FOMO drives traders to impulsively buy assets fearing they will miss out on potential gains, often leading to overvalued positions and increased market risk. FUD triggers widespread fear, uncertainty, and doubt, causing panic selling and sharp price declines that can create buying opportunities for disciplined investors. Understanding the psychological impact of FOMO and FUD helps traders maintain emotional control and make rational decisions in volatile markets.
Table of Comparison
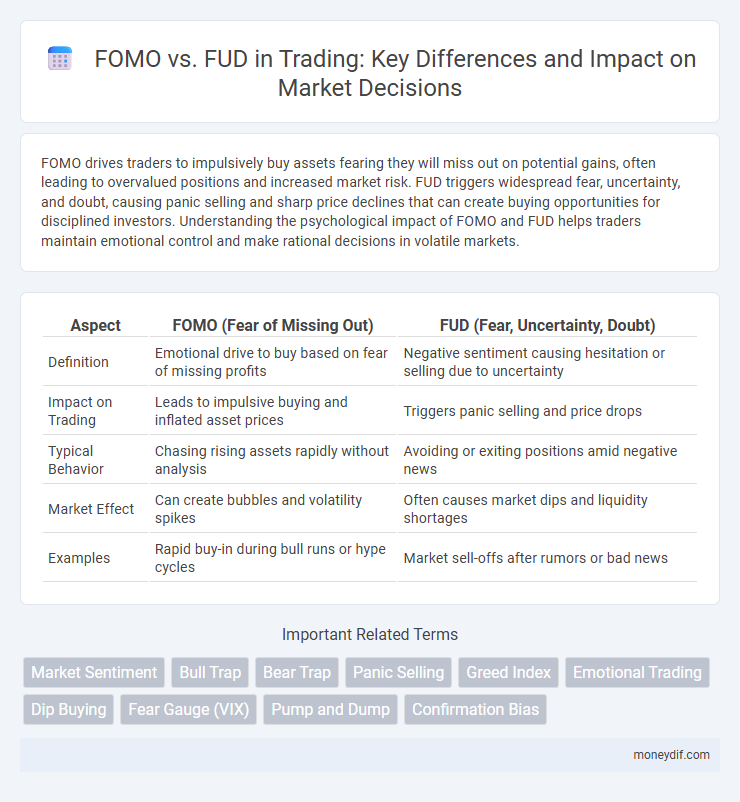
| Aspect | FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) | FUD (Fear, Uncertainty, Doubt) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Emotional drive to buy based on fear of missing profits | Negative sentiment causing hesitation or selling due to uncertainty |
| Impact on Trading | Leads to impulsive buying and inflated asset prices | Triggers panic selling and price drops |
| Typical Behavior | Chasing rising assets rapidly without analysis | Avoiding or exiting positions amid negative news |
| Market Effect | Can create bubbles and volatility spikes | Often causes market dips and liquidity shortages |
| Examples | Rapid buy-in during bull runs or hype cycles | Market sell-offs after rumors or bad news |
Understanding FOMO and FUD in Trading
FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) drives traders to make impulsive decisions based on the anxiety of missing potential profits, often leading to buying at market highs. FUD (Fear, Uncertainty, and Doubt) triggers selling pressure due to negative news or rumors, causing irrational market downturns. Recognizing these psychological triggers helps traders execute more disciplined strategies and avoid emotional pitfalls in volatile markets.
The Psychological Triggers Behind FOMO
FOMO, or Fear of Missing Out, is driven by the psychological trigger of social proof, where traders rush to buy assets based on others' actions rather than fundamental analysis. This emotion amplifies market volatility as it encourages impulsive decisions fueled by anxiety over potential losses or missed opportunities. Recognizing FOMO's impact on trading behavior can help investors maintain discipline and avoid irrational market reactions caused by herd mentality.
How FUD Impacts Market Decisions
FUD, which stands for Fear, Uncertainty, and Doubt, significantly impacts market decisions by causing traders to sell assets prematurely, often leading to sharp price declines and increased volatility. This emotional reaction undermines rational analysis, prompting panic selling that can create self-fulfilling downward trends. Understanding the psychological effects of FUD helps investors remain disciplined and avoid making impulsive trades based on misinformation or speculative fear.
Identifying FOMO and FUD Signals
FOMO signals in trading include sudden surges in buying volume, rapid price spikes, and overwhelming positive social media sentiment, indicating fear of missing out on potential gains. FUD signals manifest as sharp declines in asset value, increased selling pressure, and widespread negative news or rumors, reflecting fear, uncertainty, and doubt among investors. Recognizing these emotional market drivers helps traders make more rational decisions by distinguishing genuine market trends from sentiment-driven fluctuations.
FOMO vs FUD: Key Differences
FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) drives traders to make impulsive decisions fueled by the anxiety of missing profitable opportunities, often leading to overbought assets and market bubbles. FUD (Fear, Uncertainty, Doubt) causes hesitation or panic selling due to negative news or rumors, typically resulting in sharp price drops and undervalued assets. Understanding the key differences between FOMO and FUD is crucial for developing disciplined trading strategies and avoiding emotional biases.
Effects of FOMO on Trading Performance
FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) often causes traders to make impulsive decisions, leading to premature entries and increased exposure to market volatility. This emotional bias amplifies risk-taking behaviors, resulting in suboptimal trade timing and reduced overall profitability. Persistent FOMO undermines disciplined strategy adherence, negatively impacting long-term trading performance and risk management.
Managing FUD During Market Downturns
Managing FUD during market downturns involves maintaining a disciplined trading strategy and relying on data-driven analysis rather than emotional reactions. Traders should monitor key indicators such as volume trends, support levels, and market sentiment to distinguish between genuine market shifts and fear-induced noise. Utilizing stop-loss orders and diversified portfolios can help mitigate losses while avoiding impulsive decisions fueled by Fear, Uncertainty, and Doubt.
Strategies to Overcome FOMO and FUD
Traders combat FOMO by setting strict entry and exit points based on technical analysis and maintaining disciplined risk management to avoid impulsive decisions driven by fear of missing out. To overcome FUD, they rely on thorough research, verify news sources, and focus on long-term market trends instead of reacting to short-term rumors or negative sentiment. Utilizing tools like stop-loss orders and maintaining a well-diversified portfolio also mitigates emotional trading reactions tied to FOMO and FUD.
Case Studies: FOMO and FUD in Real Markets
In real market scenarios, instances of FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) often drive sudden surges in asset prices, exemplified by the 2017 cryptocurrency boom where investors rapidly bought Bitcoin anticipating continued gains. Conversely, FUD (Fear, Uncertainty, Doubt) has caused sharp sell-offs, as seen during the 2020 stock market crash triggered by pandemic fears leading to widespread panic selling. These case studies highlight how emotional responses can significantly impact market volatility and investor behavior.
Building Emotional Discipline Against FOMO and FUD
Building emotional discipline against FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) and FUD (Fear, Uncertainty, Doubt) is crucial for successful trading, as these emotional reactions often lead to impulsive decisions and financial losses. Developing a structured trading plan, setting predefined entry and exit points, and adhering strictly to risk management rules helps traders mitigate the impact of market noise and psychological pressures. Consistent practice of mindfulness and reflective journaling enhances self-awareness, enabling traders to recognize and control emotional triggers associated with FOMO and FUD.
Important Terms
Market Sentiment
Market sentiment significantly influences trading decisions by driving Fear of Missing Out (FOMO), which prompts investors to buy rapidly during bullish trends, and Fear, Uncertainty, and Doubt (FUD), which causes panic selling in downturns. Understanding these psychological triggers helps traders anticipate market volatility and make informed investment strategies.
Bull Trap
A Bull Trap occurs when investors, driven by FOMO (Fear of Missing Out), prematurely enter a rising market expecting continued gains, only to face a swift reversal due to underlying FUD (Fear, Uncertainty, Doubt) causing a sudden sell-off. This deceptive price movement lures traders into false optimism before triggering losses as market sentiment shifts abruptly.
Bear Trap
A Bear Trap occurs when market sentiment driven by FUD (Fear, Uncertainty, Doubt) causes investors to sell prematurely, only for prices to rapidly rebound and trap bears expecting further declines. This phenomenon exploits FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) as traders rush back into positions to capitalize on price recoveries, intensifying short squeezes in assets like stocks or cryptocurrencies.
Panic Selling
Panic selling occurs when investors rapidly offload assets due to Fear of Missing Out (FOMO) driving initial overbuying, followed by overwhelming Fear, Uncertainty, and Doubt (FUD) that triggers abrupt market exits. This emotional volatility often leads to sharp price drops and increased market instability as FOMO inflates asset values before FUD induces mass sell-offs.
Greed Index
The Greed Index measures market sentiment by quantifying investor emotions like Fear of Missing Out (FOMO) and Fear, Uncertainty, and Doubt (FUD), which significantly influence asset price volatility. High Greed Index values correlate with aggressive buying patterns driven by FOMO, while low values indicate prevailing FUD leading to cautious or sell-off behavior.
Emotional Trading
Emotional trading often stems from FOMO (Fear of Missing Out), which drives impulsive buying based on hype, while FUD (Fear, Uncertainty, Doubt) triggers panic selling due to negative market sentiment. Both psychological factors disrupt rational decision-making, leading to increased market volatility and suboptimal investment outcomes.
Dip Buying
Dip buying leverages market dips driven by Fear of Missing Out (FOMO) as investors rush to capitalize on lower prices, while Fear, Uncertainty, and Doubt (FUD) often create short-term sell-offs that can serve as strategic entry points for patient buyers. Identifying genuine dips requires analyzing market sentiment and fundamental indicators to distinguish between temporary panic and long-term downturns for optimized investment decisions.
Fear Gauge (VIX)
The Fear Gauge (VIX) measures market volatility and investor sentiment, often spiking during episodes of FUD (Fear, Uncertainty, Doubt) when investors anticipate market downturns. Conversely, low VIX levels can indicate heightened FOMO (Fear of Missing Out), reflecting bullish investor behavior and increased risk appetite.
Pump and Dump
Pump and dump schemes manipulate FOMO by artificially inflating asset prices, enticing investors to buy before a rapid sell-off occurs; simultaneously, FUD spreads misinformation to trigger panic selling, amplifying market volatility and enabling scammers to maximize profits. Understanding the interplay of Fear of Missing Out (FOMO) and Fear, Uncertainty, and Doubt (FUD) is crucial for investors to recognize and avoid these deceptive market tactics.
Confirmation Bias
Confirmation bias intensifies the psychological impact of FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) and FUD (Fear, Uncertainty, Doubt) by causing individuals to selectively seek information that reinforces their existing fears or desires. This cognitive bias skews decision-making processes in financial markets, social media, and consumer behavior by distorting risk assessment and opportunity evaluation.
FOMO vs FUD Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com