Swing trading involves holding positions for several days to weeks to capitalize on expected price movements, offering flexibility and less time commitment compared to day trading. Day trading requires executing multiple trades within a single day to profit from short-term market volatility, demanding constant market monitoring and quick decision-making. Both strategies have distinct risk profiles and align with different trader personalities and time availability.
Table of Comparison
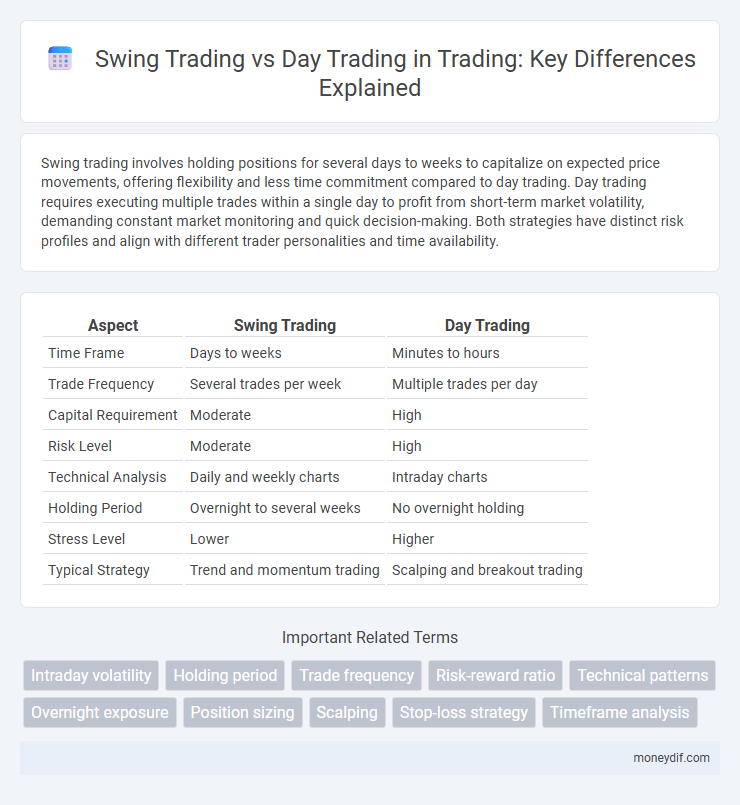
| Aspect | Swing Trading | Day Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Time Frame | Days to weeks | Minutes to hours |
| Trade Frequency | Several trades per week | Multiple trades per day |
| Capital Requirement | Moderate | High |
| Risk Level | Moderate | High |
| Technical Analysis | Daily and weekly charts | Intraday charts |
| Holding Period | Overnight to several weeks | No overnight holding |
| Stress Level | Lower | Higher |
| Typical Strategy | Trend and momentum trading | Scalping and breakout trading |
Introduction to Swing Trading and Day Trading
Swing trading involves holding positions for several days to weeks, capitalizing on short- to medium-term price movements in stocks, commodities, or forex. Day trading requires executing multiple trades within a single trading day, aiming to profit from intraday volatility without holding positions overnight. Both strategies demand disciplined risk management and thorough technical analysis to identify entry and exit points.
Key Differences Between Swing Trading and Day Trading
Swing trading involves holding positions for several days to weeks, capitalizing on medium-term price movements, whereas day trading closes all positions within the same trading day to avoid overnight risk. Swing traders rely on technical analysis and market trends to identify potential entry and exit points, while day traders focus on intraday volatility and rapid execution strategies. Risk management differs as swing trading requires patience and tolerance for overnight market fluctuations, while day trading demands quick decisions and strict stop-loss orders to minimize intraday losses.
Pros and Cons of Swing Trading
Swing trading allows traders to hold positions for several days to weeks, capturing medium-term market trends with less time commitment compared to day trading. This approach reduces the need for constant monitoring and can be more suitable for individuals balancing trading with other responsibilities, but it requires strong risk management to handle overnight market volatility. Lower transaction costs and fewer stress factors are benefits, though swing traders may face greater exposure to market gaps and unpredictable news events.
Pros and Cons of Day Trading
Day trading offers the advantage of rapid profit potential by capitalizing on intraday price volatility and leveraging high-frequency trades. It demands intense focus, quick decision-making, and carries significant risk due to market fluctuations and transaction costs that can erode profits. Traders benefit from immediate market feedback but must manage stress and maintain strict discipline to avoid substantial financial losses.
Required Skills for Swing Trading vs Day Trading
Swing trading demands strong technical analysis skills and the ability to interpret chart patterns for medium-term market movements, while day trading requires rapid decision-making, high concentration, and mastery of short-term price fluctuations. Swing traders should excel in risk management over several days to weeks, whereas day traders must manage real-time risks with precise entry and exit points within a single trading day. Both styles benefit from a solid understanding of market indicators, but day trading emphasizes speed and discipline under pressure more intensely than swing trading.
Risk Management Strategies
Swing trading employs risk management strategies like setting wider stop-loss orders to accommodate market fluctuations over multiple days, while day trading uses tighter stops to limit losses within a single trading session. Position sizing in swing trading is often larger due to the extended exposure, requiring careful analysis of volatility and trend strength; day traders prioritize rapid trade execution and quick adjustments to limit downside risk. Effective risk management in both styles hinges on disciplined adherence to preset stop-loss levels and regular review of market conditions to minimize potential drawdowns.
Time Commitment and Lifestyle Considerations
Swing trading requires less daily time commitment, allowing traders to analyze markets and execute trades over several days or weeks, making it suitable for those with full-time jobs or busy lifestyles. Day trading demands continuous monitoring of the markets throughout the trading day, often requiring traders to be fully engaged for several hours, which can lead to higher stress and limited personal time. Lifestyle considerations between swing trading and day trading include the flexibility of swing trading versus the intensive, fast-paced environment of day trading that often demands rapid decision-making and immediate action.
Profit Potential and Earning Opportunities
Swing trading offers higher profit potential by capturing medium-term market trends, allowing traders to capitalize on larger price movements over days or weeks. Day trading provides more frequent earning opportunities through multiple trades executed within a single day but typically yields smaller individual profits. Both strategies require strict risk management to maximize returns in volatile markets.
Tools and Resources Needed
Swing trading requires robust charting software and reliable technical indicators for analyzing medium-term price patterns, while day trading demands ultra-fast execution platforms, real-time market data feeds, and advanced risk management tools to capitalize on short-term volatility. Both strategies benefit from access to comprehensive news sources and educational resources, but day traders often rely more heavily on direct market access and high-speed internet connections to execute numerous trades within a single day. Effective risk assessment tools and customizable alerts are essential for managing trades efficiently in both swing and day trading environments.
Choosing the Right Trading Style for You
Swing trading suits traders seeking to capitalize on medium-term market trends, holding positions from several days to weeks to maximize price momentum. Day trading demands rapid decision-making and technical analysis skills, with positions opened and closed within a single trading day, ideal for those who can monitor markets actively. Assessing your risk tolerance, time availability, and market knowledge is crucial to selecting a trading style that aligns with your financial goals and lifestyle.
Important Terms
Intraday volatility
Intraday volatility measures price fluctuations within a single trading day, heavily influencing both swing trading and day trading strategies by determining entry and exit points. Swing traders leverage moderate intraday volatility to capture short- to medium-term price movements, while day traders rely on high intraday volatility to capitalize on rapid, minute-to-minute price changes.
Holding period
Swing trading typically involves holding positions for several days to weeks to capitalize on medium-term price movements, while day trading requires closing all positions within the same trading day to avoid overnight risks. The holding period significantly influences risk management, capital allocation, and trading strategies tailored to market volatility and liquidity.
Trade frequency
Trade frequency in swing trading averages 1 to 4 trades per week based on holding positions for several days to weeks, whereas day trading involves executing multiple trades per day, often exceeding 10 to 20 trades daily, capitalizing on intraday price fluctuations. The higher trade frequency in day trading requires rapid decision-making and increased transaction costs, while swing trading focuses on longer-term trends with lower trading volume and reduced market noise exposure.
Risk-reward ratio
Swing trading typically targets a higher risk-reward ratio, often aiming for 2:1 or greater, due to holding positions over several days to capture larger price movements. Day trading usually involves a lower risk-reward ratio around 1:1 or 1.5:1, focusing on quick trades and smaller price fluctuations within a single trading session.
Technical patterns
Technical patterns like head and shoulders and cup and handle are commonly used in swing trading to identify potential trend reversals over several days or weeks. In contrast, day trading relies on intraday patterns such as flag formations and double tops to capture quick price movements within minutes or hours.
Overnight exposure
Overnight exposure in swing trading involves holding positions for multiple days to capture larger price movements, increasing the risk of market gaps and overnight volatility. Day trading eliminates overnight exposure by closing positions before market close, reducing risk from after-hours news but limiting profit potential to intraday price fluctuations.
Position sizing
Position sizing in swing trading typically involves holding larger positions for several days or weeks to capture medium-term price movements, whereas day trading requires smaller, more flexible positions to manage rapid intraday volatility and minimize risk exposure. Effective position sizing strategies adjust trade size based on volatility, risk tolerance, and trade duration specific to each trading style.
Scalping
Scalping involves executing numerous quick trades to capture small price movements, differing from swing trading, which targets larger gains over several days or weeks by capitalizing on market trends. Day trading shares scalping's short-term focus but contrasts by holding positions for hours rather than minutes, requiring distinct risk management and technical analysis strategies.
Stop-loss strategy
Stop-loss strategy in swing trading typically involves setting wider stop-loss limits to accommodate longer market fluctuations over several days or weeks, while day trading requires tighter stop-loss placements to manage rapid price changes within the same trading session. Effective stop-loss implementation in both methods reduces potential losses and enhances risk management by automatically exiting positions at predetermined price points.
Timeframe analysis
Timeframe analysis in swing trading focuses on daily to weekly charts to identify medium-term price trends and potential reversal points, optimizing entry and exit strategies over several days to weeks. In contrast, day trading relies on intraday charts such as 1-minute, 5-minute, and 15-minute intervals to capture short-term price movements, emphasizing rapid decision-making and tighter risk management within a single trading session.
swing trading vs day trading Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com