Synergistic value represents the enhanced worth created when two companies combine, leveraging complementary strengths to generate greater cash flows and efficiencies than operating independently. Standalone value reflects the individual company's intrinsic valuation based on its own operational performance and assets without considering potential partnerships. Understanding the difference is crucial for investors assessing mergers and acquisitions, as synergistic benefits often justify premium offers above standalone valuations.
Table of Comparison
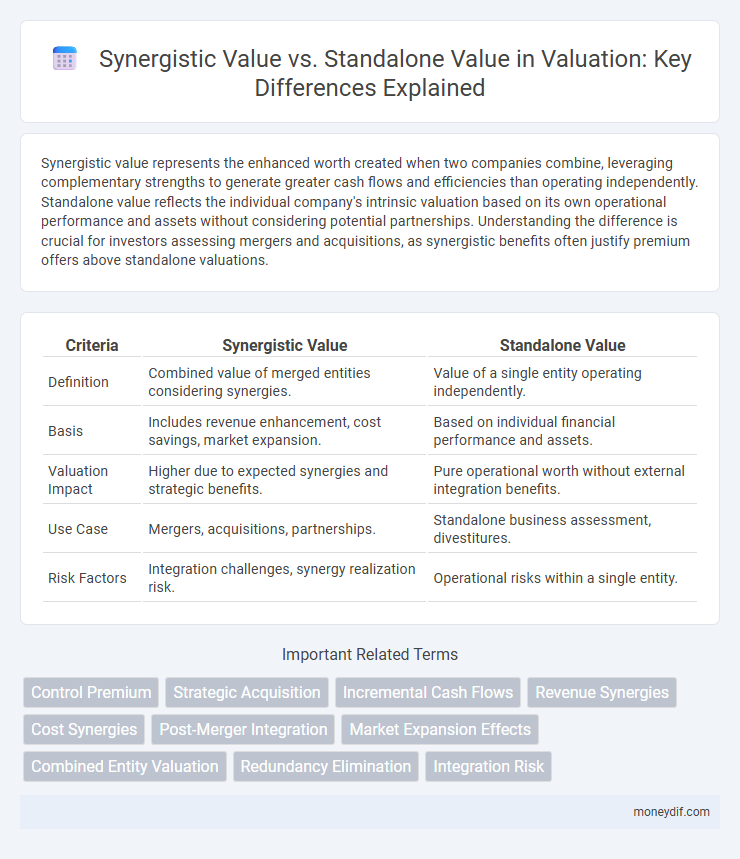
| Criteria | Synergistic Value | Standalone Value |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combined value of merged entities considering synergies. | Value of a single entity operating independently. |
| Basis | Includes revenue enhancement, cost savings, market expansion. | Based on individual financial performance and assets. |
| Valuation Impact | Higher due to expected synergies and strategic benefits. | Pure operational worth without external integration benefits. |
| Use Case | Mergers, acquisitions, partnerships. | Standalone business assessment, divestitures. |
| Risk Factors | Integration challenges, synergy realization risk. | Operational risks within a single entity. |
Understanding Synergistic Value in Valuation
Synergistic value in valuation reflects the enhanced worth generated when combining two entities, exceeding the sum of their standalone values due to operational efficiencies, market expansion, or cost reductions. This value considers strategic fit, overlapping resources, and incremental cash flows that arise uniquely from the merger or acquisition synergy. Thorough analysis of synergies, including revenue enhancements and expense savings, is essential for accurate valuation and informed investment decisions.
Defining Standalone Value: A Baseline Perspective
Standalone value represents the intrinsic worth of a business or asset operating independently without influence from mergers or acquisitions. It serves as a baseline metric, reflecting fundamental cash flows, risk profiles, and growth projections based solely on internal operations. Accurate assessment of standalone value is critical for benchmarking synergistic gains and guiding strategic investment decisions.
Key Differences Between Synergistic and Standalone Values
Synergistic value represents the combined worth that exceeds the sum of individual entities due to integration benefits, such as cost savings and enhanced market reach, while standalone value reflects the intrinsic value of a single entity operating independently. Key differences include the influence of potential synergies on future cash flows, risk profiles, and strategic advantages inherent in synergistic value but absent in standalone valuation. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for accurate merger and acquisition analysis, as synergistic value often drives premium offers above standalone valuations.
Factors Influencing Synergistic Value Creation
Synergistic value creation is influenced by factors such as the degree of operational integration, potential cost savings, and the ability to leverage complementary assets or markets. The extent of managerial expertise and innovation capacity also plays a critical role in realizing synergies beyond standalone value. Market conditions and regulatory environments further impact the successful extraction of synergistic value in mergers or acquisitions.
Methods for Quantifying Standalone Value
Methods for quantifying standalone value primarily include discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis, which projects the expected free cash flows of an asset or business independently and discounts them to present value using an appropriate cost of capital. Comparable company analysis (CCA) involves benchmarking financial metrics such as EBITDA multiples against similar firms operating autonomously. Asset-based valuation calculates the net asset value by summing the fair market values of individual assets minus liabilities, providing a fundamental measure of standalone worth.
Practical Approaches to Synergy Assessment
Practical approaches to synergy assessment involve quantifying incremental cash flows generated from combining business units beyond their standalone values. Methods include discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis adjusted for integration costs, scenario modeling to estimate revenue enhancements and cost savings, and benchmarking against comparable transactions to validate synergy assumptions. Accurate synergy valuation requires rigorous due diligence, incorporating operational, financial, and market data to isolate true incremental benefits.
Real-World Examples of Synergistic Value in M&A
Synergistic value in M&A arises when combined companies generate greater value than their standalone worth, exemplified by Disney's acquisition of Pixar, which enhanced creative capabilities and expanded market share. The merger between Exxon and Mobil created substantial operational efficiencies and cost savings, reflecting the synergistic premium beyond their individual valuations. Real-world deals often realize synergies through cost reductions, revenue enhancements, and improved market positioning, driving acquirers to pay a premium over standalone values.
Risks and Challenges in Realizing Synergies
Synergistic value often faces significant risks such as integration challenges, cultural clashes, and overestimated cost savings, which can prevent the realization of projected benefits. Standalone value may be more stable as it relies on the company's existing operations without the complexity of merging systems or processes. Overcoming execution risk and aligning management teams are critical steps to unlock true synergistic potential in valuation scenarios.
Impact of Synergistic Value on Deal Pricing
Synergistic value significantly influences deal pricing by reflecting the additional worth generated through the combination of merging entities, surpassing the standalone value of each company. This premium captures efficiencies, market expansion, and cost savings realized post-acquisition, driving higher bid prices. Accurately quantifying synergistic value is critical for investors to justify deal premiums and avoid overpaying during mergers and acquisitions.
Best Practices for Integrating Synergies into Valuation Models
Incorporating synergistic value into valuation models requires a rigorous identification and quantification of revenue enhancements and cost reductions attributable to post-transaction integration. Analysts should employ scenario analysis and sensitivity testing to capture the range of potential synergy realizations and adjust discount rates to reflect integration risks accurately. Transparent documentation of assumptions and alignment with operational metrics ensures that synergistic value is credibly integrated alongside standalone business valuations.
Important Terms
Control Premium
Control premium represents the additional value a buyer is willing to pay for acquiring control over a company, reflecting the synergistic value over its standalone value.
Strategic Acquisition
Strategic acquisition focuses on identifying targets whose combined synergistic value exceeds their standalone value, resulting in enhanced competitive advantage and increased shareholder returns. The integration process leverages complementary resources, cost efficiencies, and expanded market reach to unlock greater value than operating independently.
Incremental Cash Flows
Incremental cash flows measure the additional cash generated by a project or acquisition, capturing synergistic value beyond the standalone value of individual business units.
Revenue Synergies
Revenue synergies arise when combined business entities generate higher sales than the sum of their standalone revenues due to cross-selling, expanded market reach, or enhanced product offerings. Synergistic value reflects this incremental revenue growth potential, exceeding the combined standalone value of each company operating independently.
Cost Synergies
Cost synergies increase synergistic value by reducing combined operational expenses below the sum of standalone values, enhancing overall acquisition profitability.
Post-Merger Integration
Post-Merger Integration maximizes synergistic value by combining resources, capabilities, and operations to create greater efficiency and enhanced market competitiveness than the sum of the standalone values of the merging companies. Achieving effective integration involves aligning business processes, cultures, and strategic goals to unlock cost savings, revenue growth, and innovation potential that standalone entities cannot realize independently.
Market Expansion Effects
Market expansion enhances synergistic value by leveraging combined assets and resources, resulting in greater overall returns compared to standalone value generated by individual business units.
Combined Entity Valuation
Combined entity valuation measures the total worth of merged businesses by integrating synergistic value, which reflects enhanced cash flows and cost savings, versus standalone value, the sum of individual entities' valuations without synergies. Synergistic value quantifies benefits from operational efficiencies, market expansion, and risk diversification that increase the combined firm's financial performance beyond the simple aggregation of standalone values.
Redundancy Elimination
Redundancy elimination enhances synergistic value by removing overlapping resources and functions that reduce inefficiencies within combined operations, leading to greater overall performance than the sum of standalone values. This process uncovers hidden cost savings and operational improvements that are unattainable when entities operate independently.
Integration Risk
Integration risk significantly impacts the realization of synergistic value in mergers and acquisitions, as failure to effectively combine operations, cultures, and systems can erode expected benefits and reduce total value below the combined standalone values of the entities. Quantifying integration risk involves assessing potential disruptions, costs, and delays that diminish synergies, highlighting the critical need for detailed integration planning to preserve or enhance value beyond the sum of standalone valuations.
Synergistic Value vs Standalone Value Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com