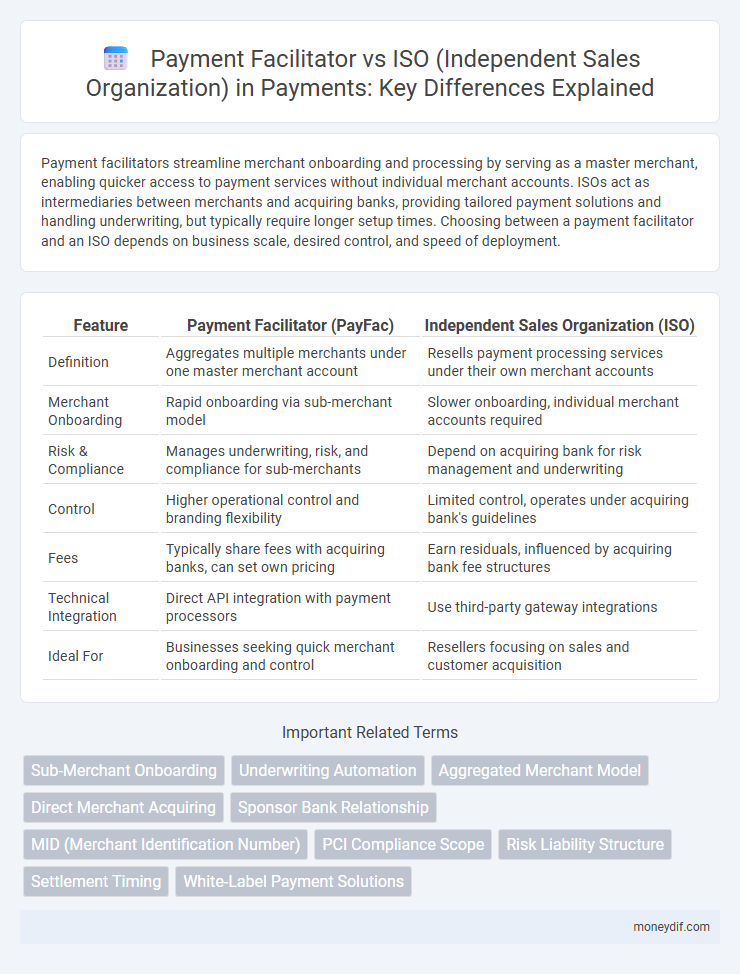
Payment facilitators streamline merchant onboarding and processing by serving as a master merchant, enabling quicker access to payment services without individual merchant accounts. ISOs act as intermediaries between merchants and acquiring banks, providing tailored payment solutions and handling underwriting, but typically require longer setup times. Choosing between a payment facilitator and an ISO depends on business scale, desired control, and speed of deployment.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Payment Facilitator (PayFac) | Independent Sales Organization (ISO) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Aggregates multiple merchants under one master merchant account | Resells payment processing services under their own merchant accounts |
| Merchant Onboarding | Rapid onboarding via sub-merchant model | Slower onboarding, individual merchant accounts required |
| Risk & Compliance | Manages underwriting, risk, and compliance for sub-merchants | Depend on acquiring bank for risk management and underwriting |
| Control | Higher operational control and branding flexibility | Limited control, operates under acquiring bank's guidelines |
| Fees | Typically share fees with acquiring banks, can set own pricing | Earn residuals, influenced by acquiring bank fee structures |
| Technical Integration | Direct API integration with payment processors | Use third-party gateway integrations |
| Ideal For | Businesses seeking quick merchant onboarding and control | Resellers focusing on sales and customer acquisition |
Payment Facilitator vs ISO: Key Differences
Payment Facilitators (PayFacs) act as master merchants enabling sub-merchants to process payments under a single master account, streamlining onboarding and underwriting processes. Independent Sales Organizations (ISOs) operate as third-party agents acquiring merchant accounts directly from payment processors, requiring individual underwriting for each merchant. The main differences lie in the operational model, risk management responsibilities, and merchant onboarding speed, with PayFacs providing faster integration but shouldering more compliance obligations compared to ISOs.
How Payment Facilitators Work
Payment Facilitators (PayFacs) streamline merchant onboarding by aggregating multiple sub-merchants under a master merchant account, enabling faster activation and simplified payment processing. They handle underwriting, risk management, and compliance on behalf of sub-merchants, reducing friction compared to Independent Sales Organizations (ISOs) that require individual merchant accounts. PayFacs leverage APIs and integrated platforms to provide seamless payment acceptance, fraud monitoring, and transaction settlement services efficiently for businesses of all sizes.
Understanding the ISO Model
The Independent Sales Organization (ISO) model involves third-party entities authorized by acquiring banks to resell payment processing services, enabling merchants to accept electronic payments without directly partnering with banks. ISOs manage merchant relationships, underwriting, and customer support, earning revenue through residual fees based on transaction volumes. This model contrasts with Payment Facilitators, as ISOs handle merchant onboarding individually, requiring more comprehensive risk management and compliance responsibilities.
Merchant Onboarding: PayFacs vs ISOs
Payment Facilitators (PayFacs) streamline merchant onboarding by aggregating multiple sub-merchants under a single master account, enabling faster approval and simplified underwriting compared to Independent Sales Organizations (ISOs) that require individual merchant accounts and distinct underwriting processes. PayFacs utilize automated onboarding platforms integrating identity verification, risk assessment, and compliance checks, while ISOs often rely on traditional manual underwriting, leading to longer onboarding times. Leveraging PayFacs reduces friction for merchants seeking quick access to payment processing, whereas ISOs offer more customized service but with increased complexity and delayed onboarding.
Compliance Requirements: Payment Facilitators vs ISOs
Payment facilitators are required to implement rigorous compliance programs including underwriting, merchant monitoring, and adherence to PCI DSS standards, often bearing direct liability for merchants' actions. In contrast, Independent Sales Organizations (ISOs) typically operate under the umbrella of a sponsoring acquiring bank, relying on the bank's compliance framework while managing merchant relationships and payment processing. Both must comply with Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations and Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), but payment facilitators face more stringent direct regulatory scrutiny due to their aggregated merchant model.
Revenue Models: Comparing PayFacs and ISOs
Payment facilitators (PayFacs) generate revenue primarily through transaction fees, taking a small percentage from each payment processed under their master merchant account, enabling faster onboarding and simplified compliance. Independent Sales Organizations (ISOs) earn income via reseller agreements with acquiring banks, collecting fees through markup on interchange rates and monthly statement fees while managing merchant accounts independently. PayFacs benefit from scalable, volume-based revenue models, whereas ISOs rely on traditional fee structures and merchant retention strategies for consistent income.
Risk Management in PayFacs and ISOs
Payment Facilitators (PayFacs) assume greater risk management responsibilities by underwriting sub-merchants and maintaining direct relationships with payment processors, which requires robust fraud detection and compliance systems. Independent Sales Organizations (ISOs) typically operate under sponsor banks, sharing risk management duties but relying on the financial institution for underwriting and transaction monitoring. Effective risk mitigation strategies in PayFacs include real-time transaction monitoring, KYC protocols, and chargeback management, whereas ISOs emphasize risk controls through their partnerships with acquiring banks.
Technology Stack: PayFacs vs ISO Solutions
Payment Facilitators leverage advanced technology stacks that enable seamless onboarding, real-time transaction monitoring, and aggregated processing under a single master merchant account, providing faster activation and streamlined compliance management. Independent Sales Organizations (ISOs) often rely on traditional payment gateway integrations and multiple acquiring bank relationships, which can result in longer setup times and more complex reconciliation processes. PayFacs typically utilize cloud-based, API-driven platforms designed for scalability and automation, whereas ISO solutions may depend on legacy systems requiring manual intervention and more extensive customer support infrastructure.
Choosing Between Payment Facilitator and ISO
Choosing between a Payment Facilitator and an Independent Sales Organization (ISO) depends on business needs, risk tolerance, and control preferences. Payment Facilitators offer faster merchant onboarding and unified payment processing, ideal for businesses seeking streamlined operations and quicker scalability. ISOs provide greater flexibility in pricing models and branding but require more compliance management and longer setup times.
Future Trends: PayFac vs ISO in Payment Industry
Payment Facilitators (PayFacs) are rapidly advancing with embedded payments and streamlined onboarding, driving faster merchant activation compared to traditional ISOs (Independent Sales Organizations) that rely on more established, yet slower, underwriting processes. The future of the payment industry favors PayFacs leveraging AI-driven fraud prevention, integrated payment solutions, and real-time data analytics, enabling enhanced scalability and personalized merchant services. ISOs are increasingly adopting hybrid models to incorporate PayFac technology, but the shift toward platform-based, API-driven payment facilitation underscores the growing dominance of PayFacs in a digital-first payments ecosystem.
Important Terms
Sub-Merchant Onboarding
Sub-merchant onboarding for payment facilitators involves faster integration and streamlined underwriting, enabling multiple merchants to operate under a single master merchant account, while ISOs require individual merchant accounts and longer approval processes. Payment facilitators manage risk and compliance centrally, whereas ISOs act as intermediaries selling payment services but must independently handle merchant underwriting and account setup.
Underwriting Automation
Underwriting automation streamlines risk assessment and decision-making processes for Payment Facilitators by instantly analyzing merchant data and transaction patterns, enhancing fraud detection and compliance efficiency. Independent Sales Organizations (ISOs) benefit from automated underwriting by accelerating merchant onboarding and reducing manual errors, enabling better scalability in payment processing partnerships.
Aggregated Merchant Model
The Aggregated Merchant Model enables Payment Facilitators (PayFacs) to onboard multiple sub-merchants under a single master merchant account, streamlining payment processing and reducing underwriting complexity compared to the Independent Sales Organization (ISO) model, where ISOs establish individual merchant accounts for each client. This model enhances scalability and risk management by centralizing transaction authorization and settlement while providing faster merchant approval times and improved control over compliance.
Direct Merchant Acquiring
Direct Merchant Acquiring streamlines payment processing by enabling Payment Facilitators (PayFacs) to onboard sub-merchants under a master merchant account, offering faster approvals and simplified underwriting compared to Independent Sales Organizations (ISOs), which require each merchant to have individual accounts. PayFacs leverage technology and aggregated risk management to provide seamless payment solutions, while ISOs typically focus on personalized sales and support but with more complex merchant onboarding and funding processes.
Sponsor Bank Relationship
A Sponsor Bank relationship is crucial for Payment Facilitators (PayFacs) as it enables them to underwrite and manage merchant accounts under a master merchant ID, streamlining payment processing and risk management. Independent Sales Organizations (ISOs) also rely on Sponsor Banks but typically maintain individual merchant accounts, focusing on sales and marketing without bearing underwriting responsibilities.
MID (Merchant Identification Number)
MID (Merchant Identification Number) uniquely identifies a merchant account within the payment processing network, crucial for tracking transactions and settlements. Payment Facilitators use a single MID to onboard multiple sub-merchants under their umbrella, while ISOs typically obtain individual MIDs for each merchant they sponsor, enabling distinct transaction routing and risk management.
PCI Compliance Scope
PCI compliance scope for a Payment Facilitator (PayFac) involves securing cardholder data across multiple sub-merchants under its umbrella, requiring comprehensive network segmentation and strict access controls to manage varied transaction environments. In contrast, an Independent Sales Organization (ISO) typically has a narrower PCI scope focused on its own systems and processes, as ISO functions mainly as a reseller with fewer direct interactions with cardholder data.
Risk Liability Structure
Risk liability structure in a Payment Facilitator model involves the facilitator assuming primary responsibility for underwriting, transaction monitoring, and chargebacks, directly impacting merchant risk management and compliance. In contrast, an ISO (Independent Sales Organization) operates under the sponsoring acquirer's risk umbrella, with limited liability, focusing mainly on merchant acquisition and relationship management without direct transaction liability.
Settlement Timing
Settlement timing for Payment Facilitators is typically faster than for Independent Sales Organizations (ISOs) due to direct control over the merchant accounts and streamlined fund distribution processes. ISOs often experience longer settlement periods because payments must pass through acquiring banks and third-party processors before reaching the merchant.
White-Label Payment Solutions
White-label payment solutions enable Payment Facilitators (PayFacs) to streamline onboarding processes by integrating their services under a single master merchant account, contrasting with Independent Sales Organizations (ISOs) that typically act as intermediaries managing multiple merchant accounts individually. PayFacs benefit from faster transaction approvals and centralized risk management, while ISOs focus on expanding merchant portfolios through direct sales and individualized account setups.
Payment Facilitator vs ISO (Independent Sales Organization) Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com