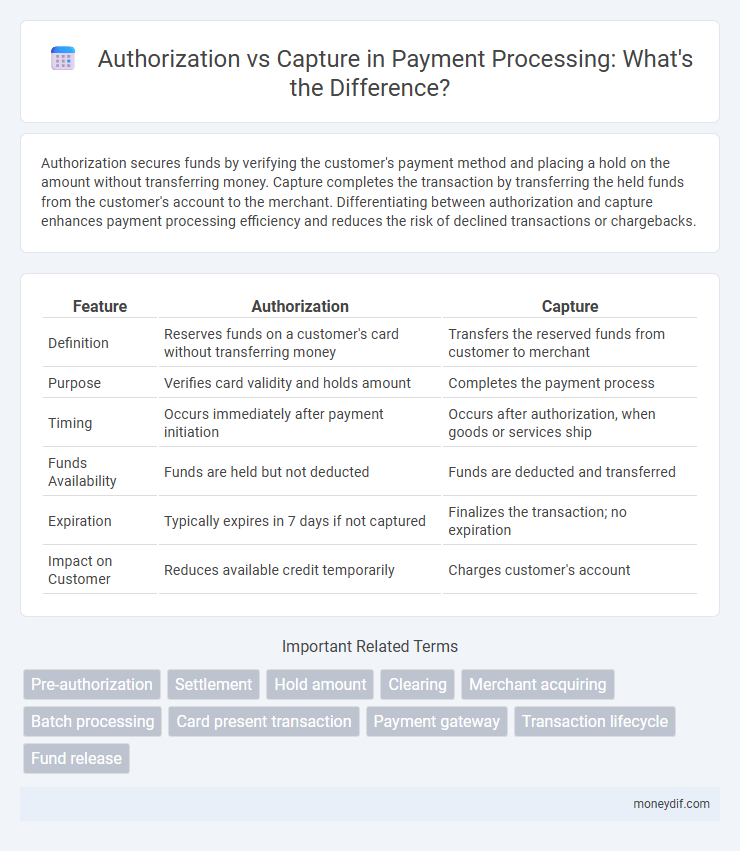
Authorization secures funds by verifying the customer's payment method and placing a hold on the amount without transferring money. Capture completes the transaction by transferring the held funds from the customer's account to the merchant. Differentiating between authorization and capture enhances payment processing efficiency and reduces the risk of declined transactions or chargebacks.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Authorization | Capture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reserves funds on a customer's card without transferring money | Transfers the reserved funds from customer to merchant |
| Purpose | Verifies card validity and holds amount | Completes the payment process |
| Timing | Occurs immediately after payment initiation | Occurs after authorization, when goods or services ship |
| Funds Availability | Funds are held but not deducted | Funds are deducted and transferred |
| Expiration | Typically expires in 7 days if not captured | Finalizes the transaction; no expiration |
| Impact on Customer | Reduces available credit temporarily | Charges customer's account |
Understanding Payment Authorization and Capture
Payment authorization is the process where a cardholder's bank verifies the availability of funds and reserves the amount for a transaction without transferring money immediately. Capture occurs when the merchant completes the transaction by requesting the transfer of the authorized funds from the cardholder's bank to the merchant's account. Understanding the distinction between authorization and capture is crucial for managing cash flow and reducing chargebacks in payment processing.
Key Differences Between Authorization and Capture
Authorization secures approval from the card issuer to hold funds but does not transfer money, ensuring the customer's account has sufficient balance. Capture finalizes the transaction by transferring the authorized funds from the customer's account to the merchant. Authorization typically occurs immediately, while capture may be delayed, enabling merchants to confirm product availability before payment settlement.
How Payment Authorization Works
Payment authorization confirms the availability of funds by placing a hold on the customer's credit or debit card without immediately transferring money. This process involves the issuer bank verifying the card details, checking for sufficient credit or balance, and reserving the authorized amount for the merchant. Authorization ensures the transaction's legitimacy and secures the funds before the capture stage, where the actual payment is completed.
The Process of Payment Capture
Payment capture is the critical step where authorized funds are transferred from the customer's account to the merchant's account, confirming the transaction and securing payment. During this process, the payment gateway communicates with the issuing bank to finalize the transaction amount initially held during authorization. Successful payment capture ensures funds are settled, enabling order fulfillment and reducing the risk of payment failure or chargebacks.
Importance of Authorization in Fraud Prevention
Authorization serves as a critical checkpoint in the payment process, verifying the validity of the cardholder's credentials and available funds before completing a transaction. By confirming these details, authorization helps to detect and prevent fraudulent activities, reducing chargebacks and financial losses for merchants. Ensuring robust authorization protocols enhances security and builds consumer trust in digital payment systems.
When to Use Authorization vs Capture
Use authorization to verify fund availability and hold the amount without immediately charging the customer, ideal for pre-orders or reservations. Opt for capture when ready to complete the transaction and transfer funds, typically after goods are shipped or services rendered. Combining authorization with deferred capture reduces fraud risk and ensures payment accuracy before finalizing the sale.
Authorization Holds vs Captured Funds
Authorization holds temporarily reserve funds on a customer's payment method without transferring money, ensuring the cardholder has sufficient credit or balance. Captured funds represent the actual transfer of money from the customer's account to the merchant, finalizing the payment. Understanding the distinction between authorization holds and captured funds is crucial for managing cash flow and preventing chargebacks in payment processing.
Impact on Merchant Settlement and Cash Flow
Authorization secures a hold on the customer's funds, ensuring the merchant that payment is approved, but does not transfer the funds immediately, delaying actual settlement. Capture initiates the transfer of funds from the customer to the merchant, directly impacting cash flow by finalizing the transaction and triggering settlement. Delays between authorization and capture can cause cash flow disruptions and affect the timing of merchant settlements.
Best Practices for Managing Authorization and Capture
Best practices for managing authorization and capture include separating the two processes to minimize risk and improve cash flow control. Authorized amounts should be validated and held securely to prevent fraud and ensure funds are available before capture. Implementing time limits for capture after authorization reduces the chance of transaction declines and enhances customer satisfaction.
Common Issues and Solutions in Payment Authorization and Capture
Payment authorization often faces common issues such as declined transactions due to insufficient funds, expired cards, or incorrect billing information. Capture problems may arise from delayed processing times or partial captures leading to discrepancies in customer billing and merchant payouts. Solutions include implementing real-time validation of payment data, using tokenization to reduce errors, and ensuring seamless communication between authorization and capture systems to improve transaction accuracy and customer experience.
Important Terms
Pre-authorization
Pre-authorization temporarily holds funds on a customer's credit card to ensure availability without finalizing the transaction, while authorization versus capture involves first approving the payment and then separately completing the charge. This two-step process optimizes cash flow management and reduces fraud risk by validating funds before the actual capture of payment.
Settlement
Settlement refers to the process where funds from an authorized transaction are transferred from the customer's bank to the merchant's account, finalizing the payment. Authorization holds the funds temporarily, while capture confirms the transaction amount, triggering settlement to complete the financial transfer.
Hold amount
Hold amount refers to the temporary reservation of funds on a credit card during the authorization phase, ensuring availability without transferring money until the capture is completed. Capture finalizes the transaction by converting the authorized hold into an actual charge, deducting the reserved funds from the cardholder's account.
Clearing
Clearing in payment processing refers to the transfer of transaction data from the merchant to the acquiring bank for authorization, which verifies the availability of funds. Capture occurs after authorization, where the funds are actually transferred from the customer's account to the merchant's account, completing the payment cycle.
Merchant acquiring
Merchant acquiring involves the process where the acquirer bank facilitates transaction authorization by validating cardholder information and available funds, ensuring transaction legitimacy. Capture occurs after authorization, where the merchant submits the transaction for settlement, transferring funds from the cardholder's account to the merchant's account.
Batch processing
Batch processing streamlines the handling of multiple credit card transactions by grouping authorization holds and later submitting them for capture in a consolidated batch, reducing processing time and errors. This method is essential for businesses managing high volumes of sales, allowing funds to be secured at authorization and finalized upon shipment or service delivery through batch capture.
Card present transaction
Card present transactions involve the physical presence of the cardholder and the card during the payment process, typically resulting in faster authorization due to direct communication with the issuer. Authorization approves the transaction amount by reserving the funds, while capture completes the payment by transferring the reserved funds from the cardholder's account to the merchant, often occurring immediately in card present scenarios.
Payment gateway
Payment gateway authorization verifies the cardholder's funds and reserves the transaction amount without transferring funds, ensuring the payment method is valid. Capture completes the transaction by finalizing the transfer of authorized funds from the customer's account to the merchant.
Transaction lifecycle
The transaction lifecycle involves two key stages: authorization, where the payment is approved but funds are not yet transferred, and capture, where the authorized amount is actually charged to the customer's account. Authorization holds the funds to ensure availability, while capture finalizes the transaction by settling the payment with the acquiring bank.
Fund release
Fund release occurs when a merchant captures the authorized amount on a credit card transaction, converting the hold into a finalized payment. Authorization secures the funds temporarily, while capture completes the transfer, ensuring the merchant receives payment and the cardholder's account is charged accordingly.
authorization vs capture Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com