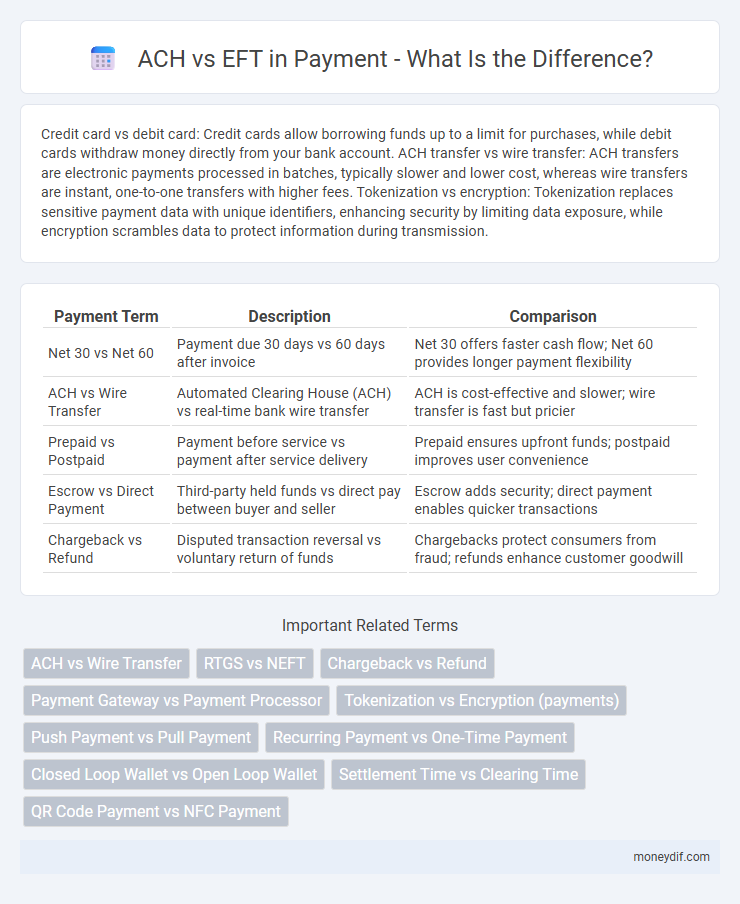
Credit card vs debit card: Credit cards allow borrowing funds up to a limit for purchases, while debit cards withdraw money directly from your bank account. ACH transfer vs wire transfer: ACH transfers are electronic payments processed in batches, typically slower and lower cost, whereas wire transfers are instant, one-to-one transfers with higher fees. Tokenization vs encryption: Tokenization replaces sensitive payment data with unique identifiers, enhancing security by limiting data exposure, while encryption scrambles data to protect information during transmission.
Table of Comparison
| Payment Term | Description | Comparison |
|---|---|---|
| Net 30 vs Net 60 | Payment due 30 days vs 60 days after invoice | Net 30 offers faster cash flow; Net 60 provides longer payment flexibility |
| ACH vs Wire Transfer | Automated Clearing House (ACH) vs real-time bank wire transfer | ACH is cost-effective and slower; wire transfer is fast but pricier |
| Prepaid vs Postpaid | Payment before service vs payment after service delivery | Prepaid ensures upfront funds; postpaid improves user convenience |
| Escrow vs Direct Payment | Third-party held funds vs direct pay between buyer and seller | Escrow adds security; direct payment enables quicker transactions |
| Chargeback vs Refund | Disputed transaction reversal vs voluntary return of funds | Chargebacks protect consumers from fraud; refunds enhance customer goodwill |
ACH vs Wire Transfer
ACH transfers offer cost-effective, batch-processed payments ideal for recurring transactions, while wire transfers provide real-time, high-value funds transfer with immediate settlement. ACH payments typically take 1-3 business days to clear, beneficial for payroll and vendor payments, contrasting with wire transfers that settle within hours, suitable for urgent or large-scale international transfers. Financial institutions prefer ACH for low-fee domestic transactions, whereas wire transfers are favored for their speed and security in high-value or cross-border payments.
Prepaid Card vs Debit Card
Prepaid cards require users to load funds before spending, offering controlled budgeting without linking to a bank account, while debit cards directly access the user's checking account balance for transactions. Prepaid cards often lack overdraft facilities and may have activation or reload fees, whereas debit cards typically provide overdraft protection and fewer upfront charges. Both cards facilitate electronic payments, with debit cards being widely accepted for ATM withdrawals and online purchases, unlike some prepaid cards with limited usage.
Payment Gateway vs Payment Processor
Payment Gateway vs Payment Processor centers on their distinct roles in online transactions; a Payment Gateway securely captures and transmits customer payment data, while a Payment Processor handles the actual transaction authorization and fund transfer between banks. Payment Gateways often include encryption and fraud detection features to protect sensitive information during checkout, whereas Payment Processors interact with card networks and issuing banks to complete the payment. Understanding the technical integration and operational scope of each is crucial for e-commerce businesses aiming to streamline payment workflows and improve customer experience.
Escrow Payment vs Direct Payment
Escrow Payment involves a third-party holding funds securely until contractual obligations are met, ensuring protection for both buyer and seller. Direct Payment transfers funds immediately between parties without intermediaries, providing faster but less secure transactions. Choosing between Escrow Payment vs Direct Payment depends on the need for security versus speed in financial transactions.
Mobile Wallet vs Digital Wallet
Mobile Wallet vs Digital Wallet highlights distinct payment ecosystems where Mobile Wallets are smartphone-based applications enabling contactless payments via NFC or QR codes, while Digital Wallets encompass broader platforms that store various payment methods, including credit cards, cryptocurrencies, and loyalty cards for online and offline transactions. Mobile Wallets prioritize quick, in-store payments through devices like Apple Pay or Google Pay, whereas Digital Wallets such as PayPal or Venmo offer comprehensive wallet services supporting peer-to-peer transfers and e-commerce payments. Understanding these differences optimizes payment solutions tailored for merchants and consumers seeking seamless, secure financial interactions.
Push Payments vs Pull Payments
Push payments transfer funds directly from the payer's account to the payee without intermediary authorization, enhancing speed and control over outgoing funds. Pull payments authorize the payee to initiate debit transactions from the payer's account, commonly used in recurring billing or subscriptions. Push payments reduce fraud risks by requiring payer initiation, whereas pull payments rely on trust and authorization parameters set by the payer.
Invoice Financing vs Factoring
Invoice financing provides businesses with cash flow by borrowing against outstanding invoices, allowing firms to retain control over customer collections. Factoring involves selling invoices to a third-party factor who assumes responsibility for debt collection and provides immediate payment, often at a discounted rate. Choosing between invoice financing and factoring depends on the company's need for control, cost structure, and urgency of cash flow.
Tokenization vs Encryption in Payments
Tokenization replaces sensitive payment data with unique identification symbols, reducing fraud risk without exposing actual card details, while encryption transforms data into unreadable code during transmission to protect information from interceptors. Tokenization enhances security by ensuring that stored payment information remains non-sensitive, unlike encryption which primarily secures data in transit. Both methods are critical in modern payment processing, but tokenization offers superior protection for stored payment credentials against breaches.
Tap-to-Pay vs QR Code Payment
Tap-to-Pay uses near-field communication (NFC) technology for contactless transactions, enabling users to simply tap their card or smartphone on a payment terminal, while QR Code Payment requires scanning a barcode with a mobile device to initiate the payment process. Tap-to-Pay offers faster and more seamless checkouts, typically supported by major credit cards and digital wallets like Apple Pay and Google Pay, whereas QR Code Payment is highly accessible for merchants without NFC-enabled terminals and is popular in regions with widespread smartphone usage. Security protocols in Tap-to-Pay include tokenization and biometric authentication, whereas QR Code Payment relies on dynamic QR codes and encrypted payment gateways to prevent fraud.
Subscription Billing vs One-Time Payment
Subscription billing involves recurring charges at regular intervals, ensuring continuous access to a service, whereas one-time payment requires a single upfront transaction for permanent ownership or access. Subscription billing supports predictable revenue streams and customer retention, while one-time payments provide immediate full payment without recurring obligations. Businesses leverage subscription billing for invoicing automation and customer lifecycle management, contrasting with one-time payment models suited for standalone product sales.
Important Terms
ACH vs Wire Transfer
ACH transfers are typically slower, taking 1-3 business days for processing, but they offer lower fees and are ideal for recurring payments. Wire transfers provide faster, often same-day settlement with higher security and fees, making them suitable for urgent or high-value transactions.
RTGS vs NEFT
RTGS (Real-Time Gross Settlement) processes high-value transactions instantly and individually, making it ideal for urgent fund transfers above Rs2 lakh, while NEFT (National Electronic Funds Transfer) batches transactions in hourly settlements suitable for smaller, non-urgent payments. RTGS guarantees immediate clearing with minimal delay, whereas NEFT operates in half-hourly batches, resulting in varied transaction timings depending on the bank's processing schedule.
Chargeback vs Refund
Chargeback vs Refund highlights the critical difference where a chargeback is initiated by the cardholder disputing a transaction through their bank, often involving fraud or dissatisfaction, while a refund is a voluntary reimbursement issued directly by the merchant. Understanding chargeback ratios and refund processing times is essential for businesses to optimize payment dispute management and enhance customer satisfaction.
Payment Gateway vs Payment Processor
Payment gateways securely capture and transmit customer payment information from a website to payment processors, acting as the virtual point of sale, while payment processors handle the authorization, processing, and settlement of transactions between the merchant's bank and the customer's bank. Sure! Here's a list of niche payment terms in the "Payment Gateway vs Payment Processor" format: Merchant Account vs Payment Processor, Tokenization vs Encryption, Payment Gateway API vs SDK, Authorization vs Capture, Hosted Payment Page vs Integrated Payment Page, Payment Gateway Fees vs Payment Processor Fees.
Tokenization vs Encryption (payments)
Tokenization replaces sensitive payment data with unique, non-sensitive tokens that are useless if breached, enhancing data security without altering transaction processes. Encryption scrambles payment information into unreadable code requiring decryption keys, protecting data during transmission but still exposing sensitive information temporarily.
Push Payment vs Pull Payment
Push payment requires the payer to initiate and authorize the transfer of funds directly to the payee, enhancing control and immediacy in transactions. Pull payment allows the payee to request and withdraw funds from the payer's account based on pre-approved permissions, facilitating recurring billing and automated payments.
Recurring Payment vs One-Time Payment
Recurring payment involves automatic, scheduled transactions typically used for subscriptions or ongoing services, ensuring continuous access and cash flow. One-time payment refers to a single transaction made for a standalone purchase or service without future charges, ideal for one-off sales or products.
Closed Loop Wallet vs Open Loop Wallet
Closed Loop Wallets operate within a specific merchant's ecosystem, offering faster transactions and enhanced loyalty rewards but limited usability outside the network. Open Loop Wallets, linked to major payment networks like Visa or Mastercard, provide broader acceptance and versatility across multiple merchants and platforms worldwide.
Settlement Time vs Clearing Time
Settlement time refers to the duration it takes for a payment transaction to be completed and funds to be transferred to the recipient's account, while clearing time is the process period during which the transaction is verified, authorized, and processed by the payment network or bank. Understanding the difference between these times is crucial for businesses to manage cash flow and reconcile accounts effectively in payment processing systems.
QR Code Payment vs NFC Payment
QR code payment leverages camera scanning technology to authenticate transactions by encoding payment details in a two-dimensional barcode, ideal for peer-to-peer transfers and online purchases. NFC payment uses near-field communication chips embedded in devices or cards for secure, contactless exchanges, favored in retail environments for speed and enhanced security.
Sure! Here’s a list of niche payment terms in the "term1 vs term2" format: Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com