3D Secure provides an advanced layer of authentication by requiring users to verify their identity through a password or biometric check, significantly reducing the risk of fraudulent transactions. CVV verification, while essential for confirming cardholder possession, offers a basic level of security by validating the three-digit code on the back of the card during online payments. Combining 3D Secure with CVV verification enhances overall payment security, minimizing chargebacks and unauthorized use.
Table of Comparison
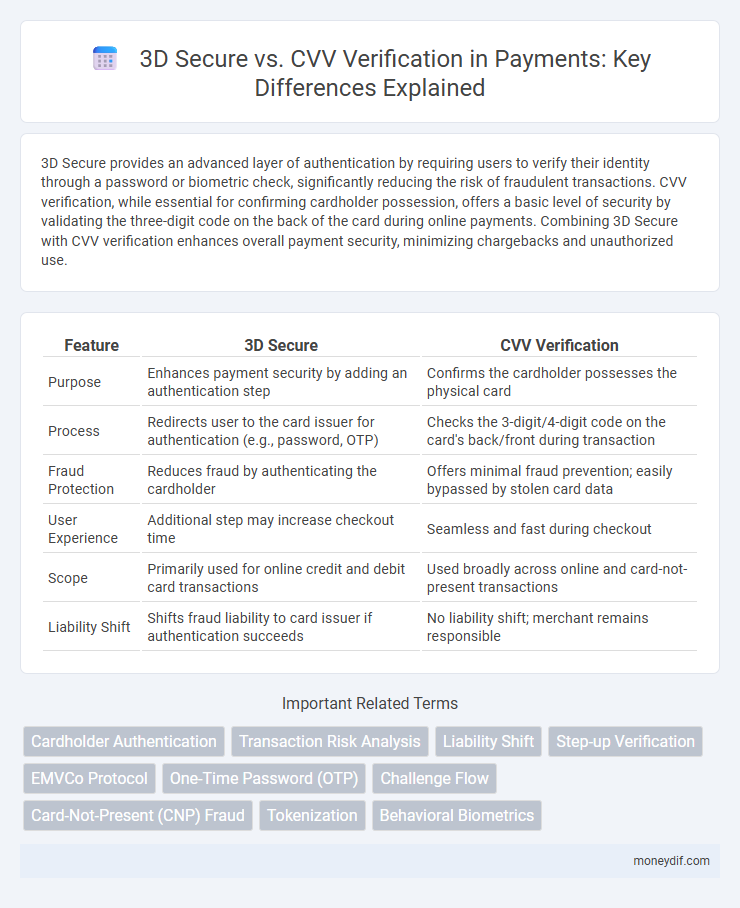
| Feature | 3D Secure | CVV Verification |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Enhances payment security by adding an authentication step | Confirms the cardholder possesses the physical card |
| Process | Redirects user to the card issuer for authentication (e.g., password, OTP) | Checks the 3-digit/4-digit code on the card's back/front during transaction |
| Fraud Protection | Reduces fraud by authenticating the cardholder | Offers minimal fraud prevention; easily bypassed by stolen card data |
| User Experience | Additional step may increase checkout time | Seamless and fast during checkout |
| Scope | Primarily used for online credit and debit card transactions | Used broadly across online and card-not-present transactions |
| Liability Shift | Shifts fraud liability to card issuer if authentication succeeds | No liability shift; merchant remains responsible |
Understanding 3D Secure: An Overview
3D Secure is an advanced payment authentication protocol designed to reduce fraud by requiring cardholders to complete an additional verification step during online transactions. Unlike CVV verification, which only confirms card details from the cardholder, 3D Secure adds a layer of security through password or biometric authentication. This enhanced protection helps merchants and banks minimize chargebacks while providing customers with safer e-commerce experiences.
What is CVV Verification?
CVV verification is a security feature used in card-not-present transactions to validate the cardholder possesses the physical credit or debit card by requiring the Card Verification Value, a three or four-digit code printed on the card. Unlike 3D Secure, which adds an additional authentication step through the card issuer, CVV verification prevents fraudulent transactions by confirming the card's authenticity during the payment process. This method enhances transaction security but does not provide real-time authentication or liability shift benefits that 3D Secure offers.
How 3D Secure Works in Online Payments
3D Secure enhances online payment security by adding an authentication layer where cardholders confirm their identity through a password, biometric data, or a one-time code during checkout. Unlike CVV verification, which only checks card details, 3D Secure actively involves the card issuer in real-time authentication to prevent unauthorized transactions. This process reduces fraud and chargebacks by ensuring the actual cardholder approves the payment before completion.
CVV Verification Process Explained
CVV verification involves the customer entering the three- or four-digit Card Verification Value found on the back or front of their credit or debit card during an online transaction. This process enhances security by confirming the cardholder possesses the physical card, reducing fraud risk in card-not-present transactions. Unlike 3D Secure, CVV verification does not require user authentication through a password or biometric method but relies solely on the unique card code.
Security Benefits of 3D Secure
3D Secure enhances payment security by requiring online shoppers to complete an authentication step with the card issuer, significantly reducing fraud and unauthorized transactions. Unlike CVV verification, which only confirms the card's physical details, 3D Secure adds a dynamic authentication layer that protects against stolen card data misuse. This protocol boosts consumer confidence and reduces chargebacks for merchants by verifying the cardholder's identity in real-time during checkout.
Strengths and Weaknesses of CVV Verification
CVV verification provides a simple and quick method to confirm cardholder presence during online transactions but lacks protection against fraudulent usage if card data is compromised. It does not authenticate the user beyond the physical card information, making it vulnerable to phishing and data breaches. Despite its ease of use, CVV verification alone offers limited security compared to more robust methods like 3D Secure, which incorporates dynamic authentication factors.
User Experience: 3D Secure vs CVV
3D Secure enhances payment security by requiring user authentication through a password or biometric verification, reducing fraud but sometimes causing friction due to extra steps. CVV verification offers a simpler user experience by requiring only the card's three-digit code, which speeds up checkout but provides less robust fraud protection. Balancing security and convenience, many merchants combine both methods to optimize user experience while minimizing fraudulent transactions.
Fraud Prevention: Comparing Effectiveness
3D Secure offers an advanced layer of authentication by requiring cardholder identity verification through a password or biometric, significantly reducing fraudulent transactions in e-commerce. CVV verification, while useful for confirming physical card possession, lacks dynamic authentication and is more susceptible to fraud such as card-not-present scams. Studies indicate 3D Secure reduces fraud rates by up to 70%, making it more effective than CVV alone in securing online payments.
Industry Adoption and Compliance
3D Secure has seen broader adoption across e-commerce platforms due to its enhanced fraud prevention capabilities and compliance with PSD2 regulations, making it a preferred choice among global payment processors. CVV verification remains a fundamental security measure but is often supplemented by 3D Secure to meet stricter industry compliance standards, especially in regions with high fraud risk. Payment networks and regulatory bodies increasingly mandate 3D Secure to ensure transaction authentication, driving widespread industry compliance and reducing chargebacks.
Choosing the Right Payment Verification Method
Choosing the right payment verification method depends on transaction risk, user experience, and fraud prevention priorities. 3D Secure provides enhanced security by requiring authentication through the card issuer, reducing chargebacks and liability in online purchases. CVV verification offers a quick check to confirm cardholder possession but lacks the dynamic authentication layer that 3D Secure provides, making it less effective against sophisticated fraud attempts.
Important Terms
Cardholder Authentication
Cardholder authentication enhances online transaction security by verifying the identity of the cardholder, primarily using 3D Secure or CVV verification methods. 3D Secure provides an additional authentication layer through password or biometric confirmation, reducing fraud risk more effectively than CVV verification, which only validates the card's security code without confirming the cardholder's identity.
Transaction Risk Analysis
Transaction Risk Analysis enhances payment security by evaluating the likelihood of fraudulent activity based on behavioral and transactional data, improving decision accuracy beyond CVV verification alone. 3D Secure protocols add an authentication layer that significantly reduces chargebacks by confirming cardholder identity during the transaction, providing stronger protection compared to the static CVV code verification.
Liability Shift
Liability shift in payments favors merchants using 3D Secure authentication over CVV verification, as 3D Secure shifts fraud liability to the card issuer during disputed transactions. Implementing 3D Secure reduces chargeback risks and enhances transaction security by verifying cardholder identity beyond static CVV codes.
Step-up Verification
Step-up Verification enhances transaction security by requiring additional authentication, often through 3D Secure, which verifies cardholder identity via a password or biometric check during checkout. Compared to CVV verification, which only confirms card details, 3D Secure adds a dynamic layer of protection that reduces fraud and chargebacks in online payments.
EMVCo Protocol
EMVCo Protocol facilitates secure payment authentication by supporting both 3D Secure and CVV verification methods, with 3D Secure providing dynamic, multifactor authentication to reduce fraud, while CVV verification relies on static card information for transaction validation. Integration of EMVCo standards enhances interoperability and security across payment networks, ensuring compliant, efficient processing of cardholder authentication.
One-Time Password (OTP)
One-Time Password (OTP) authentication enhances transaction security in 3D Secure protocols by providing dynamic, time-sensitive codes that verify cardholder identity beyond static Card Verification Value (CVV) checks. Unlike CVV verification, which relies on fixed card details vulnerable to theft, OTPs generated during 3D Secure challenges significantly reduce fraud in online payments by requiring real-time user authorization.
Challenge Flow
Challenge Flow in payment security distinguishes itself by requiring real-time user authentication through 3D Secure protocols, enhancing fraud prevention beyond static CVV verification. Unlike CVV, which only confirms card information, Challenge Flow dynamically validates the cardholder's identity during the transaction, significantly reducing unauthorized access and chargebacks.
Card-Not-Present (CNP) Fraud
Card-Not-Present (CNP) fraud occurs when unauthorized transactions are made without the physical card, exploiting weaknesses in online payment authentication methods such as CVV verification. 3D Secure offers enhanced security by adding multi-factor authentication, significantly reducing fraudulent chargebacks compared to relying solely on CVV codes for transaction approval.
Tokenization
Tokenization enhances payment security by replacing sensitive card data with unique tokens during 3D Secure authentication, reducing fraud risk compared to CVV verification which only confirms card presence without encrypting data. Unlike CVV verification, 3D Secure leverages multi-factor authentication and tokenized payment credentials to provide stronger protection against unauthorized transactions in e-commerce environments.
Behavioral Biometrics
Behavioral biometrics enhances 3D Secure authentication by analyzing unique user interactions such as typing patterns and device handling, offering stronger fraud prevention compared to traditional CVV verification. Unlike CVV codes, which rely on static information, behavioral biometrics continuously verifies user identity during transactions, reducing false declines and improving security in online payments.
3D Secure vs CVV Verification Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com