Contactless payment uses RFID technology to enable quick transactions by tapping a card or device near a terminal, providing convenience without the need to carry cash or cards. Mobile wallets store card information securely on smartphones, allowing users to make payments, track expenses, and access loyalty programs through apps. Both methods enhance transaction speed and security but mobile wallets offer added features like digital receipts and integration with other financial services.
Table of Comparison
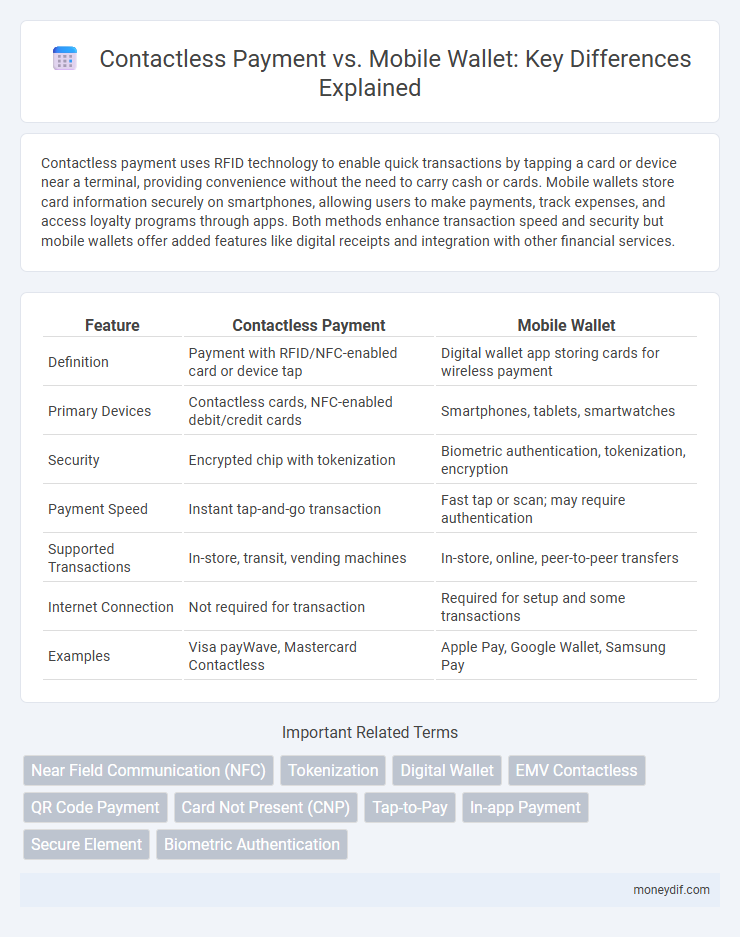
| Feature | Contactless Payment | Mobile Wallet |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Payment with RFID/NFC-enabled card or device tap | Digital wallet app storing cards for wireless payment |
| Primary Devices | Contactless cards, NFC-enabled debit/credit cards | Smartphones, tablets, smartwatches |
| Security | Encrypted chip with tokenization | Biometric authentication, tokenization, encryption |
| Payment Speed | Instant tap-and-go transaction | Fast tap or scan; may require authentication |
| Supported Transactions | In-store, transit, vending machines | In-store, online, peer-to-peer transfers |
| Internet Connection | Not required for transaction | Required for setup and some transactions |
| Examples | Visa payWave, Mastercard Contactless | Apple Pay, Google Wallet, Samsung Pay |
Understanding Contactless Payment Technologies
Contactless payment technologies utilize short-range wireless communication, primarily near-field communication (NFC), to enable secure and rapid transactions without physical card swipes or cash. Mobile wallets integrate these contactless capabilities with digital platforms, storing encrypted payment credentials on smartphones or wearable devices for seamless tap-to-pay experiences. Understanding the underlying NFC protocols and tokenization methods is crucial for assessing the security and convenience differences between traditional contactless cards and mobile wallet applications.
What Is a Mobile Wallet?
A mobile wallet is a digital application that securely stores payment information, such as credit or debit card details, on a smartphone or other mobile device, enabling users to make contactless payments via near-field communication (NFC) technology. Unlike traditional contactless payment methods that rely solely on physical cards, mobile wallets offer added features including transaction history, loyalty programs, and biometric authentication for enhanced security. Leading mobile wallet platforms include Apple Pay, Google Wallet, and Samsung Pay, each supporting seamless in-store and online payment experiences.
Key Differences Between Contactless Payment and Mobile Wallet
Contactless payment uses physical cards embedded with NFC chips to complete transactions by tapping on a payment terminal, while mobile wallets rely on smartphone apps to store digital cards and enable payments through NFC or QR codes. Mobile wallets often provide added features such as loyalty programs, transaction tracking, and multi-card management, which are not available with traditional contactless cards. Security also differs, with mobile wallets typically employing biometric authentication and tokenization, offering enhanced protection compared to standard contactless card payments.
Security Features: Contactless vs. Mobile Wallet
Contactless payment uses encrypted radio-frequency technology, minimizing data exposure during transactions, while mobile wallets incorporate multi-factor authentication, biometric verification, and tokenization to enhance security. Contactless cards limit transaction data to a single-use token, reducing fraud risk, whereas mobile wallets store multiple payment credentials secured by device-level encryption and secure element chips. Both methods offer robust protection, but mobile wallets provide an additional layer of user authentication and remote disabling capabilities for lost or stolen devices.
User Experience: Speed and Convenience Compared
Contactless payment offers unparalleled speed by enabling transactions with just a tap of a card or device, eliminating the need for PIN entry or signatures, which enhances convenience during busy shopping or transit scenarios. Mobile wallets provide added convenience by storing multiple payment methods, loyalty cards, and coupons in one app, streamlining the checkout process and reducing the need to carry physical items. Both technologies improve user experience significantly, but mobile wallets excel in offering personalized features and seamless integration with other digital services.
Popular Examples of Contactless Payment Methods
Popular examples of contactless payment methods include NFC-enabled credit and debit cards, which allow quick tap-to-pay transactions at retail terminals worldwide. Mobile wallets such as Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Samsung Pay integrate contactless technology with smartphones, enabling secure, tokenized payments without physical cards. Contactless payments are widely adopted across transportation systems, retail stores, and hospitality industries due to their convenience and enhanced security features.
Leading Mobile Wallet Providers in the Market
Leading mobile wallet providers such as Apple Pay, Google Wallet, and Samsung Pay dominate the contactless payment market by offering seamless, secure transactions through NFC technology. These platforms integrate with major credit and debit cards, enabling users to make quick payments via smartphones or wearable devices at compatible point-of-sale terminals. Their widespread acceptance and robust security features like tokenization and biometric authentication drive the growing preference for mobile wallets over traditional contactless payment cards.
Adoption Rates: Consumer Preferences and Trends
Contactless payment adoption rates have surged globally, with surveys indicating that over 70% of consumers prefer using tap-to-pay cards due to speed and convenience. Mobile wallets, integrating features like loyalty programs and biometric authentication, show a 60% adoption rate, particularly among younger demographics aged 18-34. Trends reveal a steady shift towards mobile wallets as smartphone penetration rises, yet contactless cards maintain strong usage in retail environments favoring quick transactions.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Payment Method
Contactless payment offers rapid transactions by simply tapping a card or device, enhancing convenience and reducing physical contact, though it may face limitations with transaction limits and merchant acceptance. Mobile wallets provide secure payments through tokenization and support additional features like loyalty programs and transaction tracking, but they require smartphone compatibility and can be hindered by battery life or software issues. Both methods improve payment efficiency but vary in accessibility, security measures, and hardware dependency.
Future Trends in Digital Payment Technologies
Contactless payment methods and mobile wallets are rapidly evolving with advances in near-field communication (NFC) and biometric authentication technologies. Future trends indicate increased integration of artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance transaction security and personalized user experiences. The rise of blockchain technology and digital currencies is expected to further revolutionize digital payment ecosystems by enabling faster, more transparent, and decentralized transactions.
Important Terms
Near Field Communication (NFC)
Near Field Communication (NFC) enables secure contactless payment transactions by allowing devices to communicate wirelessly at short distances, commonly used in contactless credit cards and mobile wallets such as Apple Pay and Google Wallet. Unlike traditional contactless payment methods limited to physical cards, mobile wallets leverage NFC technology to store multiple payment options, loyalty cards, and authentication features, enhancing convenience and security for consumers.
Tokenization
Tokenization enhances security by replacing sensitive card information with unique digital tokens in both contactless payments and mobile wallets, reducing the risk of fraud during transactions. Contactless payment systems utilize tokenization to authorize quick tap-to-pay actions, while mobile wallets leverage this technology to securely store and transmit tokenized payment credentials across multiple devices.
Digital Wallet
Digital wallets enable secure contactless payments by storing encrypted card information for tap-and-go transactions at NFC-enabled terminals, enhancing convenience compared to traditional magnetic stripe cards. Mobile wallets integrate contactless payment functionality within smartphones or wearables, offering added features like loyalty programs, transaction history, and biometric authentication for elevated security and user experience.
EMV Contactless
EMV Contactless technology enables secure, tap-to-pay transactions by transmitting encrypted payment data between the card and the terminal, enhancing transaction speed and reducing physical contact. Mobile wallets integrate EMV Contactless protocols to store card credentials digitally, allowing users to make payments with smartphones or wearable devices while benefiting from tokenization and biometric authentication for added security.
QR Code Payment
QR Code payment offers a secure and efficient contactless payment method by scanning a code displayed on a merchant's terminal, enabling transactions without physical card interaction. Mobile wallets integrate QR code payments with stored card information and loyalty programs, streamlining purchases and enhancing user convenience compared to traditional contactless card payments.
Card Not Present (CNP)
Card Not Present (CNP) transactions occur when payments are made without physically presenting a card, commonly seen in mobile wallet and contactless payment methods. Mobile wallets offer encrypted tokenization and biometric authentication, enhancing security beyond traditional contactless payments that rely solely on NFC technology.
Tap-to-Pay
Tap-to-Pay technology enables seamless contactless payments by allowing users to simply tap their NFC-enabled cards or devices on a payment terminal, offering enhanced speed and security compared to traditional card swiping. Mobile wallets, such as Apple Pay or Google Pay, use Tap-to-Pay functionality but add layers of encrypted tokenization and biometric authentication, making transactions more secure and convenient than standard contactless card payments.
In-app Payment
In-app payment systems integrate seamlessly with mobile wallets, enabling users to complete transactions swiftly without entering card details, leveraging contactless payment technology for enhanced security and convenience. Mobile wallets store encrypted payment information, facilitating in-app contactless payments through NFC or tokenization, reducing fraud risk and streamlining the checkout experience.
Secure Element
Secure Element is a tamper-resistant hardware chip embedded in devices that stores sensitive payment data and cryptographic keys, ensuring secure processing of contactless payments by isolating transaction information from the main device operating system. It provides a higher level of security compared to some mobile wallets, which may rely on software-based encryption and cloud storage, making Secure Elements critical for protecting against fraud and unauthorized access during NFC-based contactless transactions.
Biometric Authentication
Biometric authentication enhances security in contactless payment systems by using unique physiological traits such as fingerprints or facial recognition to verify user identity, reducing fraud risk. Mobile wallets integrate biometric authentication to streamline transaction approvals, enabling faster and more secure payments compared to traditional contactless cards.
Contactless Payment vs Mobile Wallet Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com