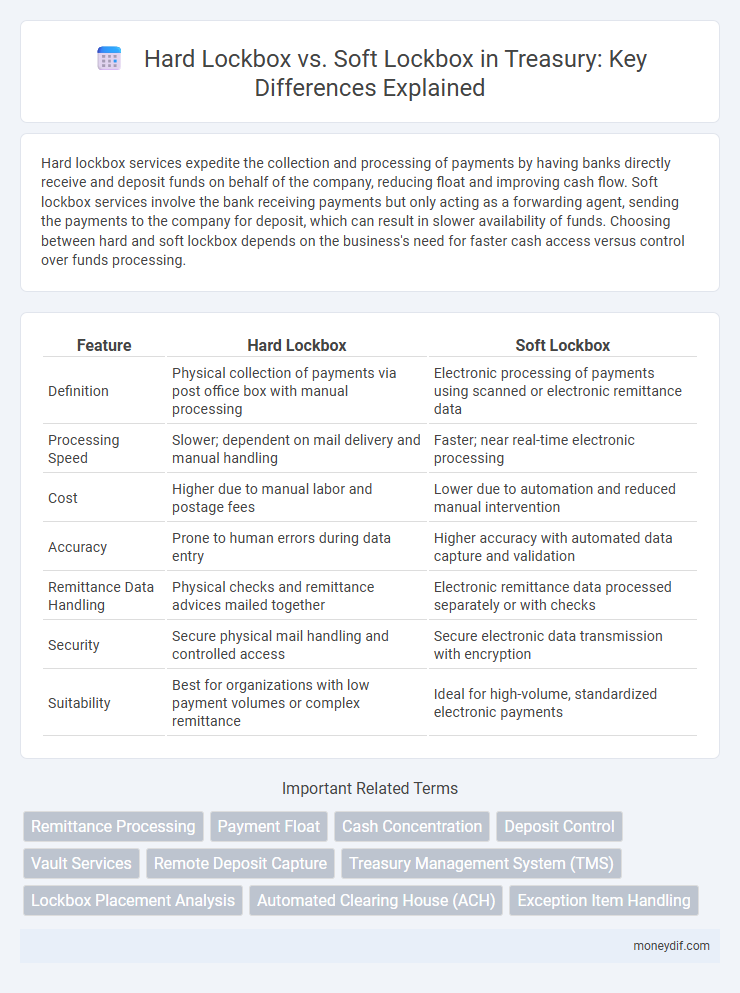
Hard lockbox services expedite the collection and processing of payments by having banks directly receive and deposit funds on behalf of the company, reducing float and improving cash flow. Soft lockbox services involve the bank receiving payments but only acting as a forwarding agent, sending the payments to the company for deposit, which can result in slower availability of funds. Choosing between hard and soft lockbox depends on the business's need for faster cash access versus control over funds processing.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hard Lockbox | Soft Lockbox |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Physical collection of payments via post office box with manual processing | Electronic processing of payments using scanned or electronic remittance data |
| Processing Speed | Slower; dependent on mail delivery and manual handling | Faster; near real-time electronic processing |
| Cost | Higher due to manual labor and postage fees | Lower due to automation and reduced manual intervention |
| Accuracy | Prone to human errors during data entry | Higher accuracy with automated data capture and validation |
| Remittance Data Handling | Physical checks and remittance advices mailed together | Electronic remittance data processed separately or with checks |
| Security | Secure physical mail handling and controlled access | Secure electronic data transmission with encryption |
| Suitability | Best for organizations with low payment volumes or complex remittance | Ideal for high-volume, standardized electronic payments |
Introduction to Lockbox Services in Treasury
Lockbox services streamline the collection and processing of payments, improving cash flow management and reducing administrative costs in treasury operations. Hard lockbox involves payments being sent directly to a bank-operated post office box for immediate processing, enhancing speed and efficiency. Soft lockbox processes payments initially at the company's location before forwarding them to the bank, providing greater control but slower processing times.
Defining Hard Lockbox: Features and Functionality
A Hard Lockbox is a treasury management tool where payments are sent directly to a secure post office box monitored by a bank, which promptly processes and deposits funds on behalf of the company. Key features include enhanced payment security, accelerated cash application, and reduced risk of fraud through limited company access to incoming payments. Functionality centers on the bank's exclusive control over check handling, enabling faster clearing times and improved cash flow management.
Understanding Soft Lockbox: Key Characteristics
Soft Lockbox services primarily handle remittance processing by electronically receiving and depositing payments, which accelerates cash application and reduces manual data entry errors. These systems integrate seamlessly with a company's existing accounting software, providing enhanced visibility and control over receivables management. By automating the collection and recording of payment information, Soft Lockbox improves cash flow forecasting and streamlines reconciliation processes.
Speed and Efficiency: Hard vs Soft Lockbox Comparison
Hard lockboxes provide faster processing by receiving and depositing payments directly through the postal service, reducing manual handling time. Soft lockboxes involve an intermediary who opens and processes payments before sending them to the bank, resulting in slower deposit timelines. Efficiency in cash flow management improves significantly with hard lockboxes due to accelerated clearance and reduced float times.
Security Measures: Safeguarding Funds in Lockbox Solutions
Hard lockbox solutions provide enhanced security measures by utilizing physical addresses controlled by banks to receive payments, reducing the risk of fraud through direct handling and immediate deposit processing. Soft lockbox systems rely on digital workflows and electronic payment processing, incorporating encryption and secure portals to protect sensitive data and ensure transaction integrity. Both methods emphasize safeguarding funds, but hard lockboxes prioritize physical security while soft lockboxes focus on cybersecurity protocols to mitigate financial risks.
Cost Analysis: Evaluating Hard and Soft Lockbox Expenses
Hard lockboxes typically incur higher costs due to physical deposit processing, including transportation, security, and manual handling fees, while soft lockboxes reduce expenses by leveraging electronic remittance processing and automated deposit systems. Evaluating operational costs reveals that soft lockbox solutions offer significant savings in labor and courier services, with lower overhead for transaction processing and faster funds availability. Treasury departments benefit from cost efficiency and improved cash flow management by analyzing expense components tied to lockbox types and choosing solutions that optimize overall treasury operations.
Integration with Treasury Management Systems
Hard Lockbox services provide direct integration with Treasury Management Systems (TMS) by automating deposit data capture, accelerating cash application, and reducing manual input errors. Soft Lockbox solutions, while improving remittance processing efficiency, typically require additional data transformation steps before syncing with TMS, potentially delaying real-time cash position visibility. Optimizing lockbox integration streamlines cash flow forecasting and enhances overall treasury operations accuracy.
Suitability for Different Business Sizes and Industries
Hard lockbox services suit large enterprises with high volume receivables due to their physical processing of payments at a bank's secure facility, optimizing cash flow and reducing processing time. Soft lockbox solutions cater to small and medium-sized businesses and varied industries by leveraging electronic receipt capture and remote processing, offering flexibility and cost savings. Industries with complex payment remittance requirements often prefer hard lockboxes for enhanced security, while those seeking efficiency and lower operational costs lean towards soft lockbox systems.
Decision Factors: When to Choose Hard or Soft Lockbox
Hard lockboxes are ideal for businesses requiring faster cash availability and stringent payment processing controls, especially when handling large volumes of paper checks from diverse geographic locations. Soft lockboxes suit companies emphasizing cost efficiency with minimal handling of physical payments, leveraging electronic check conversion and faster electronic processing. Decision factors include transaction volume, urgency of funds availability, geographic spread of payers, and the level of control needed over the payment process.
Future Trends in Lockbox Solutions for Treasury
Future trends in lockbox solutions for treasury emphasize increased automation and cloud-based platforms to enhance processing speed and data accuracy. Integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning enables predictive analytics for cash flow forecasting and fraud detection, significantly improving treasury decision-making. Adoption of real-time payment processing and blockchain technology is expected to further streamline reconciliations and strengthen security in lockbox operations.
Important Terms
Remittance Processing
Hard lockbox remittance processing involves physical handling of payments by the bank, speeding funds availability, while soft lockbox uses electronic data capture, reducing manual processing errors and improving reconciliation efficiency.
Payment Float
Payment float is reduced by using a Hard Lockbox because it directly deposits payments into the account, whereas a Soft Lockbox involves additional processing steps that delay funds availability.
Cash Concentration
Cash concentration improves liquidity management by pooling funds from multiple accounts into a central account, with Hard Lockbox providing faster access to funds through direct bank control and Soft Lockbox offering quicker processing flexibility via electronic remittance. Hard Lockbox solutions typically reduce float time by handling payments directly at the bank, while Soft Lockbox systems enhance reconciliation and reporting through advanced data capture technologies.
Deposit Control
Deposit Control enhances cash flow accuracy by utilizing Hard Lockbox for physical check processing and Soft Lockbox for electronic payment management.
Vault Services
Vault services ensure secure storage and management of valuable assets and documents, with Hard Lockboxes providing physical security through tamper-resistant steel containers, while Soft Lockboxes leverage digital encryption and cloud-based platforms for secure electronic access and transaction handling. Businesses often choose Hard Lockboxes for high-security cash handling and legal documents, whereas Soft Lockboxes are preferred for efficient payment processing and streamlined receivables management.
Remote Deposit Capture
Remote Deposit Capture enhances business efficiency by enabling the electronic scanning and transmission of checks, eliminating the physical handling associated with Hard Lockbox, which requires manual processing of mailed payments. Soft Lockbox streamlines collections by outsourcing lockbox services to financial institutions that provide digital check imaging and clearing, offering faster funds availability compared to traditional Hard Lockbox systems.
Treasury Management System (TMS)
A Treasury Management System (TMS) enhances cash flow efficiency by integrating payment processing methods such as Hard Lockbox and Soft Lockbox services, where Hard Lockbox involves physical check handling by a bank and Soft Lockbox digitizes check images for faster electronic processing. Implementing these lockbox solutions within a TMS improves accounts receivable management, reduces processing time, and accelerates fund availability for optimized liquidity management.
Lockbox Placement Analysis
Lockbox Placement Analysis evaluates the efficiency and security differences between Hard Lockboxes, which require physical key access, and Soft Lockboxes, which use digital authorization for streamlined payment processing.
Automated Clearing House (ACH)
Automated Clearing House (ACH) transactions streamline payments directly between bank accounts, offering faster processing and reduced handling costs compared to traditional Hard Lockbox services, which physically process mailed checks. Soft Lockbox services leverage electronic capture and ACH payments to accelerate deposit posting and improve cash flow efficiency by minimizing manual intervention.
Exception Item Handling
Exception item handling in Hard Lockbox involves physical mail retrieval and manual processing, whereas Soft Lockbox uses electronic data capture and automated exception resolution for faster transaction efficiency.
Hard Lockbox vs Soft Lockbox Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com