Swing trading capitalizes on price fluctuations over several days to weeks, allowing traders to benefit from medium-term market trends with less time commitment. Day trading involves executing multiple trades within a single day, aiming to profit from intraday price volatility while avoiding overnight market risks. Each strategy demands distinct risk tolerance, analytical approaches, and time management skills for optimal results.
Table of Comparison
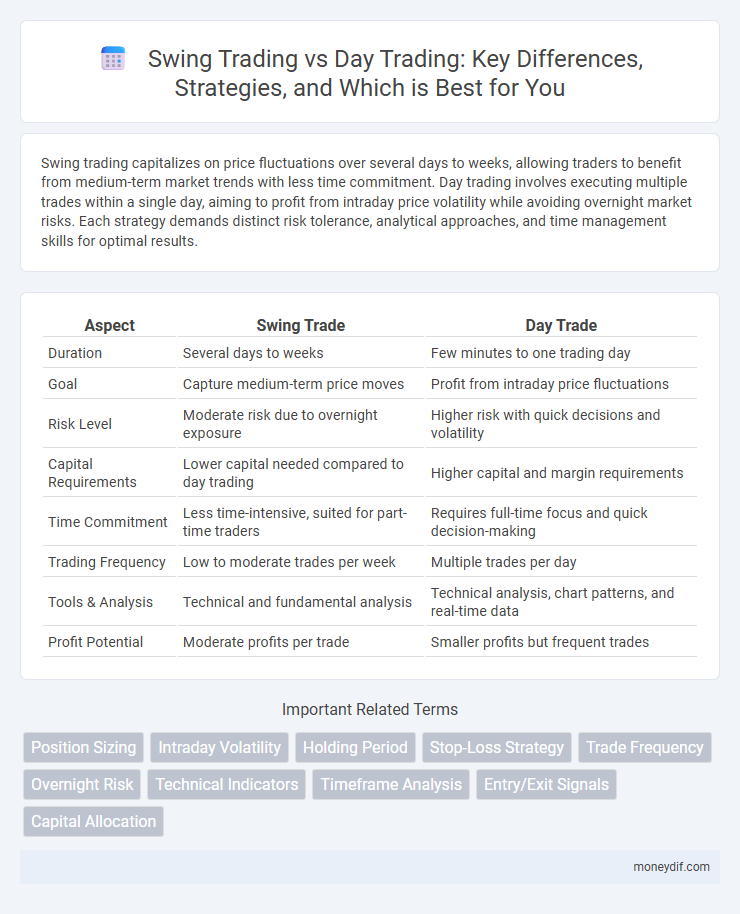
| Aspect | Swing Trade | Day Trade |
|---|---|---|
| Duration | Several days to weeks | Few minutes to one trading day |
| Goal | Capture medium-term price moves | Profit from intraday price fluctuations |
| Risk Level | Moderate risk due to overnight exposure | Higher risk with quick decisions and volatility |
| Capital Requirements | Lower capital needed compared to day trading | Higher capital and margin requirements |
| Time Commitment | Less time-intensive, suited for part-time traders | Requires full-time focus and quick decision-making |
| Trading Frequency | Low to moderate trades per week | Multiple trades per day |
| Tools & Analysis | Technical and fundamental analysis | Technical analysis, chart patterns, and real-time data |
| Profit Potential | Moderate profits per trade | Smaller profits but frequent trades |
Understanding Swing Trading and Day Trading
Swing trading capitalizes on short- to medium-term price movements, typically holding positions from several days to weeks, aiming to capture market momentum. Day trading involves executing multiple trades within a single trading day, closing all positions before market close to avoid overnight risk. Both strategies require technical analysis, but swing trading emphasizes trend identification while day trading focuses on intraday price volatility.
Key Differences Between Swing Trading and Day Trading
Swing trading involves holding positions for several days to weeks to capitalize on medium-term price movements, while day trading requires executing multiple trades within a single day to profit from intraday volatility. Swing traders rely heavily on technical analysis, trend patterns, and longer-term charts, whereas day traders focus on real-time data, high liquidity, and rapid order execution strategies. Risk management varies, with swing traders enduring overnight market risks and day traders avoiding overnight exposure to minimize gaps and sudden price swings.
Pros and Cons of Swing Trading
Swing trading offers the advantage of capturing larger price movements by holding positions for several days to weeks, allowing traders to benefit from medium-term trends without the need for constant monitoring. This strategy requires less time commitment compared to day trading, making it suitable for part-time traders or those balancing other responsibilities. However, swing trading exposes positions to overnight and weekend market risks, which can result in unexpected price gaps and increased volatility compared to intraday trades.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Day Trading
Day trading offers the advantage of potential for quick profits by capitalizing on intraday price volatility, enabling traders to avoid overnight market risks. However, it requires intense concentration, rapid decision-making, and access to real-time data and advanced trading platforms to succeed. The high transaction costs and emotional stress linked to frequent trades can lead to significant losses if not managed properly.
Risk Management in Swing Trading vs Day Trading
Swing trading involves holding positions for several days or weeks, exposing traders to overnight market risks and requiring robust stop-loss strategies to manage potential adverse price movements. Day trading, by contrast, closes positions within the same trading day, minimizing exposure to after-hours volatility but demanding quick decision-making and tighter risk controls to handle intraday price fluctuations. Effective risk management in swing trading emphasizes position sizing and trend analysis, while day trading focuses on real-time market monitoring and rapid execution.
Ideal Market Conditions for Swing and Day Trading
Swing trading thrives in moderately volatile markets with clear trend patterns, allowing traders to capitalize on price swings over several days to weeks. Day trading demands highly liquid markets with significant intraday volatility for rapid entry and exit within the same trading session. Optimal market conditions for swing trading include steady uptrends or downtrends, while day trading performs best during major economic announcements or market openings featuring sharp price movements.
Time Commitment: Swing Trading vs Day Trading
Swing trading requires a lower time commitment compared to day trading, as positions are held for several days to weeks, allowing traders to review markets outside regular hours. Day trading demands intense focus throughout the market session, with multiple trades executed within the same day, necessitating constant monitoring of price movements. Time commitment directly influences trader lifestyle and strategy choice between these two approaches.
Strategies Used in Swing Trading and Day Trading
Swing trading strategies primarily involve technical analysis using chart patterns, moving averages, and momentum indicators to capture short- to medium-term price swings over days or weeks. Day trading strategies emphasize real-time market data, leveraging intraday price action, volume analysis, and quick execution techniques like scalping and momentum trading to capitalize on minute-to-minute price fluctuations. Risk management tools such as stop-loss orders and position sizing are critical in both approaches but are tailored to the holding period and volatility specific to each trading style.
Profit Potential: Swing Trade vs Day Trade
Swing trading offers greater profit potential by capturing larger price movements over several days or weeks, benefiting from broader market trends. Day trading focuses on smaller, quick gains within a single trading session, limiting profit per trade but increasing trade frequency. Swing traders often capitalize on medium-term momentum, while day traders rely on intraday volatility to maximize returns.
Which Trading Style Suits You Best?
Swing trading suits traders who prefer holding positions for several days to weeks, capitalizing on medium-term price movements with less time commitment. Day trading fits those who thrive in fast-paced environments, executing multiple trades within a single day to exploit short-term volatility. Assessing your risk tolerance, available time, and market knowledge helps determine whether swing trading's patience or day trading's immediacy aligns best with your trading goals.
Important Terms
Position Sizing
Position sizing in swing trading typically involves larger trade sizes held over several days to weeks, leveraging medium-term price momentum and aiming to capture significant market moves. In contrast, day trading employs smaller, more conservative position sizes due to intraday volatility and the need for quick entry and exit, minimizing exposure to overnight risk.
Intraday Volatility
Intraday volatility significantly impacts both swing trading and day trading by influencing price fluctuations within the trading day; day traders rely on high intraday volatility to capitalize on short-term price movements, while swing traders focus on slightly longer time frames, using intraday volatility to identify optimal entry and exit points over several days. Understanding the patterns of intraday volatility helps traders manage risk and maximize profit potential by aligning strategies with market momentum and price swings.
Holding Period
Holding period for swing trades typically spans several days to weeks, allowing traders to capitalize on medium-term price movements and trends, whereas day trades involve holding positions for minutes to hours, focusing on intraday volatility and rapid market fluctuations. Understanding the difference in holding periods is crucial for selecting appropriate risk management strategies and optimizing trade execution in both swing trading and day trading.
Stop-Loss Strategy
The stop-loss strategy in swing trading is typically set wider, allowing for market fluctuations over several days, whereas day trading employs tighter stop-loss limits to minimize risk within intraday price movements. Effective stop-loss placement in swing trading often relies on technical support levels, while day traders focus on immediate price action and volatility to manage potential losses.
Trade Frequency
Trade frequency in swing trading typically involves holding positions for several days to weeks, resulting in fewer trades per month compared to day trading, which executes multiple trades daily to capitalize on short-term market fluctuations. Swing traders prioritize larger price movements and trend analysis, while day traders focus on intraday volatility and quick profit realization.
Overnight Risk
Overnight risk in swing trading involves exposure to market volatility and unexpected events during non-trading hours, which can lead to significant price gaps impacting positions held overnight, unlike day trading where positions are closed before market close to avoid such risks. Managing overnight risk requires strategic use of stop-loss orders and position sizing to mitigate potential losses from after-hours news or global market fluctuations.
Technical Indicators
Technical indicators such as Moving Averages, Relative Strength Index (RSI), and Bollinger Bands are essential for both swing trading and day trading, but their application varies; swing traders rely on longer timeframes like daily or weekly charts to capture medium-term trends, while day traders focus on shorter intervals like 1-minute to 15-minute charts for rapid decision-making. The Average True Range (ATR) helps swing traders set stop-loss levels based on volatility, whereas day traders use volume indicators to gauge intraday momentum and liquidity.
Timeframe Analysis
Timeframe analysis in swing trading typically focuses on daily and weekly charts to identify medium-term price trends and key support or resistance levels, optimizing entry and exit points over several days to weeks. In contrast, day trading relies heavily on intraday timeframes such as 1-minute to 15-minute charts, emphasizing rapid price movements and liquidity to capitalize on short-term volatility within a single trading session.
Entry/Exit Signals
Entry and exit signals in swing trading rely heavily on technical indicators such as moving averages, RSI, and MACD to capitalize on medium-term price trends, whereas day trading focuses on real-time momentum indicators and volume spikes for rapid entries and exits within the same trading session. Swing traders emphasize chart patterns and trend reversals over several days, while day traders prioritize high-frequency signals like scalp trades and intraday support/resistance levels to optimize trade timing and minimize overnight risk.
Capital Allocation
Capital allocation in swing trading often involves committing larger positions over several days to capture medium-term price movements, optimizing risk-reward by leveraging technical indicators and fundamental analysis. Day trading requires allocating smaller, highly liquid capital portions to execute multiple rapid trades within the same day, emphasizing quick decision-making and minimizing overnight exposure to market volatility.
Swing Trade vs Day Trade Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com