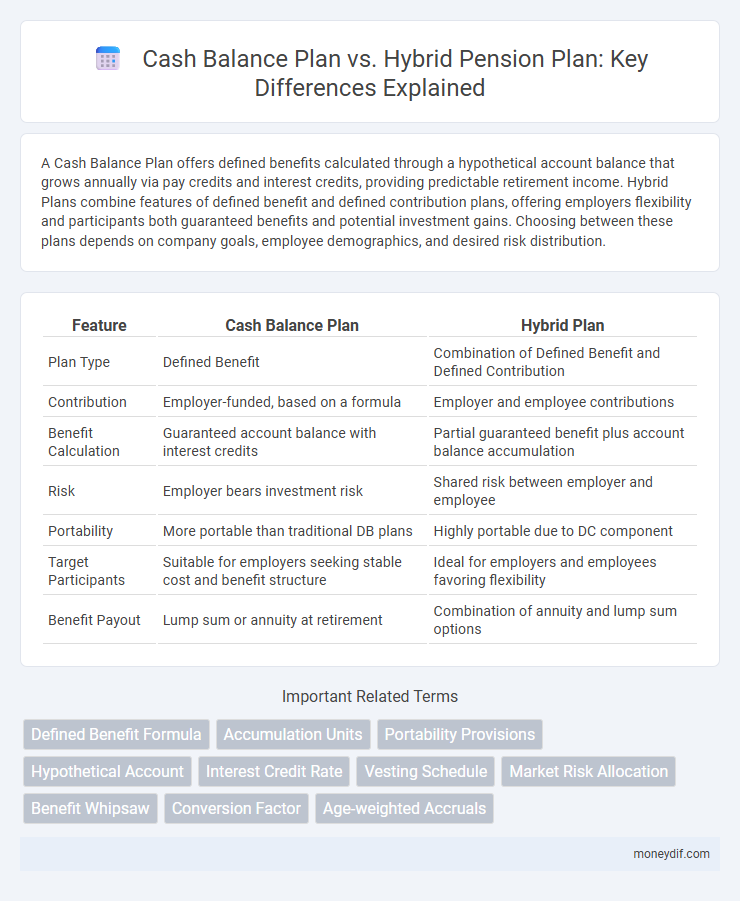
A Cash Balance Plan offers defined benefits calculated through a hypothetical account balance that grows annually via pay credits and interest credits, providing predictable retirement income. Hybrid Plans combine features of defined benefit and defined contribution plans, offering employers flexibility and participants both guaranteed benefits and potential investment gains. Choosing between these plans depends on company goals, employee demographics, and desired risk distribution.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cash Balance Plan | Hybrid Plan |
|---|---|---|
| Plan Type | Defined Benefit | Combination of Defined Benefit and Defined Contribution |
| Contribution | Employer-funded, based on a formula | Employer and employee contributions |
| Benefit Calculation | Guaranteed account balance with interest credits | Partial guaranteed benefit plus account balance accumulation |
| Risk | Employer bears investment risk | Shared risk between employer and employee |
| Portability | More portable than traditional DB plans | Highly portable due to DC component |
| Target Participants | Suitable for employers seeking stable cost and benefit structure | Ideal for employers and employees favoring flexibility |
| Benefit Payout | Lump sum or annuity at retirement | Combination of annuity and lump sum options |
Understanding Cash Balance Plans: A Brief Overview
Cash Balance Plans combine elements of defined benefit and defined contribution plans, providing employees with a guaranteed account balance that grows annually through employer contributions and interest credits. These plans offer predictable retirement benefits by specifying a cash account rather than a traditional monthly pension payment, making them attractive for business owners and high-income employees seeking tax advantages. Unlike Hybrid Plans, which blend features of defined benefit and defined contribution components separately, Cash Balance Plans streamline benefits into a single, portable account structure.
What Defines a Hybrid Pension Plan?
A Hybrid Pension Plan combines elements of both defined benefit and defined contribution plans, offering a balance between guaranteed retirement income and individual account growth. Typically, it provides a fixed benefit based on salary and years of service while allowing participants to accumulate contributions in a personal account that may earn investment returns. This structure aims to reduce employer risk compared to traditional defined benefit plans while providing employees with potential for higher retirement savings than purely defined contribution plans.
Key Differences Between Cash Balance and Hybrid Plans
Cash Balance Plans offer defined benefits with individual hypothetical accounts that grow annually with pay credits and interest credits, providing predictable retirement income. Hybrid Plans combine features of defined benefit and defined contribution plans, offering more flexible benefits but with variable retirement income depending on investment performance. Key differences include the guarantee of benefits in Cash Balance Plans versus the potential variability and participant control found in Hybrid Plans.
Advantages of Cash Balance Plans for Employers
Cash Balance Plans offer employers predictable annual contributions and defined benefit security while maintaining the flexibility of defined contribution plans. These plans enhance employee retention by providing a portable, easily understandable retirement benefit that can boost workforce morale. Employers benefit from potential tax advantages and simplified funding requirements compared to traditional pension plans.
Employee Benefits Under Hybrid Pension Plans
Hybrid pension plans combine the features of defined benefit and defined contribution plans, providing employees with a guaranteed minimum benefit alongside the potential for investment growth. Employee benefits under hybrid plans often include a stable retirement income floor through a cash balance component, alongside the flexibility and risk-sharing of defined contributions. This structure enhances retirement security by balancing predictable payouts with opportunities for higher returns, improving overall financial stability for plan participants.
Contribution Structures: Cash Balance vs Hybrid Plans
Cash Balance Plans feature employer-defined contribution amounts credited annually with a guaranteed interest rate, providing predictable growth similar to a defined benefit plan. Hybrid Plans combine elements of defined benefit and defined contribution plans, often including a traditional pension formula alongside employee contributions, resulting in more variable funding. Contribution structures in Hybrid Plans can involve both fixed employer contributions and employee elective deferrals, whereas Cash Balance Plans primarily rely on employer contributions.
Portability and Vesting: Comparing Plan Mobility
Cash Balance Plans offer greater portability by converting retirement benefits into a lump-sum account balance that employees can easily roll over when changing jobs. Hybrid Plans combine features of Defined Benefit and Defined Contribution plans, often resulting in more complex vesting schedules and less straightforward portability of accrued benefits. Vesting in Cash Balance Plans is typically faster, enhancing employees' control over their funds compared to the slower vesting and limited mobility seen in many Hybrid Plans.
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
Cash Balance Plans must adhere to specific Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA) rules and Internal Revenue Service (IRS) contribution limits, requiring annual actuarial valuations to ensure plan solvency. Hybrid Plans combine defined benefit and defined contribution elements, necessitating complex compliance with both IRS funding requirements and Department of Labor fiduciary standards. Both plans are subject to mandatory reporting, nondiscrimination testing, and strict vesting schedules to maintain tax-qualified status and avoid penalties.
Suitability for Different Workforce Demographics
Cash Balance Plans offer predictable benefits and portability ideal for younger employees or those with shorter tenures, providing steady retirement savings growth through defined contribution-like statements. Hybrid Plans combine elements of defined benefit and defined contribution plans, making them suitable for workforces with diverse age groups by balancing guaranteed income with potential for investment returns. Employers with multi-generational staff often select Hybrid Plans to address varied retirement needs and risk tolerances across employee demographics.
Choosing the Right Plan: Factors to Consider
When choosing between a Cash Balance Plan and a Hybrid Plan, consider factors such as employer contribution flexibility, participant benefit predictability, and administrative complexity. Cash Balance Plans offer defined contributions with a guaranteed growth rate, appealing for employees valuing steady retirement savings, while Hybrid Plans combine elements of defined benefit and defined contribution plans, catering to diverse workforce needs. Assessing business financial stability, employee demographics, and long-term retirement goals is crucial for selecting the optimal pension plan.
Important Terms
Defined Benefit Formula
The Defined Benefit Formula calculates retirement benefits based on salary and years of service in both Cash Balance Plans, which credit hypothetical accounts with interest, and Hybrid Plans, which combine elements of defined benefit and defined contribution plans.
Accumulation Units
Accumulation units in Cash Balance Plans represent hypothetical account balances linked to guaranteed interest credits, while Hybrid Plans combine features of defined benefit and defined contribution plans, allowing accumulation units to reflect both guaranteed benefits and investment performance.
Portability Provisions
Portability provisions in Cash Balance Plans enable participants to transfer vested benefits as lump sums or rollovers upon job change, preserving accrued retirement assets. Hybrid Plans combine defined benefit and defined contribution elements but often have complex portability rules that may affect the ease of transferring benefits compared to Cash Balance Plans.
Hypothetical Account
A Hypothetical Account in a Cash Balance Plan provides a guaranteed interest credit and pay credit, whereas in a Hybrid Plan it combines features of both defined benefit and defined contribution plans to create individualized retirement benefits.
Interest Credit Rate
The Interest Credit Rate in Cash Balance Plans is typically a fixed or variable rate guaranteed by the plan, whereas Hybrid Plans may feature interest credits combined with additional benefit components reflecting both defined benefit and defined contribution characteristics.
Vesting Schedule
A Vesting Schedule in a Cash Balance Plan typically follows a graded or cliff vesting method, allowing employees to earn ownership of employer contributions over a set period, enhancing retirement security. Hybrid Plans combine features of both defined benefit and defined contribution plans, often incorporating a cash balance component with distinct vesting schedules to balance risk and benefits for employees and employers.
Market Risk Allocation
Market risk allocation in Cash Balance Plans typically results in fixed interest crediting rates, whereas Hybrid Plans combine defined benefit and defined contribution features to balance market risk exposure between employers and participants.
Benefit Whipsaw
Benefit Whipsaw occurs when participants in a Hybrid Plan experience discrepancies in cash balance credits versus traditional benefit accruals, potentially causing fluctuations in retirement benefits compared to a pure Cash Balance Plan.
Conversion Factor
The conversion factor in retirement planning determines how account balances are translated into annuity payments, varying significantly between Cash Balance Plans and Hybrid Plans. Cash Balance Plans use a fixed interest credit rate combined with a predetermined conversion factor, while Hybrid Plans often incorporate variable interest credits and more complex conversion factors reflecting both defined benefit and defined contribution elements.
Age-weighted Accruals
Age-weighted Accruals in Cash Balance Plans allocate pension benefits based on participant age and salary, whereas Hybrid Plans combine traditional defined benefit features with defined contribution elements for tailored retirement accruals.
Cash Balance Plan vs Hybrid Plan Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com