Forex spot trading involves the immediate exchange of currencies at the current market rate, providing quick settlement usually within two business days. Forex forward contracts lock in an exchange rate for a transaction that will occur at a specified future date, offering protection against currency fluctuations. Traders use spot for swift execution and liquidity, while forwards are preferred for hedging long-term currency exposure.
Table of Comparison
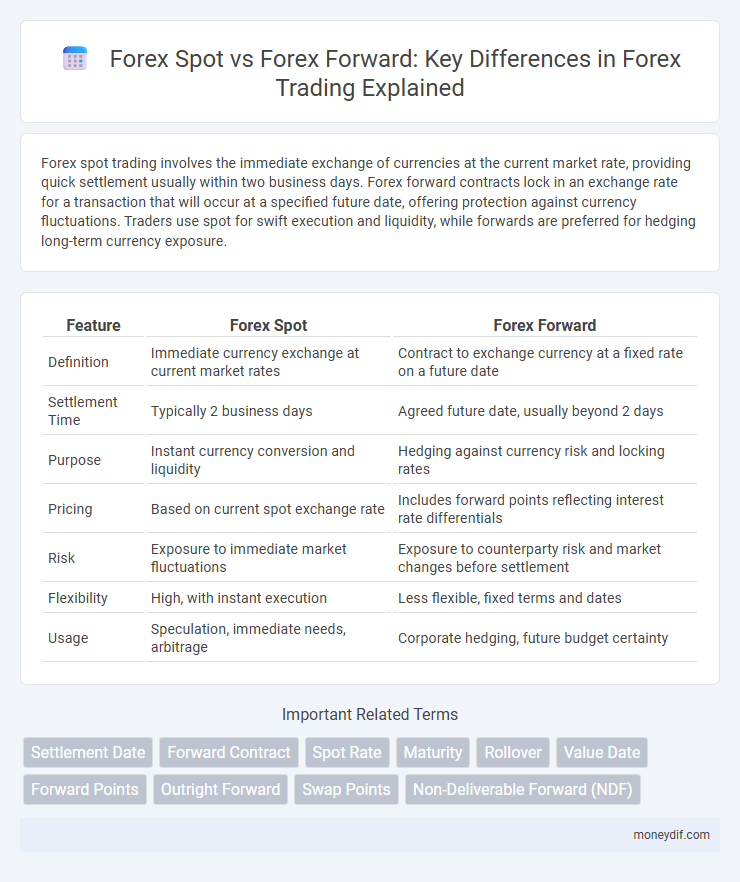
| Feature | Forex Spot | Forex Forward |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Immediate currency exchange at current market rates | Contract to exchange currency at a fixed rate on a future date |
| Settlement Time | Typically 2 business days | Agreed future date, usually beyond 2 days |
| Purpose | Instant currency conversion and liquidity | Hedging against currency risk and locking rates |
| Pricing | Based on current spot exchange rate | Includes forward points reflecting interest rate differentials |
| Risk | Exposure to immediate market fluctuations | Exposure to counterparty risk and market changes before settlement |
| Flexibility | High, with instant execution | Less flexible, fixed terms and dates |
| Usage | Speculation, immediate needs, arbitrage | Corporate hedging, future budget certainty |
Understanding Forex Spot and Forex Forward Contracts
Forex spot contracts involve the immediate exchange of currencies at the current market rate, typically settled within two business days. Forex forward contracts allow traders to lock in an exchange rate today for a currency transaction that will occur at a specified future date, mitigating exposure to currency fluctuations. Understanding the differences between these instruments is crucial for effective risk management and strategic currency trading.
Key Differences Between Spot and Forward Forex Trades
Forex spot trades involve the immediate exchange of currency at the current market rate with settlement typically occurring within two business days. Forex forward contracts lock in a fixed exchange rate for a currency pair at a future date, allowing traders to hedge against currency risk and volatility. The key differences lie in timing and price certainty: spot trades settle quickly at the prevailing rate, while forward trades provide rate certainty but defer settlement, reducing exposure to market fluctuations.
How Forex Spot Transactions Work
Forex spot transactions involve the immediate exchange of one currency for another at the current market rate, known as the spot rate, with settlement typically occurring within two business days. Traders use spot Forex to capitalize on real-time currency value fluctuations, providing liquidity and enabling quick access to foreign currencies. This contrasts with Forex forward contracts, which lock in exchange rates for future settlements, offering protection against adverse currency movements.
How Forward Forex Contracts Function
Forex forward contracts function by locking in an exchange rate for a currency pair on a specific future date, allowing traders to hedge against currency risk and protect profit margins. These contracts involve an agreement between two parties to exchange currencies at a predetermined rate, irrespective of market fluctuations at the contract's maturity. By utilizing forward forex contracts, businesses and investors can manage exposure to volatile currency movements and stabilize cash flow for future transactions.
Advantages of Trading Forex Spot
Forex Spot trading offers immediate execution and settlement, enabling traders to capitalize on real-time price fluctuations with high liquidity and tight spreads. It provides transparency and ease of access, making it suitable for short-term strategies and quick profit opportunities. The simplicity of spot contracts avoids the complexities and costs associated with forwards, such as rollover fees and credit risk.
Benefits of Using Forex Forward Contracts
Forex forward contracts provide traders with the advantage of locking in exchange rates for future transactions, eliminating uncertainty caused by market volatility. These contracts enable better budget forecasting and risk management by securing a fixed rate, protecting businesses from adverse currency fluctuations. Companies engaged in international trade benefit from forex forwards by stabilizing cash flows and maintaining profit margins in unpredictable forex markets.
Risks Associated with Spot vs Forward Forex Trading
Forex spot trading exposes traders to immediate market volatility, leading to potential rapid gains or losses due to real-time price fluctuations. In contrast, forex forward contracts mitigate this risk by locking in exchange rates for future transactions, reducing exposure to unfavorable currency movements. However, forward contracts carry counterparty risk and potential liquidity issues, which can impact settlement and overall trade execution.
Determining the Best Option: Spot or Forward Forex
Evaluating Forex Spot versus Forex Forward requires analyzing key factors such as risk tolerance, price certainty, and market volatility. Forex Spot offers immediate currency exchange at current market rates, ideal for transactions needing quick settlement and straightforward pricing. In contrast, Forex Forward contracts lock in exchange rates for future dates, providing protection against unfavorable currency fluctuations and enhancing budgeting accuracy in international trading strategies.
Use Cases: When to Choose Spot or Forward Forex
Forex Spot trading suits businesses and traders requiring immediate currency exchange to settle transactions or capitalize on current exchange rates, ensuring swift payment and delivery. Forex Forward contracts benefit companies aiming to hedge against future currency fluctuations by locking in exchange rates for transactions scheduled beyond the spot settlement date. Choosing between Spot and Forward hinges on the timing of payment obligations and the necessity of rate certainty to manage foreign exchange risk effectively.
Impact of Market Volatility on Spot and Forward Forex
Market volatility significantly affects Forex spot rates by causing immediate and often sharp fluctuations in currency prices, creating opportunities and risks for traders seeking quick execution. In contrast, Forex forward contracts lock in exchange rates for future transactions, providing hedging advantages by mitigating exposure to unpredictable market swings. This risk management feature of forwards helps businesses and investors stabilize cash flows and budget forecasts amid volatile currency markets.
Important Terms
Settlement Date
The settlement date for Forex spot transactions typically occurs two business days after the trade date, ensuring immediate currency exchange at the current market rate, while Forex forward contracts fix the settlement date beyond the spot date, allowing parties to lock in an exchange rate for future currency delivery. This distinction in settlement dates enables businesses to manage currency risk effectively by choosing between instant conversion or delayed settlement with predetermined pricing.
Forward Contract
A forward contract in forex is an agreement to buy or sell a currency at a predetermined rate on a future date, providing protection against exchange rate volatility unlike a forex spot transaction which settles instantly at the current market rate. Forex forward contracts are commonly used by businesses and investors to hedge exposure and lock in costs or revenues, while forex spot is preferred for immediate currency exchange needs.
Spot Rate
Spot rate in forex refers to the current exchange rate at which currencies can be bought or sold for immediate delivery, typically settled within two business days. Forex forward contracts use agreed-upon forward rates derived from the spot rate adjusted by interest rate differentials, allowing traders to lock in exchange rates for future transactions and hedge against currency risk.
Maturity
Maturity in Forex Spot refers to the immediate settlement of currency transactions, typically within two business days, whereas Forex Forward involves a contract agreeing to exchange currencies at a specified date beyond the spot settlement, allowing for hedging against future exchange rate fluctuations. The differing maturities between spot and forward contracts impact liquidity, risk management strategies, and pricing models in foreign exchange markets.
Rollover
Rollover in Forex trading refers to the process of extending the settlement date of an open position from the spot value date to the next trading day, which involves a small interest fee or credit depending on the interest rate differential between the two currencies. Unlike Forex forwards that lock in an exchange rate for a future date, rollovers are short-term, automatically applied adjustments that reflect interest rate differences without fixing the price ahead.
Value Date
Value Date in Forex Spot transactions typically refers to two business days after the trade date, representing the standard settlement time for currency exchange. In contrast, Forex Forward contracts specify a negotiated value date beyond the standard spot date, allowing parties to lock in exchange rates for future settlement, mitigating currency risk.
Forward Points
Forward points represent the difference between the spot rate and the forward rate in forex trading, reflecting interest rate differentials between two currencies over the contract period. These points are added or subtracted from the spot rate to calculate the forward rate, enabling traders to hedge exchange rate risk or speculate on currency movements over time.
Outright Forward
An Outright Forward contract in forex trading locks in an exchange rate for a currency pair to be settled at a future date, unlike a Forex Spot transaction which involves immediate delivery, typically within two business days. Trading Outright Forwards mitigates exchange rate risk by allowing businesses and investors to hedge against currency fluctuations beyond the standard spot settlement period.
Swap Points
Swap points in Forex represent the interest rate differential between two currencies in a currency pair and are applied when rolling over a Forex spot position to a forward settlement date. These points adjust the spot exchange rate to derive the Forex forward rate, reflecting the cost or gain of holding a position overnight due to interest rate differences.
Non-Deliverable Forward (NDF)
A Non-Deliverable Forward (NDF) is a financial derivative used to hedge or speculate on foreign exchange rates where physical currency delivery is restricted, settling the net difference between the contracted forward rate and the spot rate at maturity. Unlike traditional Forex forwards that involve actual currency exchange on a future date, NDFs are cash-settled contracts primarily utilized for currencies with capital controls or limited convertibility.
Forex Spot vs Forex Forward Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com