EMV technology uses chip cards that require physical insertion into a payment terminal for secure authentication, while NFC enables contactless transactions by allowing cards or mobile devices to communicate with terminals via short-range wireless signals. EMV offers enhanced security through dynamic data verification, reducing fraud in card-present scenarios, whereas NFC provides convenience and speed by enabling tap-to-pay functionality. Both technologies are integral in modern payment systems, balancing security and user experience in different transaction environments.
Table of Comparison
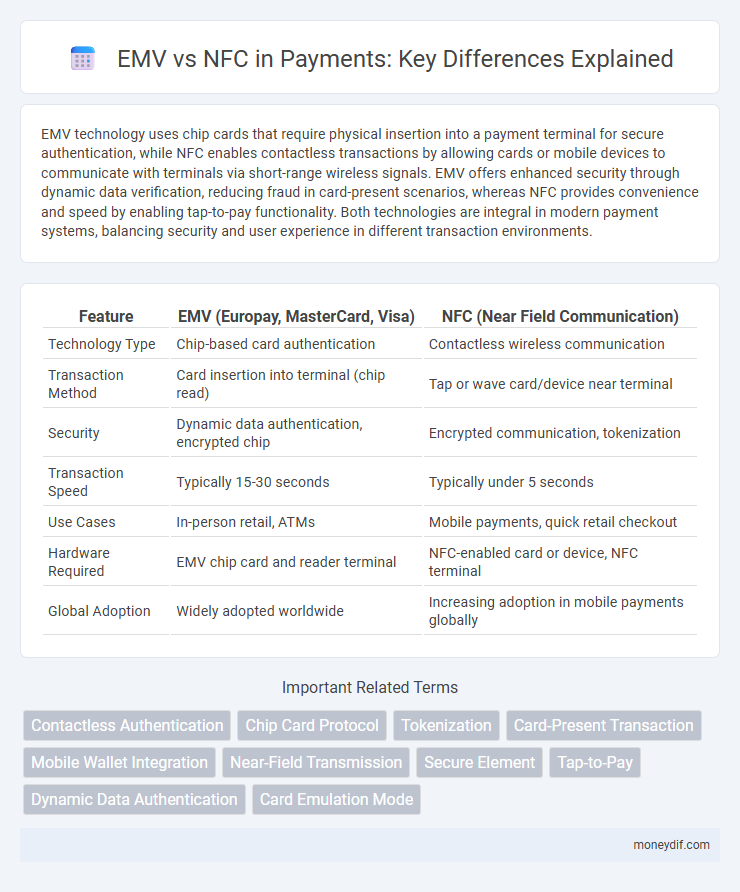
| Feature | EMV (Europay, MasterCard, Visa) | NFC (Near Field Communication) |
|---|---|---|
| Technology Type | Chip-based card authentication | Contactless wireless communication |
| Transaction Method | Card insertion into terminal (chip read) | Tap or wave card/device near terminal |
| Security | Dynamic data authentication, encrypted chip | Encrypted communication, tokenization |
| Transaction Speed | Typically 15-30 seconds | Typically under 5 seconds |
| Use Cases | In-person retail, ATMs | Mobile payments, quick retail checkout |
| Hardware Required | EMV chip card and reader terminal | NFC-enabled card or device, NFC terminal |
| Global Adoption | Widely adopted worldwide | Increasing adoption in mobile payments globally |
Understanding EMV and NFC: Payment Technologies Explained
EMV (Europay, MasterCard, and Visa) is a global standard for chip card payments that enhances transaction security through cryptographic authentication, reducing fraud in point-of-sale environments. NFC (Near Field Communication) technology enables contactless payments by allowing secure data exchange between devices within a few centimeters, typically used in mobile wallets and tap-and-go cards. Understanding the differences highlights EMV's focus on chip card security versus NFC's emphasis on convenience and speed in contactless transactions.
Core Differences Between EMV and NFC Payments
EMV payments rely on chip cards requiring physical contact or insertion into a terminal, providing enhanced security through dynamic data authentication during transactions. NFC payments utilize contactless technology allowing secure transactions via smartphones or contactless cards by tapping near a reader, offering convenience and speed. Core differences include transaction methods--EMV is contact-based, while NFC is contactless--and user experience, where NFC emphasizes quick, touch-free payments compared to EMV's card insertion process.
Security Features: EMV vs NFC Transactions
EMV transactions utilize dynamic cryptographic authentication, generating unique transaction codes that significantly reduce the risk of card cloning and fraud. NFC payments leverage tokenization, replacing sensitive card data with secure, one-time-use tokens that protect user information during contactless transactions. Both technologies incorporate multi-layered security protocols, but EMV's chip-based verification offers enhanced protection against counterfeit attacks compared to NFC's reliance on secure element or host card emulation environments.
User Experience: EMV Chip Cards vs Contactless NFC
EMV chip cards require physical insertion into a terminal, often resulting in longer transaction times and occasional card retention issues, which can impact user convenience. In contrast, contactless NFC payments enable faster, tap-to-pay transactions that enhance user experience by reducing waiting times and minimizing physical contact. NFC also supports seamless integration with mobile wallets, providing added flexibility and security for consumers during payments.
Adoption Rates: EMV vs NFC Worldwide
EMV payment cards have achieved widespread adoption globally, with over 70 countries implementing EMV chip technology to enhance transaction security. In contrast, NFC payments, driven by smartphone penetration and contactless terminal availability, are rapidly increasing but have lower overall adoption, particularly in regions with emerging markets. Japan, the UK, and parts of Europe lead NFC adoption, while EMV remains the dominant standard for card-present transactions worldwide.
Costs and Infrastructure: Implementing EMV vs NFC
Implementing EMV requires significant investment in secure chip card readers and extensive backend infrastructure to support encryption and transaction authorizations, often leading to higher upfront costs for merchants. NFC technology leverages contactless payment methods with lower hardware expenses since many smartphones already support NFC, reducing the need for additional devices and enabling faster deployment. While EMV ensures robust security through chip authentication, NFC's streamlined infrastructure and compatibility with mobile wallets offer cost-effective scalability for businesses aiming to enhance payment convenience.
Fraud Prevention: How EMV and NFC Stack Up
EMV chip cards offer robust fraud prevention by generating unique transaction codes for each purchase, significantly reducing counterfeit card use, while NFC payments leverage tokenization and biometric authentication to protect against unauthorized transactions. EMV's dynamic data makes it highly effective against card cloning, whereas NFC's encrypted wireless communication minimizes data exposure during contactless payments. Together, EMV and NFC technologies enhance payment security by mitigating different fraud vectors in both physical and mobile transactions.
Compatibility With Mobile Wallets: EMV vs NFC
NFC technology offers seamless compatibility with mobile wallets such as Apple Pay, Google Wallet, and Samsung Pay, enabling contactless payments through smartphones and wearables. EMV chip cards, while highly secure for physical card transactions, do not inherently support mobile wallet integration without NFC capability. The widespread adoption of NFC facilitates smoother, faster payment experiences across diverse devices and platforms compared to traditional EMV chip-only systems.
Future Trends: EMV Chip Evolution and NFC Innovations
EMV chip technology is advancing towards enhanced security features such as biometric authentication and dynamic data encryption, reinforcing fraud prevention in card-present transactions. Near Field Communication (NFC) innovations are expanding contactless payment capabilities with improved speed, interoperability, and integration with digital wallets and wearable devices. These evolutions signal a convergence of EMV and NFC technologies, fostering a seamless, secure, and user-friendly payment ecosystem.
Choosing the Right Solution: EMV vs NFC for Merchants
Merchants must evaluate their transaction environments to decide between EMV and NFC payment solutions, considering factors like transaction speed, security, and customer preferences. EMV offers robust authentication with chip card technology ideal for in-person payments, while NFC enables contactless, fast processing suitable for mobile wallets and tap-to-pay devices. Selecting the right solution enhances payment efficiency, reduces fraud risk, and aligns with evolving consumer payment behaviors.
Important Terms
Contactless Authentication
Contactless authentication leverages EMV (Europay, Mastercard, Visa) standards to ensure secure transactions through embedded chip technology, while NFC (Near Field Communication) enables wireless data exchange between devices within a short range. EMV provides robust encryption and dynamic data authentication, making it a preferred protocol for secure mobile payments via NFC-enabled smartphones and contactless cards.
Chip Card Protocol
Chip card protocol standards, primarily EMV (Europay, MasterCard, and Visa), ensure secure transactions through embedded microprocessor chips, while NFC (Near Field Communication) technology enables contactless payments by facilitating communication between compatible devices. EMV focuses on robust cryptographic validation in physical chip cards, whereas NFC extends chip card capabilities to mobile wallets and contactless terminals, enhancing transaction speed and convenience.
Tokenization
Tokenization enhances payment security by replacing sensitive EMV card data with unique tokens during transactions, reducing fraud risk in both physical EMV chip and contactless NFC payments. In NFC-enabled mobile wallets, tokenization ensures encrypted, dynamic data exchange, safeguarding cardholder information from interception or unauthorized use.
Card-Present Transaction
Card-present transactions leverage EMV chip technology to enhance security by generating unique cryptograms for each purchase, reducing fraud compared to traditional magnetic stripe cards. NFC-based contactless payments in card-present scenarios offer swift transaction times and similar cryptographic protections, promoting convenience while maintaining EMV-level security standards.
Mobile Wallet Integration
Mobile wallet integration leverages NFC technology for secure, contactless payments by enabling data transmission between devices and EMV-compliant terminals that authenticate chip-based card credentials. This fusion ensures enhanced security standards and widespread acceptance across retailers supporting EMV contactless payment protocols.
Near-Field Transmission
Near-Field Transmission relies on electromagnetic induction to enable secure short-range communication between devices, commonly used in EMV payment systems and NFC technology. EMV utilizes near-field communication standards to facilitate contactless card transactions with encrypted data exchange, enhancing transaction speed and security.
Secure Element
Secure Element (SE) is a tamper-resistant hardware chip that stores sensitive payment credentials and cryptographic keys, ensuring secure transactions in EMV and NFC-based payment systems. In EMV card payments, the SE is embedded within the card or terminal to authenticate and protect data, while in NFC payments, the SE enables secure communication between the payment device and the terminal by safeguarding sensitive information against unauthorized access and cloning.
Tap-to-Pay
Tap-to-Pay technology utilizes NFC (Near Field Communication) for contactless payments, enabling quick and secure transactions by exchanging encrypted data between a card or mobile device and a payment terminal. EMV (Europay, Mastercard, and Visa) standards enhance Tap-to-Pay security through dynamic authentication methods such as tokenization and cryptographic authentication, reducing fraud compared to traditional magnetic stripe cards.
Dynamic Data Authentication
Dynamic Data Authentication (DDA) enhances EMV card security by generating unique cryptographic codes for each transaction, preventing replay attacks and counterfeiting. Near Field Communication (NFC) enables contactless EMV payments, leveraging DDA to authenticate card data dynamically during wireless transactions for increased protection.
Card Emulation Mode
Card Emulation Mode enables smartphones to mimic EMV contactless cards, allowing secure NFC transactions by transmitting payment data through embedded secure elements or host-based card emulation. This technology supports EMV-compliant payment protocols, ensuring interoperability and security consistent with traditional payment card standards during NFC-based mobile payments.
EMV vs NFC Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com