VWAP measures the average price weighted by volume over a trading period, providing insight into market liquidity and real-time price trends. TWAP calculates the average price over a set time interval, helping execute large orders without significantly impacting the market. Traders often choose VWAP for volume-sensitive strategies and TWAP for time-based execution to minimize market impact.
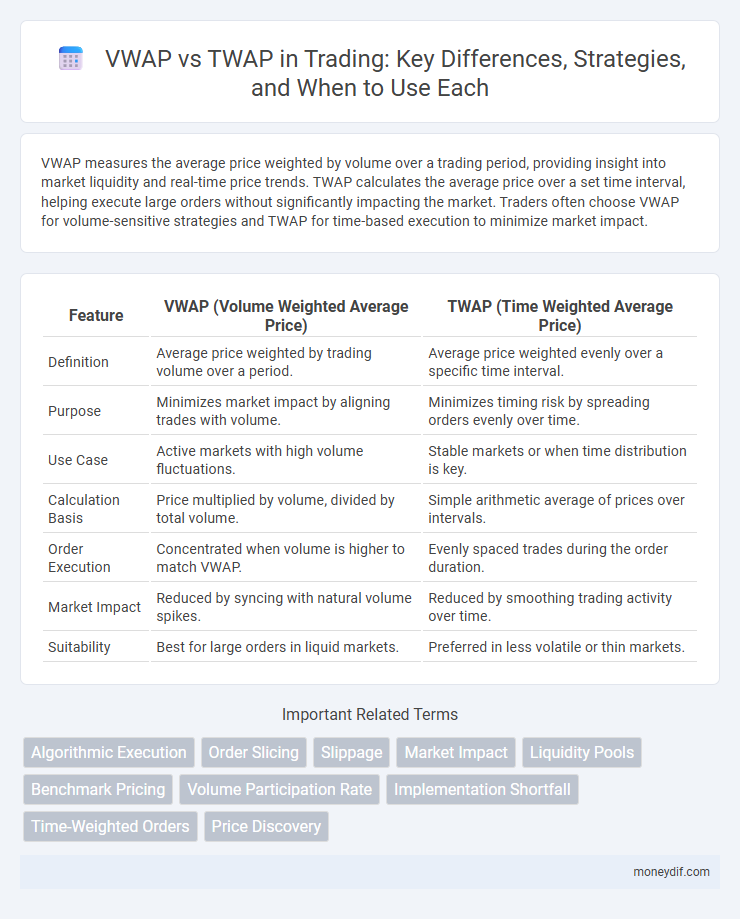
Table of Comparison
| Feature | VWAP (Volume Weighted Average Price) | TWAP (Time Weighted Average Price) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Average price weighted by trading volume over a period. | Average price weighted evenly over a specific time interval. |
| Purpose | Minimizes market impact by aligning trades with volume. | Minimizes timing risk by spreading orders evenly over time. |
| Use Case | Active markets with high volume fluctuations. | Stable markets or when time distribution is key. |
| Calculation Basis | Price multiplied by volume, divided by total volume. | Simple arithmetic average of prices over intervals. |
| Order Execution | Concentrated when volume is higher to match VWAP. | Evenly spaced trades during the order duration. |
| Market Impact | Reduced by syncing with natural volume spikes. | Reduced by smoothing trading activity over time. |
| Suitability | Best for large orders in liquid markets. | Preferred in less volatile or thin markets. |
Understanding VWAP and TWAP: Key Definitions
VWAP (Volume Weighted Average Price) calculates the average price of a security weighted by total traded volume over a specific time period, providing insight into market liquidity and trade execution efficiency. TWAP (Time Weighted Average Price) averages the price of a security evenly over a set time interval, helping to minimize the market impact of large orders by distributing trades uniformly. Traders use VWAP for benchmarking against intraday volume patterns, while TWAP suits strategies requiring steady execution without volume bias.
Core Differences Between VWAP and TWAP
VWAP (Volume Weighted Average Price) calculates the average price of a security by weighting each trade price by its volume, reflecting the true market activity, while TWAP (Time Weighted Average Price) spreads trades evenly over a specified time interval, ignoring volume fluctuations. VWAP is ideal for capturing price trends during periods of high liquidity, whereas TWAP suits traders aiming to minimize market impact by executing evenly over time. The core difference lies in VWAP's emphasis on volume-driven pricing versus TWAP's focus on time-based execution, influencing strategy choice in algorithmic trading.
Use Cases: When to Choose VWAP Over TWAP
VWAP is preferred in trading scenarios that require tracking average price relative to volume, making it ideal for minimizing market impact during high-volume periods or executing large orders aligned with the day's liquidity patterns. TWAP suits strategies seeking execution evenly over time, but VWAP's strength lies in reflecting genuine market activity for institutional investors aiming for price efficiency within volatile or volume-weighted markets. Selecting VWAP is advantageous when trades need to be benchmarked against actual volume during the trading session to optimize cost and market impact.
Algorithmic Execution Strategies: VWAP vs TWAP
VWAP (Volume Weighted Average Price) and TWAP (Time Weighted Average Price) are essential algorithmic execution strategies used to minimize market impact and achieve better trade pricing. VWAP focuses on executing trades in proportion to historical or real-time volume patterns, ensuring alignment with market liquidity, while TWAP divides orders evenly across a predetermined time interval regardless of volume fluctuations. Traders select VWAP for volume-sensitive environments and TWAP when they require consistent execution timing, optimizing efficiency based on market conditions and execution goals.
Impact on Market Liquidity and Slippage
VWAP (Volume Weighted Average Price) execution aligns orders with actual market volume, resulting in enhanced liquidity absorption and reduced slippage by matching prevailing trading activity. TWAP (Time Weighted Average Price) distributes orders evenly over time regardless of volume fluctuations, potentially increasing slippage during low liquidity periods and causing larger market impact. Traders seeking minimal market disturbance often prefer VWAP for its responsiveness to real-time volume, while TWAP suits strategies valuing consistent execution timing over volume sensitivity.
Advantages and Limitations of VWAP
VWAP (Volume Weighted Average Price) provides the advantage of reflecting true market activity by weighting prices according to trading volume, making it ideal for assessing execution quality in high liquidity conditions. It helps traders minimize market impact by aligning trades with the volume distribution throughout the day but may be less effective in low volume or highly volatile markets where volume spikes distort the average. Limitations include its dependence on historical volume patterns, which can delay order execution during fast-moving markets and reduce flexibility compared to TWAP (Time Weighted Average Price) that focuses on consistent execution over time.
Advantages and Limitations of TWAP
TWAP (Time-Weighted Average Price) offers advantages such as minimizing market impact by evenly distributing trades over a specified time period, making it ideal for less liquid markets or large orders. It provides simplicity and predictability in execution, reducing the risk of signaling large trades to the market compared to VWAP (Volume-Weighted Average Price), which can be more sensitive to volume spikes. However, TWAP's limitation lies in ignoring volume variations, potentially resulting in suboptimal execution prices during periods of high liquidity or volatility.
VWAP and TWAP in High-Frequency Trading
VWAP (Volume Weighted Average Price) and TWAP (Time Weighted Average Price) are crucial algorithms in High-Frequency Trading, with VWAP emphasizing trade execution aligned with volume distribution to minimize market impact. VWAP adjusts dynamically based on real-time volume, making it ideal for trading assets with varying liquidity throughout the day. TWAP, however, evenly distributes orders over a specified time, providing consistent execution but potentially ignoring volume spikes critical in high-frequency environments.
Real-World Examples: VWAP vs TWAP Performance
VWAP (Volume Weighted Average Price) outperforms TWAP (Time Weighted Average Price) in highly liquid markets by capturing the price impact of actual trading volumes, as demonstrated in equities like Apple and Microsoft where VWAP aligns closely with intraday volume spikes. TWAP is preferred in thinly traded or low-volume assets such as certain small-cap stocks or bonds, providing a steady execution price without volume dependence that reduces market impact risks. Studies in algorithmic trading confirm VWAP strategies deliver better cost efficiency during high-volume periods, while TWAP offers predictable execution profiles in volatile or illiquid conditions.
Choosing the Right Strategy: VWAP or TWAP?
Choosing between VWAP and TWAP depends on market conditions and trading objectives; VWAP targets volume-weighted price execution ideal for capturing liquidity during high-volume periods, while TWAP evenly distributes orders over time to minimize market impact in low liquidity or volatile environments. Traders focusing on minimizing slippage and aligning execution with intraday volume patterns typically prefer VWAP, whereas those seeking consistent execution regardless of volume fluctuations lean toward TWAP. Analyzing historical volume profiles and price volatility is crucial for selecting the optimal strategy to enhance trade efficiency and reduce market impact.
Important Terms
Algorithmic Execution
Algorithmic execution strategies utilize VWAP to minimize market impact by matching the volume-weighted average price throughout the trading day, while TWAP focuses on evenly distributing orders over time to reduce timing risk.
Order Slicing
Order slicing improves trade execution by breaking large orders into smaller segments timed with VWAP or TWAP to minimize market impact and achieve optimal average prices.
Slippage
Slippage occurs when the execution price deviates from the target price, often influenced by the choice between VWAP, which aims to match volume-weighted prices, and TWAP, which averages prices over time regardless of volume.
Market Impact
VWAP outperforms TWAP in minimizing market impact by aligning trades with actual volume distribution throughout the day.
Liquidity Pools
Liquidity pools enhance trading efficiency by enabling VWAP strategies to capture volume-weighted prices, while TWAP focuses on evenly timed executions to reduce market impact.
Benchmark Pricing
Benchmark pricing compares VWAP and TWAP by measuring trade execution efficiency against volume-weighted and time-weighted average prices to optimize market impact and transaction costs.
Volume Participation Rate
Volume Participation Rate measures the proportion of an order executed relative to total market volume, optimizing trade performance when comparing VWAP (Volume Weighted Average Price) against TWAP (Time Weighted Average Price) strategies.
Implementation Shortfall
Implementation Shortfall measures the cost difference between the decision price and the final execution price, often minimized by selecting optimal trading algorithms like VWAP, which targets volume-weighted price, or TWAP, which averages prices over time.
Time-Weighted Orders
Time-weighted orders distribute trades evenly over a set period, minimizing market impact by executing orders at regular intervals, while VWAP (Volume-Weighted Average Price) focuses on matching the average price based on traded volume, making Time-Weighted Average Price (TWAP) ideal for consistent execution and VWAP better suited for volume-driven strategies.
Price Discovery
VWAP measures the average trading price weighted by volume to reflect actual market activity for price discovery, while TWAP calculates the average price over time irrespective of volume, offering a time-based benchmark less sensitive to price spikes.
VWAP vs TWAP Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com