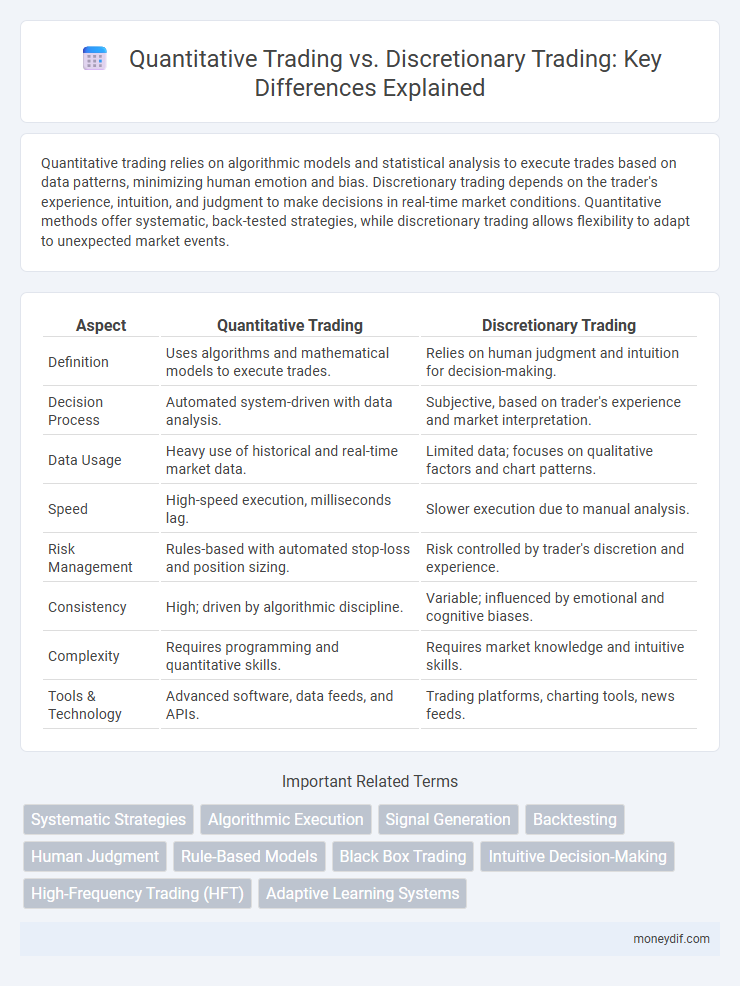
Quantitative trading relies on algorithmic models and statistical analysis to execute trades based on data patterns, minimizing human emotion and bias. Discretionary trading depends on the trader's experience, intuition, and judgment to make decisions in real-time market conditions. Quantitative methods offer systematic, back-tested strategies, while discretionary trading allows flexibility to adapt to unexpected market events.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Quantitative Trading | Discretionary Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Uses algorithms and mathematical models to execute trades. | Relies on human judgment and intuition for decision-making. |
| Decision Process | Automated system-driven with data analysis. | Subjective, based on trader's experience and market interpretation. |
| Data Usage | Heavy use of historical and real-time market data. | Limited data; focuses on qualitative factors and chart patterns. |
| Speed | High-speed execution, milliseconds lag. | Slower execution due to manual analysis. |
| Risk Management | Rules-based with automated stop-loss and position sizing. | Risk controlled by trader's discretion and experience. |
| Consistency | High; driven by algorithmic discipline. | Variable; influenced by emotional and cognitive biases. |
| Complexity | Requires programming and quantitative skills. | Requires market knowledge and intuitive skills. |
| Tools & Technology | Advanced software, data feeds, and APIs. | Trading platforms, charting tools, news feeds. |
Understanding Quantitative Trading
Quantitative trading leverages mathematical models and algorithms to execute trades based on statistical analysis and historical data patterns, minimizing human bias. It utilizes high-frequency data and automated systems to identify market inefficiencies and optimize portfolio performance. Advanced techniques such as machine learning and algorithmic execution are central to enhancing decision-making precision and risk management in quantitative trading strategies.
What Is Discretionary Trading?
Discretionary trading involves making buy or sell decisions based on a trader's judgment, intuition, and experience rather than solely relying on predefined algorithms or automated models. This approach allows traders to interpret market conditions, news, and patterns in real-time, offering flexibility to adapt strategies dynamically. Unlike quantitative trading, discretionary trading emphasizes human decision-making in risk assessment and trade execution.
Key Differences Between Quantitative and Discretionary Approaches
Quantitative trading relies on algorithmic models and statistical analysis to execute trades based on historical data patterns, minimizing emotional bias and ensuring consistency. Discretionary trading depends on human judgment, intuition, and real-time analysis, allowing flexibility to adapt to unforeseen market events but introducing subjectivity. The key difference lies in quantitative trading's systematic, data-driven approach versus discretionary trading's reliance on trader expertise and decision-making under uncertainty.
Advantages of Quantitative Trading
Quantitative trading leverages advanced algorithms and big data analytics to execute trades with precision, minimizing human error and emotional biases. This approach enables high-frequency trading and rapid market response that discretionary trading cannot match. Furthermore, quantitative models allow for backtesting strategies using historical data, enhancing risk management and optimizing profitability.
Benefits of Discretionary Trading
Discretionary trading benefits from trader intuition and experience, allowing adaptive decision-making based on market conditions that algorithms may not fully capture. It offers flexibility to respond to unexpected events and incorporates qualitative factors, such as news sentiment and geopolitical developments. Traders leveraging discretionary methods can exploit unique insights and nuanced interpretations absent in purely quantitative models.
Common Strategies Used in Quant vs. Discretionary Trading
Quantitative trading strategies often rely on algorithmic models such as statistical arbitrage, trend following, and mean reversion, leveraging vast datasets and computational power to exploit market inefficiencies. Discretionary trading strategies typically utilize technical analysis tools like chart patterns, support and resistance levels, and fundamental analysis to make subjective trading decisions based on market sentiment and macroeconomic factors. Both approaches aim to optimize profit but differ fundamentally in their reliance on systematic data-driven models versus human judgment and intuition.
Risk Management: Quantitative vs. Discretionary
Quantitative trading employs algorithmic models and statistical methods to systematically manage risk by setting predefined exit points and dynamically adjusting position sizes based on volatility metrics. Discretionary trading relies on the trader's subjective judgment and experience to assess risk, often incorporating qualitative factors like market sentiment and news events. Risk management in quantitative approaches benefits from consistency and scalability, while discretionary trading offers flexibility but may be prone to emotional biases.
Required Skills and Tools for Each Trading Style
Quantitative trading demands strong skills in mathematics, programming languages like Python or R, and expertise in statistical analysis to develop algorithmic strategies using data-driven models. Discretionary trading relies heavily on market intuition, technical analysis, and real-time decision-making, requiring proficiency in chart reading and psychological discipline. Essential tools for quantitative traders include backtesting platforms and algorithmic trading software, whereas discretionary traders primarily use advanced trading terminals and real-time news feeds.
How Technology Influences Trading Methods
Technology revolutionizes quantitative trading by enabling algorithmic strategies driven by big data, machine learning, and real-time analytics, vastly improving execution speed and accuracy. Discretionary trading benefits from advanced charting software, sentiment analysis tools, and mobile trading platforms that enhance decision-making flexibility and market responsiveness. The integration of AI and high-frequency trading platforms further intensifies the contrast, making technology a critical determinant in optimizing performance and managing risks across trading methods.
Choosing the Right Trading Approach for You
Quantitative trading relies on algorithmic models and statistical analysis to execute high-frequency trades with precision and reduced emotional bias, making it ideal for traders seeking systematic strategies and data-driven decisions. Discretionary trading depends on the trader's intuition, experience, and market analysis to make subjective decisions, offering flexibility and adaptability in unpredictable market conditions. Selecting the right approach depends on your risk tolerance, technical skills, and preference for rule-based versus adaptive trading methodologies.
Important Terms
Systematic Strategies
Systematic strategies in quantitative trading leverage algorithmic models and data-driven analysis to execute trades automatically, contrasting with discretionary trading that relies on human judgment and intuition.
Algorithmic Execution
Algorithmic execution enhances quantitative trading by automating trade decisions based on data-driven models, contrasting with discretionary trading that relies on human judgment and intuition.
Signal Generation
Signal generation in quantitative trading relies on algorithmic models and statistical analysis, whereas discretionary trading depends on human judgment and intuition for decision-making.
Backtesting
Backtesting quantitatively evaluates trading strategies using historical data to enhance algorithmic precision, whereas discretionary trading relies on trader judgment without systematic historical performance validation.
Human Judgment
Human judgment in quantitative trading focuses on algorithm design and data interpretation, while in discretionary trading it relies on experience-based decision-making and market intuition.
Rule-Based Models
Rule-based models in quantitative trading systematically execute trades using predefined algorithms, contrasting with discretionary trading which relies on trader judgment and subjective decision-making.
Black Box Trading
Black Box Trading relies on quantitative trading algorithms analyzing vast data sets for automated decision-making, contrasting with discretionary trading that depends on human judgment and intuition.
Intuitive Decision-Making
Intuitive decision-making in quantitative trading leverages algorithmic data analysis for consistent execution, while discretionary trading relies on human judgment to adapt strategies based on market intuition and experience.
High-Frequency Trading (HFT)
High-Frequency Trading (HFT) employs algorithmic, quantitative strategies using ultra-fast data processing to execute trades within milliseconds, contrasting with discretionary trading that relies on human judgment and slower decision-making processes.
Adaptive Learning Systems
Adaptive learning systems enhance quantitative trading by dynamically adjusting algorithms based on real-time market data, outperforming discretionary trading which relies heavily on human judgment and experience.
Quantitative Trading vs Discretionary Trading Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com