Swing trading involves holding positions for several days to capture medium-term price movements, allowing traders to benefit from market trends with less frequent monitoring. Scalping focuses on rapid trades lasting seconds to minutes, targeting small price fluctuations to accumulate quick profits through high-frequency executions. While swing trading suits those preferring a more relaxed pace, scalping demands intense concentration and immediate decision-making.
Table of Comparison
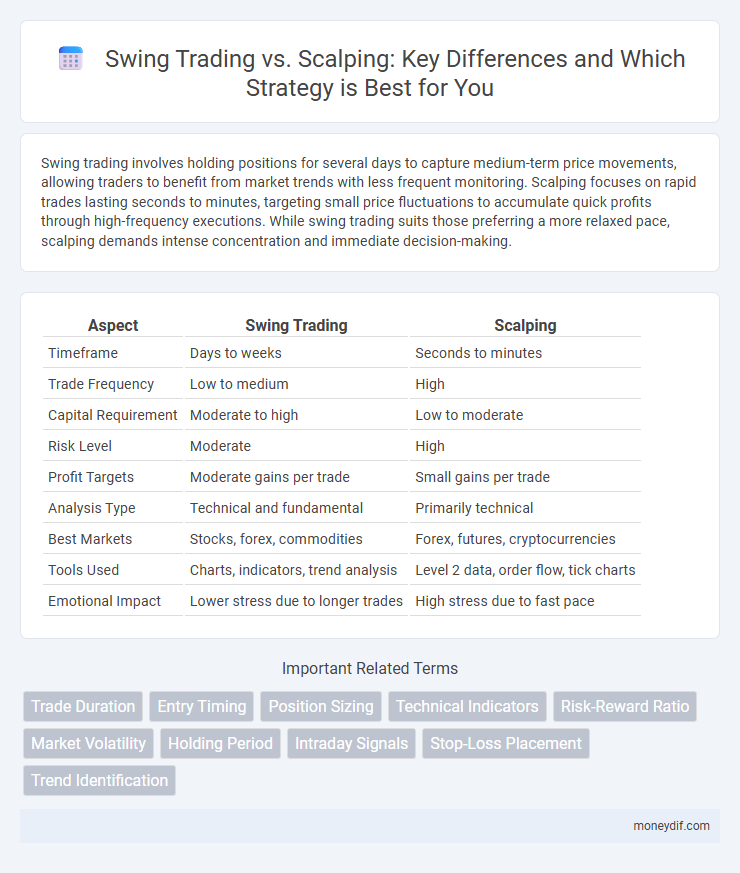
| Aspect | Swing Trading | Scalping |
|---|---|---|
| Timeframe | Days to weeks | Seconds to minutes |
| Trade Frequency | Low to medium | High |
| Capital Requirement | Moderate to high | Low to moderate |
| Risk Level | Moderate | High |
| Profit Targets | Moderate gains per trade | Small gains per trade |
| Analysis Type | Technical and fundamental | Primarily technical |
| Best Markets | Stocks, forex, commodities | Forex, futures, cryptocurrencies |
| Tools Used | Charts, indicators, trend analysis | Level 2 data, order flow, tick charts |
| Emotional Impact | Lower stress due to longer trades | High stress due to fast pace |
Introduction to Swing Trading and Scalping
Swing trading involves holding positions for several days to weeks to capitalize on expected price moves, allowing traders to benefit from medium-term market trends. Scalping targets quick, small profits by executing numerous trades within seconds to minutes, relying on high liquidity and tight spreads. Both strategies require distinct risk management techniques and suit different trader profiles based on time commitment and market volatility.
Key Differences Between Swing Trading and Scalping
Swing trading targets medium-term price movements over days to weeks, leveraging trend analysis and technical indicators to capture larger profits. Scalping involves rapid, high-frequency trades within minutes or seconds, aiming to exploit small price fluctuations with tight stop-losses and high leverage. Key differences include trade duration, risk exposure, and required market monitoring intensity, with swing trading favoring patience and scalping demanding quick decision-making and execution.
Profit Potential: Swing Trading vs Scalping
Swing trading offers higher profit potential by capturing larger price movements over days or weeks, while scalping targets smaller, quick profits from minor price fluctuations within minutes. Swing traders benefit from trend momentum and can capitalize on substantial market shifts, whereas scalpers rely on high trade frequency to accumulate gains. Risk management differs as swing trading involves holding positions longer with potentially higher rewards, contrasting with scalping's rapid entry and exit to minimize exposure.
Time Commitment Required for Each Strategy
Swing trading requires a moderate time commitment, typically involving holding positions for several days to weeks while analyzing market trends and patterns. Scalping demands intense focus and quick decision-making, with trades often lasting seconds to minutes, requiring near-constant monitoring of fast-moving price fluctuations. Traders choosing between these strategies must consider their availability and ability to dedicate time to market analysis and trade execution.
Risk Management Techniques Compared
Swing trading employs stop-loss orders and position sizing to manage risk over multiple days, reducing exposure to sudden market fluctuations. Scalping relies on tight stop-loss limits and high trade frequency to minimize losses from rapid price movements within minutes. Both strategies require disciplined risk management, but scalping demands quicker decision-making and more active monitoring due to its higher trade volume and shorter timeframes.
Tools and Indicators Used for Swing Trading and Scalping
Swing trading relies heavily on technical indicators like moving averages, Relative Strength Index (RSI), and Fibonacci retracements to identify price trends and potential entry and exit points over several days to weeks. Scalping requires ultra-short-term tools such as Level 2 market data, tick charts, and the stochastic oscillator to capture rapid price movements within minutes. Traders often use volume indicators and Bollinger Bands in both strategies but optimize settings differently to suit the trading timeframe.
Best Market Conditions for Swing Traders and Scalpers
Swing traders thrive in markets with moderate volatility and clear trends, allowing them to capture price movements over several days to weeks. Scalpers perform best in highly liquid markets with tight spreads and rapid price fluctuations, enabling quick entry and exit within seconds to minutes. Identifying the optimal market condition--steady momentum for swing trading versus intense volume and volatility for scalping--maximizes trading efficiency and profitability.
Pros and Cons of Swing Trading
Swing trading offers the advantage of capturing larger price movements over several days or weeks, allowing traders to benefit from market trends with less time spent monitoring charts compared to scalping. This strategy reduces stress and trading costs since fewer trades are executed, but it exposes traders to overnight market risks and potential gaps due to holding positions longer. Swing trading requires strong analytical skills to identify optimal entry and exit points, and it may not suit traders seeking quick profits or high-frequency trades.
Pros and Cons of Scalping
Scalping in trading offers the advantage of quick profits by capitalizing on small price movements, minimizing exposure to market risks. However, this strategy requires intense concentration, fast decision-making, and high transaction costs due to frequent trades. Scalpers rely heavily on liquidity and tight spreads, making it less effective in volatile or low-volume markets.
Choosing the Right Strategy: Swing Trading or Scalping
Selecting the optimal trading strategy requires evaluating personal risk tolerance, time commitment, and market volatility. Swing trading involves holding positions for days or weeks, targeting larger price movements with moderate risk, while scalping exploits small price fluctuations within minutes, demanding quick decision-making and high focus. Traders must consider their available time, capital, and psychological resilience to determine whether the steady pace of swing trading or the rapid execution of scalping aligns better with their financial goals.
Important Terms
Trade Duration
Trade duration in swing trading typically spans several days to weeks, whereas scalping involves holding positions for seconds to minutes.
Entry Timing
Optimal entry timing in swing trading involves identifying medium-term trend reversals over days to weeks, whereas scalping requires precise, split-second entries to exploit minute price fluctuations within seconds to minutes.
Position Sizing
Position sizing in swing trading typically involves larger trade sizes held over several days to capitalize on medium-term price movements, emphasizing risk management through calculated stop losses and risk-to-reward ratios. Scalping, by contrast, requires smaller, precise position sizes executed frequently within minutes to exploit minor price fluctuations, necessitating strict control over leverage and tight stop losses to minimize exposure in volatile, short-term markets.
Technical Indicators
Technical indicators such as Moving Averages and MACD are commonly used for swing trading to identify longer-term trends, while scalping relies heavily on fast-paced indicators like the Relative Strength Index (RSI) and Bollinger Bands to capture quick price movements.
Risk-Reward Ratio
Swing trading offers a higher risk-reward ratio by capturing larger price movements over days or weeks, while scalping focuses on smaller, quicker gains with a lower risk-reward ratio due to rapid trade execution within minutes.
Market Volatility
Swing trading capitalizes on market volatility by holding positions for days to weeks to capture larger price swings, while scalping exploits minor price fluctuations within minutes for quick, small profits.
Holding Period
Swing trading typically involves holding positions for several days to weeks to capture medium-term price movements, while scalping focuses on holding trades for seconds to minutes to exploit small price fluctuations.
Intraday Signals
Intraday signals enhance swing trading by identifying short-term trends over hours to days, while scalping relies on ultra-short-term signals for rapid trades within seconds to minutes.
Stop-Loss Placement
Stop-loss placement in swing trading typically involves wider margins to accommodate larger price fluctuations, whereas scalping requires tighter stop-losses to quickly limit losses during rapid, short-term trades.
Trend Identification
Trend identification in swing trading focuses on capturing medium-term price movements over days or weeks, while scalping relies on recognizing short-term micro-trends within minutes to execute rapid, high-frequency trades.
Swing Trading vs Scalping Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com