The laddering strategy involves spreading investments across multiple bonds with staggered maturities to reduce interest rate risk and provide regular liquidity. In contrast, the bullet strategy concentrates maturities around a single point, maximizing income at a specific time for targeted financial goals. Choosing between these savings strategies depends on the need for cash flow flexibility versus a focused payout timeline.
Table of Comparison
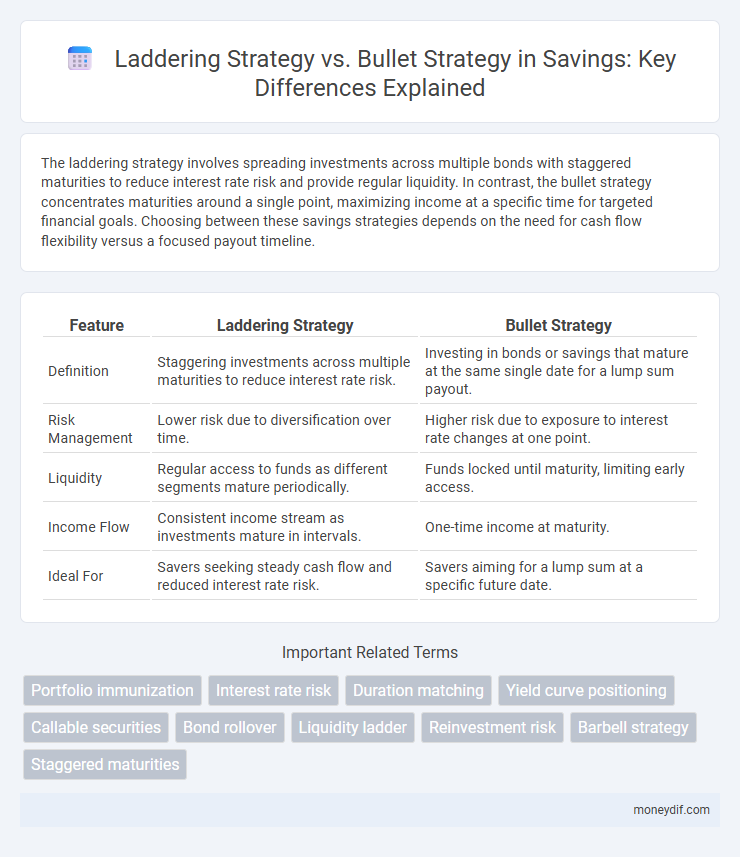
| Feature | Laddering Strategy | Bullet Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Staggering investments across multiple maturities to reduce interest rate risk. | Investing in bonds or savings that mature at the same single date for a lump sum payout. |
| Risk Management | Lower risk due to diversification over time. | Higher risk due to exposure to interest rate changes at one point. |
| Liquidity | Regular access to funds as different segments mature periodically. | Funds locked until maturity, limiting early access. |
| Income Flow | Consistent income stream as investments mature in intervals. | One-time income at maturity. |
| Ideal For | Savers seeking steady cash flow and reduced interest rate risk. | Savers aiming for a lump sum at a specific future date. |
Overview: Laddering Strategy vs Bullet Strategy
Laddering strategy involves spreading savings across multiple fixed-term investments with staggered maturities to balance liquidity and interest rate risk. Bullet strategy concentrates investments to mature simultaneously, maximizing returns at a specific future date but increasing exposure to interest rate fluctuations. Both approaches offer distinct advantages for managing cash flow timing and interest rate environments in savings portfolios.
Defining Laddering in Savings
Laddering in savings involves spreading investments across multiple fixed-term deposits with staggered maturity dates to balance liquidity and interest rate risk. This strategy allows savers to access funds periodically while potentially benefiting from higher interest rates on longer-term deposits. It contrasts with the bullet strategy, where all savings mature simultaneously, limiting flexibility.
Understanding the Bullet Strategy Approach
The Bullet Strategy involves concentrating investments to mature at a single target date, optimizing for a large, specific financial goal like a down payment or tuition payment. This approach minimizes reinvestment risk and simplifies cash flow planning by aligning all maturities to one point in time. Investors seeking predictable timing and amounts often prefer the Bullet Strategy over Laddering for focused financial commitments.
Key Differences Between Laddering and Bullet Strategies
Laddering strategy involves spreading investments across multiple bonds or savings instruments with varying maturities to reduce interest rate risk and increase liquidity. Bullet strategy concentrates investments in bonds or deposits that mature at the same time, targeting a specific financial goal with potentially higher returns but increased reinvestment risk. Laddering offers flexibility and steady income, while bullet strategy aligns with a fixed timeline and focused payout.
Advantages of Laddering Strategy for Savers
Laddering strategy offers savers enhanced liquidity by staggering maturity dates, allowing access to funds at regular intervals without penalties. This approach mitigates interest rate risk by diversifying investment periods, enabling savers to capitalize on rising rates over time. It also provides a balanced blend of steady income and flexibility, supporting effective cash flow management in fluctuating market conditions.
Benefits of Bullet Strategy in Savings Plans
The Bullet Strategy in savings plans allows investors to precisely time cash flow alignments by concentrating maturities at a single point, maximizing returns when rates are forecasted to rise. This strategy simplifies management and reduces reinvestment risk compared to laddering, making it ideal for meeting specific future financial goals. By focusing funds on a targeted maturity, investors can capitalize on higher interest rates and optimize portfolio performance within a defined timeframe.
Risk Factors: Laddering vs Bullet Strategy
Laddering strategy reduces interest rate risk by spreading bond maturities over time, allowing investors to reinvest at varying rates and maintain liquidity. Bullet strategy concentrates maturities at a single point, increasing exposure to interest rate fluctuations and reinvestment risk at that maturity date. Laddering also mitigates default risk through diversification, whereas bullet strategy has higher risk if adverse market conditions occur at maturity.
Liquidity Considerations in Laddering and Bullet Strategies
Laddering strategy enhances liquidity by staggering maturity dates across a range of intervals, allowing periodic access to funds without penalty and reducing reinvestment risk. Bullet strategy concentrates maturities at a single point, limiting interim liquidity but maximizing returns from targeted investment periods. Investors prioritizing consistent cash flow and flexibility often favor laddering for its balanced liquidity profile.
Suitability: Which Strategy Fits Your Savings Goals?
Laddering strategy suits savers seeking steady income and liquidity by staggering maturity dates across multiple fixed-income investments, reducing interest rate risk and providing flexible access to funds. Bullet strategy fits those with a specific future expense or goal, concentrating investments to mature simultaneously, maximizing returns at a targeted time but increasing reinvestment risk. Choosing between these depends on your savings horizon, need for cash flow, and risk tolerance.
Making the Right Choice: Laddering or Bullet for Optimal Growth
Laddering strategy involves spreading investments across multiple maturities to manage risk and provide consistent liquidity, while Bullet strategy focuses on concentrating investments into a single maturity date for potentially higher returns. Choosing laddering helps balance growth and risk by reinvesting funds systematically, whereas bullet suits investors targeting a specific financial goal with a fixed timeline. Optimal growth depends on individual cash flow needs, risk tolerance, and market interest rate expectations.
Important Terms
Portfolio immunization
Portfolio immunization minimizes interest rate risk by matching asset durations to liabilities, while laddering strategy staggers bond maturities over time to reduce reinvestment risk and provide liquidity, and bullet strategy concentrates maturities around a single target date to optimize cash flow timing.
Interest rate risk
The laddering strategy mitigates interest rate risk by staggering bond maturities across intervals, while the bullet strategy concentrates maturities at a single point, increasing sensitivity to rate fluctuations.
Duration matching
Duration matching aligns asset and liability maturities to minimize interest rate risk, contrasting with the Laddering strategy that staggers bond maturities evenly over time and the Bullet strategy that concentrates maturities at a single point.
Yield curve positioning
Yield curve positioning involves strategically allocating bond maturities using laddering to stagger maturities evenly for risk diversification, while bullet strategy concentrates maturities at a single point to capitalize on specific interest rate forecasts.
Callable securities
Callable securities combined with a laddering strategy diversify maturity dates to manage reinvestment risk, whereas a bullet strategy concentrates maturities at a single point for targeted cash flow timing.
Bond rollover
Bond rollover involves reinvesting maturing bonds into new issues to maintain a desired portfolio duration, enhancing flexibility and income potential. The laddering strategy staggers maturities evenly to reduce reinvestment risk and provide steady cash flow, while the bullet strategy concentrates maturities around a target date to capitalize on interest rate forecasts and achieve lump-sum reinvestment opportunities.
Liquidity ladder
The liquidity ladder strategy enhances portfolio cash flow management by staggering maturities for frequent access, contrasting with the bullet strategy's focus on concentrated investments maturing simultaneously for targeted financial goals.
Reinvestment risk
Reinvestment risk is lower in the laddering strategy due to staggered maturities providing consistent cash flows, whereas the bullet strategy concentrates maturities at a single point, increasing exposure to reinvestment uncertainty.
Barbell strategy
The Barbell strategy balances extreme allocations between short-term and long-term bonds, providing liquidity and high yield potential, unlike the Laddering strategy which evenly staggers bond maturities, enhancing cash flow predictability. Compared to the Bullet strategy that concentrates maturities around a single target date to meet specific liabilities, the Barbell approach offers greater flexibility and risk diversification.
Staggered maturities
Staggered maturities involve spreading bond investments across various maturity dates to manage interest rate risk and liquidity needs. Laddering strategy achieves this by evenly spacing bond maturities over time, providing steady cash flows, while the Bullet strategy concentrates maturities at a single point, aiming for a large lump sum investment or repayment.
Laddering strategy vs Bullet strategy Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com