ISO (Independent Sales Organization) and MSP (Merchant Service Provider) play distinct roles in payment processing, with ISOs primarily focused on recruiting and managing sales agents for merchant accounts while MSPs provide the essential payment processing services and infrastructure. ISOs act as intermediaries between merchants and acquiring banks, facilitating merchant onboarding and support, whereas MSPs handle transaction authorization, settlement, and security compliance. Understanding the differences between ISO and MSP helps businesses select the appropriate partner to optimize payment processing efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Table of Comparison
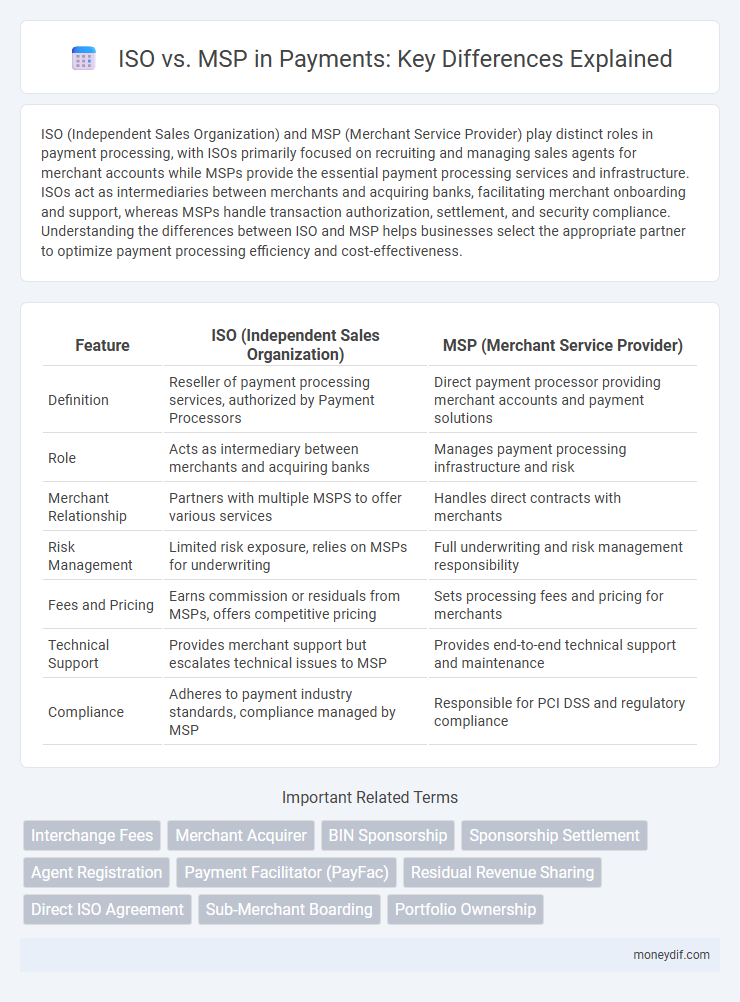
| Feature | ISO (Independent Sales Organization) | MSP (Merchant Service Provider) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reseller of payment processing services, authorized by Payment Processors | Direct payment processor providing merchant accounts and payment solutions |
| Role | Acts as intermediary between merchants and acquiring banks | Manages payment processing infrastructure and risk |
| Merchant Relationship | Partners with multiple MSPS to offer various services | Handles direct contracts with merchants |
| Risk Management | Limited risk exposure, relies on MSPs for underwriting | Full underwriting and risk management responsibility |
| Fees and Pricing | Earns commission or residuals from MSPs, offers competitive pricing | Sets processing fees and pricing for merchants |
| Technical Support | Provides merchant support but escalates technical issues to MSP | Provides end-to-end technical support and maintenance |
| Compliance | Adheres to payment industry standards, compliance managed by MSP | Responsible for PCI DSS and regulatory compliance |
Understanding ISO and MSP: Key Differences in Payment Processing
Independent Sales Organizations (ISOs) act as intermediaries between merchants and acquiring banks, offering sales and support for payment processing services. Merchant Service Providers (MSPs) directly manage payment processing, including transaction authorization and settlement, often integrating hardware and software solutions. The key difference lies in ISOs primarily facilitating service sales while MSPs deliver end-to-end payment processing operations.
Roles and Responsibilities: ISO vs MSP Explained
ISO (Independent Sales Organization) primarily focuses on merchant acquisition and sales, acting as intermediaries between merchants and payment processors. MSP (Merchant Service Provider) typically offers comprehensive payment solutions, including transaction processing, risk management, and customer support. Understanding these distinct roles helps businesses choose the right partner for payment processing and merchant account management.
Regulatory Requirements for ISOs and MSPs
ISOs (Independent Sales Organizations) and MSPs (Merchant Service Providers) both navigate complex regulatory requirements, with ISOs typically adhering to PCI DSS standards, anti-money laundering (AML) laws, and card network rules to ensure secure payment processing. MSPs must comply with similar regulations but often face additional scrutiny related to underwriting, transaction monitoring, and risk management due to their more direct relationship with merchant accounts. Both entities must maintain compliance with the latest Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) and federal regulations to mitigate fraud and ensure data protection in payment processing ecosystems.
How ISOs and MSPs Impact Merchant Onboarding
ISOs (Independent Sales Organizations) and MSPs (Merchant Service Providers) streamline merchant onboarding by offering tailored payment solutions and expedited application processes, reducing friction for new merchants. ISOs primarily act as intermediaries between acquiring banks and merchants, facilitating access to payment networks, while MSPs provide comprehensive service packages including payment gateway technology and risk management. Their combined expertise accelerates approval timelines, enhances transaction security, and improves overall merchant satisfaction.
Fee Structures: ISO vs MSP
ISO fee structures typically involve a percentage of transaction volume combined with per-transaction fees, allowing independent sales organizations to generate revenue based on merchant sales performance. MSPs often arrange tiered pricing models with fixed rates and monthly minimums, providing more predictable costs but less flexibility for merchants with fluctuating sales. Understanding the distinct fee arrangements helps merchants choose the optimal partnership for cost efficiency and scalability in payment processing.
Technology Integration: Comparing ISO and MSP Solutions
ISO (Independent Sales Organization) solutions often emphasize seamless technology integration through third-party partnerships and white-label platforms, enabling businesses to customize payment systems efficiently. MSP (Merchant Service Provider) solutions typically offer proprietary payment processing technology with built-in features for end-to-end transaction management, reducing the need for additional integrations. Choosing between ISO and MSP depends on the desired level of control, technical resources, and the complexity of integration required for smooth payment processing workflows.
Risk Management in ISO vs MSP Operations
ISO (Independent Sales Organization) and MSP (Merchant Service Provider) differ significantly in risk management within payment operations. ISOs primarily focus on underwriting merchants and monitoring transaction behaviors to mitigate fraud and chargebacks, leveraging comprehensive risk assessment tools. MSPs, on the other hand, emphasize ongoing account management and compliance monitoring, ensuring adherence to PCI DSS standards while managing operational risks linked to transaction processing and settlement.
Choosing Between an ISO and MSP for Your Business
Selecting between an Independent Sales Organization (ISO) and a Merchant Service Provider (MSP) depends on your business's payment processing needs and control preferences. ISOs typically offer more personalized service and flexibility for businesses seeking tailored merchant accounts, while MSPs provide bundled payment solutions with simplified onboarding and consolidated reporting. Evaluating factors such as pricing structures, risk management, and customer support will help determine the best payment partner to optimize transaction efficiency and compliance.
Partnership Opportunities: ISO vs MSP Collaboration
ISO and MSP partnership opportunities enhance payment processing capabilities by combining independent sales organizations' extensive merchant networks with managed service providers' technical integration expertise. Collaboration enables streamlined transaction workflows, improved customer support, and access to advanced payment technologies that drive revenue growth. Leveraging the strengths of both ISO and MSP creates a competitive advantage in the evolving payments ecosystem.
Future Trends: The Evolving Landscape of ISOs and MSPs
Future trends in the payments industry indicate a growing convergence between Independent Sales Organizations (ISOs) and Merchant Service Providers (MSPs), driven by advancements in technology such as AI-driven payment processing, blockchain integration, and enhanced security protocols like tokenization and biometric authentication. The evolving landscape sees ISOs expanding their service portfolios to include value-added solutions like data analytics and omnichannel payment capabilities, while MSPs increasingly adopt scalable, cloud-based platforms for seamless merchant onboarding and real-time transaction monitoring. This shift fosters a more competitive ecosystem, emphasizing customization, compliance with global regulatory standards, and improved customer experience in the rapidly changing payment environment.
Important Terms
Interchange Fees
Interchange fees are transaction charges set by card networks and paid by merchant service providers (MSPs) to issuing banks, governed under ISO (Independent Sales Organizations) agreements that facilitate merchant account management. MSPs manage merchant relationships and assume responsibility for interchange fees, ensuring compliance with ISO guidelines to optimize payment processing efficiency.
Merchant Acquirer
Merchant acquirers process payment transactions on behalf of merchants and must comply with ISO (Independent Sales Organization) or MSP (Merchant Service Provider) standards, where ISOs act as intermediaries authorized by acquirers, and MSPs directly manage merchant accounts and transaction settlements. Differentiation between ISO and MSP impacts risk management, fee structures, and regulatory compliance within the payment processing ecosystem.
BIN Sponsorship
BIN sponsorship enables merchants to process card payments by leveraging a payment service provider's Bank Identification Number (BIN), facilitating transaction routing and authorization. In the context of ISO vs MSP, ISOs act as resellers under an MSP's BIN, while MSPs hold the BIN sponsorship directly from the card networks, providing more comprehensive control and compliance management.
Sponsorship Settlement
Sponsorship settlement in the context of ISO (Independent Sales Organization) versus MSP (Merchant Service Provider) involves distinct contractual and financial arrangements where ISOs typically act as intermediaries managing merchant acquiring processes, while MSPs provide ongoing payment processing services directly to merchants. Effective settlement coordination ensures timely reconciliation of transaction fees, chargebacks, and residual commissions, optimizing cash flow and compliance with payment network regulations.
Agent Registration
Agent registration under ISO (Independent Sales Organization) models typically involves a streamlined onboarding process focused on compliance with payment card industry standards and merchant agreements, whereas MSP (Member Service Provider) arrangements require agents to meet stricter regulatory and underwriting criteria due to their role in directly managing merchant risk and transactions. Adhering to ISO standards ensures consistent agent validation and operational efficiency, while MSP registration emphasizes enhanced due diligence and ongoing monitoring to mitigate financial and fraud risks.
Payment Facilitator (PayFac)
A Payment Facilitator (PayFac) streamlines merchant onboarding by aggregating multiple sub-merchants under a single ISO (Independent Sales Organization) license, simplifying compliance and risk management compared to traditional Merchant Service Providers (MSPs). Unlike MSPs that manage individual merchant accounts, PayFacs leverage ISO registration to offer faster transaction processing, real-time underwriting, and consolidated payment solutions.
Residual Revenue Sharing
Residual Revenue Sharing models create ongoing income streams by allocating a portion of recurring revenue between Independent Sales Organizations (ISOs) and Managed Service Providers (MSPs), optimizing long-term profitability. ISOs typically benefit from upfront transaction fees, while MSPs focus on residuals derived from managed services, fostering collaboration and sustained financial growth.
Direct ISO Agreement
Direct ISO Agreement establishes a contractual relationship between merchants and the ISO, bypassing the need for a Master Service Provider (MSP), which typically consolidates various ISOs under one umbrella. This agreement streamlines authorization, processing, and settlement of payment transactions by directly connecting the ISO to payment networks, enhancing control and revenue potential in comparison to the layered MSP model.
Sub-Merchant Boarding
Sub-merchant boarding involves onboarding individual sellers under a larger merchant account, where Independent Sales Organizations (ISOs) primarily focus on acquiring and managing merchant relationships, while Merchant Service Providers (MSPs) handle the technical processing and underwriting aspects. Effective collaboration between ISOs and MSPs streamlines risk management, compliance, and transaction processing for sub-merchants within payment ecosystems.
Portfolio Ownership
Portfolio ownership in ISO standards emphasizes strategic alignment, value optimization, and risk management across all projects, ensuring adherence to governance frameworks. MSP (Managing Successful Programmes) focuses on coordinated management of related projects and programs within the portfolio to achieve transformational outcomes and benefits realization.
ISO vs MSP Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com