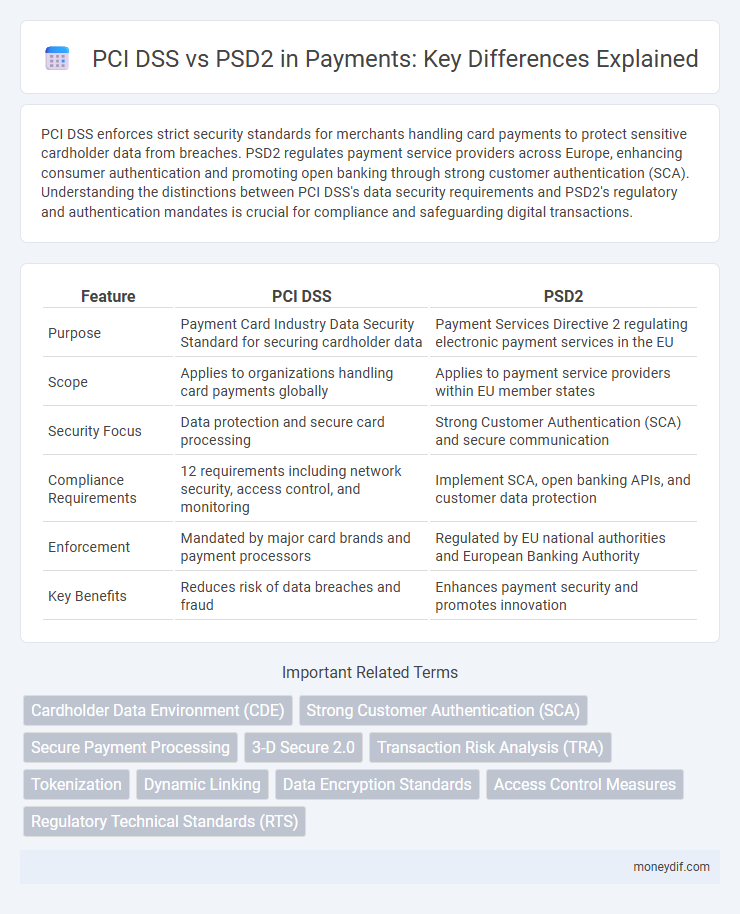
PCI DSS enforces strict security standards for merchants handling card payments to protect sensitive cardholder data from breaches. PSD2 regulates payment service providers across Europe, enhancing consumer authentication and promoting open banking through strong customer authentication (SCA). Understanding the distinctions between PCI DSS's data security requirements and PSD2's regulatory and authentication mandates is crucial for compliance and safeguarding digital transactions.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | PCI DSS | PSD2 |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard for securing cardholder data | Payment Services Directive 2 regulating electronic payment services in the EU |
| Scope | Applies to organizations handling card payments globally | Applies to payment service providers within EU member states |
| Security Focus | Data protection and secure card processing | Strong Customer Authentication (SCA) and secure communication |
| Compliance Requirements | 12 requirements including network security, access control, and monitoring | Implement SCA, open banking APIs, and customer data protection |
| Enforcement | Mandated by major card brands and payment processors | Regulated by EU national authorities and European Banking Authority |
| Key Benefits | Reduces risk of data breaches and fraud | Enhances payment security and promotes innovation |
PCI DSS vs PSD2: Understanding the Key Differences
PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) focuses on securing cardholder data through stringent technical and operational requirements for businesses handling payment cards. PSD2 (Payment Services Directive 2) emphasizes enhancing consumer protection, promoting innovation, and regulating payment services across the EU, with strong customer authentication (SCA) being a core element. While PCI DSS addresses data security standards, PSD2 primarily targets regulatory compliance and payment service transparency.
Core Objectives of PCI DSS and PSD2
PCI DSS aims to protect cardholder data by enforcing stringent security standards focused on data encryption, vulnerability management, and access control to reduce payment card fraud. PSD2 enhances payment security by mandating strong customer authentication (SCA) and promoting secure communication between banks and third-party providers to increase transaction transparency and reduce fraud. Both frameworks prioritize safeguarding sensitive payment information but target different aspects of payment security within card-based and open banking environments.
Regulatory Scope: PCI DSS and PSD2 Coverage
PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) sets security requirements specifically for organizations handling cardholder data to prevent data breaches and fraud, focusing on protecting payment card information across all entities that store, process, or transmit such data. PSD2 (Payment Services Directive 2) regulates payment services and providers within the European Economic Area, aiming to enhance consumer protection, promote innovation, and ensure secure electronic payments by imposing strong customer authentication and open banking requirements. Unlike PCI DSS's narrow focus on card data security, PSD2's regulatory scope encompasses broader payment service providers and customer rights, affecting banks, fintechs, and third-party providers in the digital payment ecosystem.
Security Requirements: A Comparative Analysis
PCI DSS mandates comprehensive security controls including encryption, firewalls, and vulnerability management to protect cardholder data, whereas PSD2 emphasizes strong customer authentication (SCA) and secure communication protocols to enhance payment security and reduce fraud. While PCI DSS focuses on data protection within payment card environments, PSD2 enforces regulatory measures for open banking and third-party payment service providers to ensure secure access and transaction authorization. Both standards complement each other by addressing different aspects of payment security, with PCI DSS targeting infrastructural safeguards and PSD2 prioritizing user authentication and transaction integrity.
Compliance Processes for PCI DSS and PSD2
PCI DSS compliance requires organizations to implement strict security controls such as encryption, vulnerability management, and regular security assessments to protect cardholder data. PSD2 compliance mandates stronger customer authentication (SCA) and secure communication protocols to enhance payment security and reduce fraud in European payments. Both standards emphasize continuous monitoring, risk assessment, and detailed documentation to maintain regulatory adherence and safeguard financial transactions.
Impact on Payment Service Providers
PCI DSS enforces stringent data security standards to protect cardholder information, requiring Payment Service Providers (PSPs) to implement robust encryption, access controls, and regular security audits. PSD2 introduces strong customer authentication (SCA) and aims to increase competition by mandating open banking APIs, compelling PSPs to enhance transparency and facilitate third-party provider integrations. The combined impact demands PSPs to strengthen cybersecurity measures while adapting to regulatory-driven innovations that improve payment security and customer experience.
Data Protection and Customer Authentication
PCI DSS mandates rigorous data protection protocols to secure payment card information, enforcing encryption, access controls, and regular security assessments to minimize fraud risks. PSD2 enhances customer authentication through Strong Customer Authentication (SCA) requirements, which demand multi-factor authentication involving at least two independent elements--knowledge, possession, or inherence--to verify user identities during electronic payments. Combining PCI DSS and PSD2 compliance ensures robust safeguarding of payment data while also elevating authentication standards to protect customers from unauthorized transactions.
Penalties for Non-Compliance: PCI DSS vs PSD2
Non-compliance with PCI DSS can result in fines ranging from $5,000 to $100,000 per month imposed by payment card brands, along with potential increased transaction fees and suspension of payment processing privileges. PSD2 violations expose financial institutions to penalties set by national regulatory authorities, often amounting to millions of euros, depending on the severity and nature of the infraction. Both frameworks enforce stringent sanctions to enhance payment security but differ in enforcement scope, with PCI DSS targeting payment card data protection and PSD2 emphasizing customer authentication and operational transparency in the European Economic Area.
Future Trends in Payment Security Standards
PCI DSS evolves to address emerging cyber threats with enhanced encryption and real-time monitoring, while PSD2 emphasizes strong customer authentication and open banking APIs to foster innovation and security. Future payment security standards will integrate AI-driven fraud detection and biometric verification to create adaptive, user-centric protection mechanisms. Collaboration between regulatory bodies and technology providers is essential to standardize these advanced security measures across global payment ecosystems.
Choosing the Right Compliance Framework for Your Business
PCI DSS focuses on securing cardholder data to prevent fraud during payment processing, making it essential for businesses handling credit card transactions. PSD2 emphasizes enhanced customer authentication and open banking regulations that improve transaction security and promote competition within the European payment ecosystem. Selecting the right compliance framework depends on your business model, geographic location, and whether you handle card payments directly or engage in financial services leveraging APIs.
Important Terms
Cardholder Data Environment (CDE)
The Cardholder Data Environment (CDE) encompasses all systems that store, process, or transmit cardholder data and must comply with PCI DSS requirements to ensure data security and protect against breaches. Under PSD2, while the focus is on strong customer authentication and secure payment initiation, maintaining a secure CDE remains critical for merchants and payment service providers to uphold PCI DSS standards and safeguard payment information.
Strong Customer Authentication (SCA)
Strong Customer Authentication (SCA) is a regulatory requirement under PSD2 designed to enhance payment security by requiring multi-factor authentication during electronic transactions. PCI DSS focuses on securing cardholder data and payment systems, whereas PSD2's SCA mandates user authentication to reduce fraud and increase trust in online payments across the European Economic Area.
Secure Payment Processing
Secure payment processing requires strict adherence to PCI DSS standards, which mandate robust measures for protecting cardholder data and preventing fraud. PSD2 complements these requirements by enforcing strong customer authentication and secure communication protocols to enhance transaction security across European payment services.
3-D Secure 2.0
3-D Secure 2.0 enhances payment authentication by aligning with PSD2 requirements for Strong Customer Authentication (SCA), improving security and user experience in online transactions. PCI DSS compliance remains essential to protect cardholder data and secure payment environments alongside the implementation of 3-D Secure 2.0 protocols.
Transaction Risk Analysis (TRA)
Transaction Risk Analysis (TRA) enhances payment security by assessing transaction data to detect and prevent fraud under PSD2 regulations, while PCI DSS focuses on securing cardholder data during payment processing. TRA aligns with PSD2's Strong Customer Authentication (SCA) requirements by enabling risk-based authentication, reducing friction for low-risk transactions without compromising compliance.
Tokenization
PCI DSS enforces strict tokenization standards to secure cardholder data by replacing sensitive information with non-sensitive tokens, minimizing data breach risks in payment systems. PSD2 encourages tokenization primarily through Strong Customer Authentication protocols to enhance transaction security and reduce fraud in open banking environments.
Dynamic Linking
Dynamic Linking, a key requirement of PSD2's Strong Customer Authentication (SCA), ensures transaction-specific authorization by cryptographically binding the payment amount and payee to the authentication process, enhancing security and reducing fraud. While PCI DSS focuses on protecting cardholder data during storage, processing, and transmission, PSD2's Dynamic Linking mandates real-time verification of transaction details to strengthen payment integrity in open banking environments.
Data Encryption Standards
Data Encryption Standards (DES) are legacy symmetric-key algorithms historically used for securing payment card data, but PCI DSS mandates stronger encryption methods like AES to protect cardholder information. PSD2 emphasizes robust encryption and secure communication protocols to enhance transaction security in open banking, aligning with PCI DSS by requiring advanced cryptographic measures to safeguard sensitive financial data.
Access Control Measures
Access control measures under PCI DSS focus on restricting cardholder data access through role-based permissions, multi-factor authentication, and rigorous encryption standards to prevent unauthorized transactions. PSD2 mandates strong customer authentication and dynamic linking, emphasizing secure access to payment accounts and transaction data to enhance security and reduce fraud in electronic payments.
Regulatory Technical Standards (RTS)
Regulatory Technical Standards (RTS) under PSD2 mandate strong customer authentication (SCA) requiring multi-factor authentication for payment services, aligning with PCI DSS requirements that enforce stringent data security standards to protect cardholder information. While PCI DSS focuses broadly on securing card data environments, RTS specifically targets the authentication processes and transaction risk analysis to enhance payment security and fraud prevention in the EU financial ecosystem.
PCI DSS vs PSD2 Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com