Bullish markets indicate rising prices driven by investor confidence and increased buying activity, signaling strong economic outlooks. Bearish markets reflect declining prices due to pessimism and selling pressure, often triggered by negative economic indicators or geopolitical concerns. Understanding the dynamics between bullish and bearish trends helps traders make informed decisions to maximize profits and manage risks effectively.
Table of Comparison
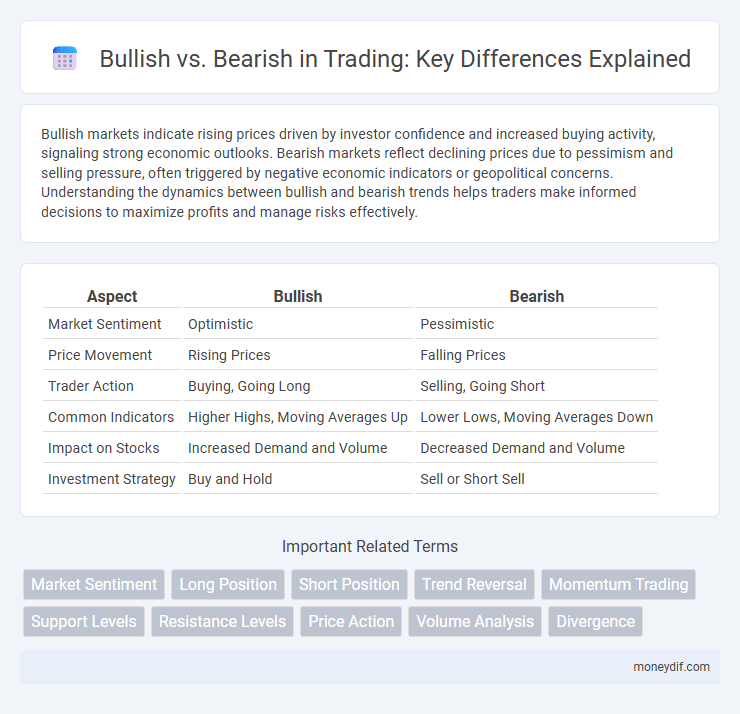
| Aspect | Bullish | Bearish |
|---|---|---|
| Market Sentiment | Optimistic | Pessimistic |
| Price Movement | Rising Prices | Falling Prices |
| Trader Action | Buying, Going Long | Selling, Going Short |
| Common Indicators | Higher Highs, Moving Averages Up | Lower Lows, Moving Averages Down |
| Impact on Stocks | Increased Demand and Volume | Decreased Demand and Volume |
| Investment Strategy | Buy and Hold | Sell or Short Sell |
Understanding Bullish and Bearish Markets
Bullish markets indicate rising prices and investor confidence, often driven by strong economic indicators and positive corporate earnings. Bearish markets reflect declining prices, widespread pessimism, and increased selling pressure, frequently triggered by economic downturns or adverse geopolitical events. Understanding these market trends is essential for developing effective trading strategies and managing investment risk.
Key Differences Between Bullish and Bearish Trends
Bullish trends indicate rising prices driven by investor confidence, higher buying volumes, and positive market sentiment. Bearish trends reflect falling prices characterized by increased selling pressure, lower trading volumes, and pessimistic outlooks. Key differences include trend direction, market psychology, and trading strategies utilized to capitalize on price movements.
Identifying Bullish Signals in Trading
Identifying bullish signals in trading involves recognizing patterns such as higher highs and higher lows on price charts, which indicate upward momentum. Key indicators include moving average crossovers, RSI levels rising above 50, and strong volume confirming buying interest. Traders often rely on bullish candlestick formations like the hammer or engulfing patterns to anticipate potential price increases.
Recognizing Bearish Patterns and Indicators
Bearish patterns such as head and shoulders, double tops, and descending triangles often signal potential market downturns. Key indicators include declining moving averages, increasing volume on down days, and bearish candlestick formations like the evening star and shooting star. Recognizing these signals helps traders anticipate price drops and manage risk effectively.
Market Sentiment: Bullish vs Bearish Perspectives
Bullish market sentiment reflects investor confidence, expecting prices to rise, often driven by strong economic indicators and positive earnings reports. Bearish sentiment indicates pessimism, with investors anticipating price declines due to factors like economic downturns or geopolitical instability. Understanding these perspectives helps traders make informed decisions by analyzing market trends and investor behavior patterns.
Common Strategies for Bullish Traders
Bullish traders commonly employ strategies like buying call options, initiating long positions, and using leveraged ETFs to capitalize on anticipated price increases. They also implement stop-loss orders to manage risk while holding assets expected to appreciate. Momentum trading and breakout strategies are popular to maximize gains during upward market trends.
Risk Management in Bearish Conditions
Effective risk management during bearish market conditions involves setting strict stop-loss orders and reducing exposure to high-volatility assets to protect capital from significant downturns. Traders often increase diversification across defensive sectors such as utilities and consumer staples to mitigate losses and preserve portfolio value. Leveraging options strategies like protective puts can provide downside protection while maintaining the opportunity for gains if market trends reverse.
Psychological Aspects of Bullish and Bearish Markets
Bullish markets often reflect investor confidence, optimism, and a general expectation of rising asset prices, driving buying behavior and risk-taking. Bearish markets tend to trigger fear, pessimism, and risk aversion, leading to selling pressure and decreased market participation. Understanding these psychological dynamics is crucial for traders to navigate market sentiment and make informed decisions.
Historical Examples of Bullish and Bearish Phases
Historical examples of bullish phases include the 1990s dot-com boom, where technology stocks soared, and the post-2008 financial crisis recovery marked by a prolonged market uptrend. Bearish phases are exemplified by the 2008 global financial crisis, which triggered widespread market declines, and the early 1970s stagflation period characterized by falling stock prices and economic stagnation. These cycles demonstrate how economic events and investor sentiment drive significant market trends in bullish and bearish phases.
Choosing the Right Approach: Bullish or Bearish?
Selecting the right trading strategy depends on market conditions and investor sentiment, with bullish approaches capitalizing on rising asset prices and bearish methods benefiting from declines. Analyzing technical indicators like moving averages and relative strength index (RSI) helps determine momentum direction for buying or shorting assets. Risk management and clear exit strategies are crucial when choosing between bullish or bearish positions to maximize gains and minimize losses.
Important Terms
Market Sentiment
Market sentiment reflects investor attitudes, where bullish sentiment indicates optimism and rising prices, while bearish sentiment signals pessimism and declining markets.
Long Position
A long position indicates a bullish outlook, expecting asset prices to rise, while a bearish stance favors short positions anticipating declines.
Short Position
A short position reflects a bearish market expectation where investors profit from a decline in asset prices, contrasting with a bullish stance anticipating price increases.
Trend Reversal
A trend reversal occurs when a bearish market shifts to bullish momentum, signaling potential investor confidence and upward price movement.
Momentum Trading
Momentum trading exploits bullish trends by buying assets with rising prices and capitalizes on bearish momentum by short-selling declining assets to maximize returns.
Support Levels
Support levels act as price floors where bullish traders anticipate demand to prevent further declines, whereas bearish traders view breaks below these levels as signals for continued downward momentum.
Resistance Levels
Resistance levels indicate price points where selling pressure typically prevents further bullish advances, often signaling a potential reversal to bearish trends.
Price Action
Price action reveals market sentiment by identifying bullish patterns, indicating upward momentum, versus bearish patterns, signaling potential downward trends.
Volume Analysis
Volume analysis in financial markets assesses the strength of price movements by examining the trading volume accompanying bullish or bearish trends. High volume during bullish movements indicates strong buying interest, while increased volume in bearish phases signals significant selling pressure, offering insights into potential trend reversals or continuations.
Divergence
Divergence occurs when price movement contradicts momentum indicators, signaling potential reversals in bullish or bearish market trends.
Bullish vs Bearish Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com