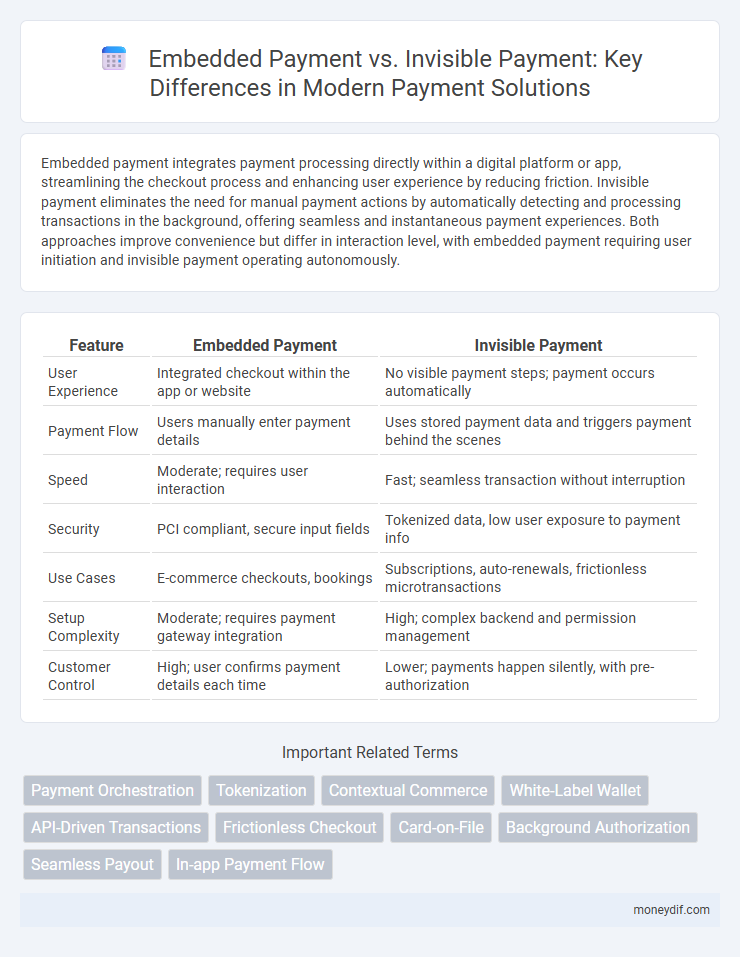
Embedded payment integrates payment processing directly within a digital platform or app, streamlining the checkout process and enhancing user experience by reducing friction. Invisible payment eliminates the need for manual payment actions by automatically detecting and processing transactions in the background, offering seamless and instantaneous payment experiences. Both approaches improve convenience but differ in interaction level, with embedded payment requiring user initiation and invisible payment operating autonomously.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Embedded Payment | Invisible Payment |
|---|---|---|
| User Experience | Integrated checkout within the app or website | No visible payment steps; payment occurs automatically |
| Payment Flow | Users manually enter payment details | Uses stored payment data and triggers payment behind the scenes |
| Speed | Moderate; requires user interaction | Fast; seamless transaction without interruption |
| Security | PCI compliant, secure input fields | Tokenized data, low user exposure to payment info |
| Use Cases | E-commerce checkouts, bookings | Subscriptions, auto-renewals, frictionless microtransactions |
| Setup Complexity | Moderate; requires payment gateway integration | High; complex backend and permission management |
| Customer Control | High; user confirms payment details each time | Lower; payments happen silently, with pre-authorization |
Understanding Embedded Payments: Definition and Use Cases
Embedded payments integrate payment processing directly within a digital platform or application, allowing users to complete transactions without redirecting to external payment gateways. Common use cases include ride-sharing apps, e-commerce marketplaces, and subscription services where seamless, in-app payments enhance user experience and increase conversion rates. This integration streamlines checkout, reduces friction, and supports real-time payment authorization, making it essential for businesses prioritizing customer convenience.
Invisible Payments Explained: Key Features and Examples
Invisible payments streamline transactions by automatically processing payments without requiring user interaction at the point of sale. Key features include real-time authorization, seamless integration with devices or apps, and enhanced security through tokenization and biometric verification. Examples of invisible payments include ride-sharing apps that charge fares upon trip completion and smart vending machines that deduct costs via linked mobile wallets.
Core Differences Between Embedded and Invisible Payments
Embedded payments integrate payment processing directly within an app or platform, allowing users to complete transactions without switching interfaces, enhancing user convenience and reducing friction. Invisible payments automate transactions in the background using technologies like tokenization and real-time data, minimizing user involvement and enabling seamless, often contactless, payment experiences. Core differences lie in user interaction levels--embedded payments require explicit user actions, whereas invisible payments operate independently, improving speed and efficiency.
How Embedded Payments Transform User Experience
Embedded payments streamline the transaction process by integrating payment options directly within apps or websites, eliminating the need for users to navigate away to third-party platforms. This seamless integration reduces friction, enhances convenience, and accelerates checkout times, thereby improving overall user satisfaction and boosting conversion rates. By embedding payment solutions, businesses create a more intuitive and efficient user experience that fosters loyalty and repeat transactions.
The Seamless Advantage of Invisible Payments
Invisible payments offer a seamless advantage by eliminating manual input and friction during transactions, enhancing user experience through real-time, automatic processing. Embedded payments require user interaction within an app or platform, while invisible payments leverage background technologies like tokenization and biometric authentication to complete purchases effortlessly. This seamless integration reduces cart abandonment rates and increases conversion by providing a frictionless checkout process.
Security Considerations: Embedded vs Invisible Payments
Embedded payments integrate payment processing within an app or website, employing encryption and secure tokenization to protect transaction data and reduce fraud risks. Invisible payments operate seamlessly in the background without user interaction, relying heavily on biometric authentication and AI-driven monitoring to ensure secure, frictionless transactions. Both methods prioritize security, but invisible payments often require advanced security protocols to compensate for the lack of explicit user verification steps.
Integration Challenges for Embedded and Invisible Payments
Embedded payment systems often face integration challenges due to the need for seamless API compatibility with diverse merchant platforms, requiring extensive customization and real-time data synchronization. Invisible payment solutions encounter difficulties in ensuring secure, frictionless user authentication and transaction processing while maintaining compliance with PCI DSS standards. Both payment types demand robust backend infrastructure to handle scalability and mitigate latency issues during high-volume transaction periods.
Impact on Business Operations: Efficiency and Cost
Embedded payment solutions streamline business operations by integrating payment processing directly within platforms, reducing transaction times and minimizing manual interventions, which enhances overall efficiency. Invisible payment systems further optimize workflows by automating payments without requiring customer input, leading to faster settlements and reduced operational costs. Both approaches decrease reliance on third-party payment interfaces, resulting in lower processing fees and improved cash flow management for businesses.
Future Trends: The Evolution of Payment Experiences
Embedded payment integrates transaction capabilities directly within apps or platforms, streamlining user experience by eliminating the need to switch between services. Invisible payment leverages AI and IoT to enable seamless, contactless transactions without user intervention, enhancing convenience and speed. Future trends point to widespread adoption of biometric authentication and blockchain for secure, frictionless payments across diverse digital ecosystems.
Choosing the Right Solution: Embedded or Invisible Payment?
Choosing between embedded and invisible payment solutions depends on user experience goals and transaction complexity. Embedded payments integrate payment options directly within the app or website interface, offering visible confirmation while maintaining user control over payment details. Invisible payments streamline the process by automating transactions in the background, ideal for recurring payments or subscription models where seamless, frictionless user experience drives higher conversion rates.
Important Terms
Payment Orchestration
Payment orchestration centralizes transaction workflows by integrating multiple payment methods, enabling seamless Embedded Payments that enhance user experience within apps, and Invisible Payments that process transactions discreetly without explicit user interaction. Both approaches rely on sophisticated orchestration platforms to optimize authorization rates, fraud prevention, and reconciliation across diverse payment gateways and processors.
Tokenization
Tokenization enhances security in embedded payment systems by replacing sensitive card data with unique tokens, reducing fraud risk during transactions. Invisible payment leverages tokenization to enable seamless, secure purchases without explicit user interaction, improving user experience while maintaining data protection.
Contextual Commerce
Contextual commerce integrates shopping experiences directly within digital environments, leveraging embedded payments that allow users to complete transactions seamlessly inside apps or platforms, enhancing convenience and reducing friction. Invisible payments further streamline the process by automating payment authorization without explicit user input, creating a frictionless and intuitive purchasing flow optimized for real-time consumer interactions.
White-Label Wallet
White-label wallets offer customizable payment solutions that integrate seamlessly with embedded payment systems, enabling businesses to provide branded user experiences while leveraging third-party payment infrastructures. Unlike embedded payments that appear within a host application, invisible payments operate entirely in the background, ensuring frictionless transactions without explicit user interaction or visible payment interfaces.
API-Driven Transactions
API-driven transactions enable seamless integration of embedded payments by allowing merchants to process payments directly within their platforms, enhancing user experience and reducing transaction friction. Invisible payments leverage API-driven technology to automate payment authorization and processing in the background, creating a smooth and uninterrupted transaction flow without explicit user interaction.
Frictionless Checkout
Frictionless checkout enhances user experience by minimizing transaction steps, with embedded payment integrating payment options directly within the application interface, allowing users to review and confirm purchases seamlessly. Invisible payment goes a step further by automating payment authorization using AI and tokenization, enabling transactions without user interaction, ideal for subscription services and IoT devices.
Card-on-File
Card-on-File (CoF) enables seamless transactions by securely storing payment credentials, facilitating both Embedded Payment systems integrated within apps or platforms and Invisible Payment solutions that process purchases without explicit payer intervention. Leveraging CoF enhances user experience by reducing friction, increases authorization rates, and supports recurring billing or subscription models inherent to Embedded and Invisible Payment frameworks.
Background Authorization
Background Authorization enables seamless transaction approvals by securely verifying payment credentials behind the scenes, enhancing user experience in both Embedded Payment and Invisible Payment systems. Embedded Payment integrates payment processing directly within digital interfaces, while Invisible Payment operates without explicit user interaction, relying heavily on robust background authorization mechanisms to ensure security and reduce friction.
Seamless Payout
Seamless Payout enhances Embedded Payment systems by integrating frictionless fund transfers directly within platforms, enabling faster, more secure transactions without redirecting users. Invisible Payment technology complements this by processing payments in the background, ensuring a user experience free from interruptions while maintaining compliance and fraud prevention.
In-app Payment Flow
In-app payment flow integrates embedded payment solutions that offer users visible, secure interfaces for transaction authorization, enhancing trust and transparency. Invisible payment methods streamline the process by automatically processing transactions in the background, improving user experience through seamless and frictionless payments without explicit user interactions.
Embedded Payment vs Invisible Payment Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com