supplier payments, and other recurring transactions.
Payment Processing Standards: NACHA vs BACS
NACHA and BACS represent prominent payment processing standards in the US and UK, respectively, each facilitating the electronic transfer of funds through ACH (Automated Clearing House) networks. NACHA files comply with strict formatting rules mandated by the National Automated Clearing House Association, ensuring efficient and secure batch payments primarily used for payroll, vendor payments, and direct deposits. BACS files, governed by the UK's BACS Payment Schemes Limited, adhere to specific structural protocols optimized for automated clearing, enabling reliable interbank payments and bulk transactions across British financial institutions.
Data Formats: Comparing NACHA and BACS Files
NACHA files utilize a fixed-width text format with strict field length requirements, optimized for ACH payments in the United States and formatted according to the NACHA Operating Rules. BACS files, used in the UK, follow a specific structured format consisting of header, detail, and control records, encoded in a fixed-width ASCII text format to facilitate Direct Debit and Direct Credit transactions. Both file formats emphasize data integrity and validation but differ in layout and field specifications tailored to their respective banking systems.
Security Measures in NACHA and BACS File Transfers
NACHA files implement strong security measures including encryption protocols like TLS and multi-factor authentication to protect ACH payments, reducing risks of fraud and data breaches. BACS file transfers also use strict security standards such as Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) and two-factor authentication to safeguard Direct Debit and Direct Credit transactions within the UK banking system. Both systems prioritize secure transmission and validation processes, ensuring sensitive payment information remains confidential and integral during electronic funds transfers.
Regional Usage: US NACHA vs UK BACS
NACHA files are predominantly used in the United States to facilitate Automated Clearing House (ACH) payments, enabling electronic funds transfers between banks within the US banking network. In contrast, BACS files are specific to the United Kingdom's payment system, serving as the standard format for direct debits and direct credits across UK banks. Regional regulatory requirements and banking infrastructures dictate the usage, with NACHA files adhering to US ACH rules and BACS files conforming to UK payment schemes governed by UK Finance.
Compliance Requirements for NACHA and BACS
NACHA files must comply with the Nacha Operating Rules that govern ACH payments in the U.S., ensuring stringent data format, transaction authorization, and security protocols. BACS files adhere to the UK's Payment Services Regulations and BACS Scheme rules, mandating accurate batch processing, transaction formatting, and anti-fraud measures. Both systems enforce strict compliance for data integrity, timely reporting, and proper authorization to maintain payment security and reduce fraud risks.
Integrating NACHA and BACS Files with Payment Systems
Integrating NACHA and BACS files with payment systems streamlines processing for ACH and UK Direct Debit transactions by enabling automated clearinghouse and bank transfer settlements. Payment platforms convert NACHA's standardized ACH formats and BACS structured bank payment files into actionable instructions, ensuring compliance with U.S. and U.K. banking regulations. This integration improves transaction accuracy, reduces settlement times, and enhances reconciliation with ledger systems.
Choosing Between NACHA and BACS for Your Business
Choosing between NACHA and BACS files hinges on your business's geographic location and payment processing needs, with NACHA dominating U.S. ACH payments and BACS prevalent in the UK. NACHA files support faster transactions and higher volume processing ideal for businesses requiring same-day payments within the United States. BACS files, while slower with a typical three-day settlement period, offer reliable and cost-effective electronic payment solutions tailored to UK payroll and vendor payments.
Important Terms
ACH (Automated Clearing House)
ACH (Automated Clearing House) payments primarily use the NACHA file format in the United States, which adheres to specific formatting and compliance rules set by Nacha for secure electronic funds transfers. In contrast, BACS files are used in the United Kingdom for processing direct debits and credits through the Bankers' Automated Clearing Services, featuring a distinct file structure and regulatory framework separate from NACHA standards.
Direct Debit Scheme
The Direct Debit Scheme enables automated bank transfers using specific file formats such as NACHA in the United States and BACS in the United Kingdom, each adhering to regional banking standards for processing payment instructions. NACHA files are formatted to comply with the Automated Clearing House (ACH) network rules, while BACS files follow the UK's payment processing protocols, ensuring secure and timely collection of funds from customers' accounts.
Standard Entry Class (SEC) Codes
Standard Entry Class (SEC) Codes in NACHA files specify the payment type and transaction characteristics within the ACH network, enabling precise processing and classification of electronic payments in the United States. In contrast, BACS files in the UK use their own formats and codes to manage similar payment instructions but do not incorporate SEC Codes, reflecting differences in regulatory frameworks and operational standards between the NACHA ACH system and the BACS payment scheme.
Service User Number (SUN)
The Service User Number (SUN) is a unique identifier assigned to organizations for processing payments through the BACS system in the UK, ensuring accurate routing and tracking of electronic transactions. In contrast, NACHA files used in the U.S. automated clearing house (ACH) network rely on originator identification codes rather than a SUN, reflecting different regulatory frameworks and payment processing standards.
Payment Settlement
Payment settlement involving NACHA files facilitates electronic funds transfers within the United States through the Automated Clearing House (ACH) network, while BACS files are used for automated payments and direct debits in the United Kingdom's banking system. Both file formats enable secure, standardized batch processing of transactions but differ in data structure, processing timelines, and regulatory frameworks aligned with their respective domestic payment ecosystems.
File Formatting Standards
NACHA files follow the standardized Automated Clearing House (ACH) format used primarily in the United States for electronic funds transfers, featuring fixed-length records and specific record types like File Header and Batch Header. BACS files, used predominantly in the United Kingdom, adhere to the BACS Standard 18 format with unique field structures, character lengths, and control totals designed for Direct Debit and Credit transactions within the UK banking system.
Bulk Payment Processing
Bulk payment processing involves handling large volumes of transactions quickly and efficiently using standardized file formats such as NACHA and BACS files. NACHA files, governed by the National Automated Clearing House Association in the U.S., facilitate ACH transfers for direct deposits and vendor payments, whereas BACS files operate within the U.K. banking system to process direct debits and credits, ensuring secure and timely settlement of bulk payments.
Prenotification (Prenote)
Prenotification (Prenote) in NACHA files involves sending a zero-dollar ACH transaction to verify account information before actual fund transfers, ensuring accuracy and reducing payment errors in the U.S. banking system. In contrast, BACS prenotification in the UK uses a similar zero-amount instruction to validate bank details within the BACS payment scheme, supporting secure and reliable electronic payments across British banks.
File Header Record
The File Header Record in NACHA files contains detailed information such as immediate destination and origin identifiers, creation date, and file ID, which are crucial for ACH payment processing in the U.S. In contrast, BACS files utilize a different header format with fields tailored to UK banking requirements, including service class codes and destination sort codes, reflecting distinct regional payment standards.
BAI2 Reporting
BAI2 reporting standard is primarily used for detailed bank account cash management information in the United States, often linked with NACHA files for ACH payments processing. In contrast, BACS files, used in the UK for automated clearing services, follow different formats and regulations, making BAI2 less applicable for direct BACS file reporting.
NACHA file vs BACS file Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com