Replacement cost measures the expense to construct a modern equivalent of a property using current materials and standards, while reproduction cost calculates the price to create an exact duplicate using original materials and techniques. Replacement cost often proves more practical for insurance purposes due to its focus on functional equivalence rather than historical accuracy. Understanding the distinction between these two valuation methods is essential for accurate property assessment and financial planning.
Table of Comparison
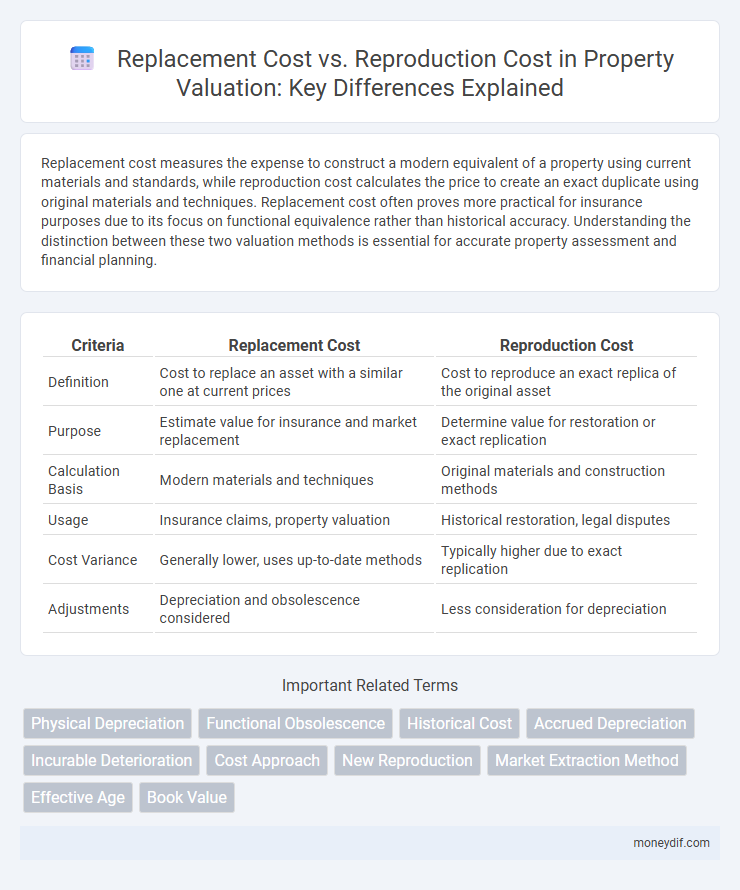
| Criteria | Replacement Cost | Reproduction Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cost to replace an asset with a similar one at current prices | Cost to reproduce an exact replica of the original asset |
| Purpose | Estimate value for insurance and market replacement | Determine value for restoration or exact replication |
| Calculation Basis | Modern materials and techniques | Original materials and construction methods |
| Usage | Insurance claims, property valuation | Historical restoration, legal disputes |
| Cost Variance | Generally lower, uses up-to-date methods | Typically higher due to exact replication |
| Adjustments | Depreciation and obsolescence considered | Less consideration for depreciation |
Understanding Replacement Cost and Reproduction Cost
Replacement cost refers to the expense of constructing a modern equivalent of a property using current materials and standards, excluding depreciation. Reproduction cost involves estimating the price to create an exact duplicate of the original property, including identical materials and craftsmanship. Understanding these distinctions is critical for accurate property valuation and insurance claims.
Key Definitions: Replacement Cost vs. Reproduction Cost
Replacement cost refers to the expense required to construct a property with similar functionality and utility using modern materials and techniques, while reproduction cost involves the expense to create an exact duplicate of the original property with the same materials and craftsmanship. Replacement cost emphasizes current building standards and efficiency, often resulting in lower costs compared to reproduction cost, which demands meticulous replication of architectural features and finishes. Understanding the distinction between replacement cost and reproduction cost is essential for accurate property valuation and insurance appraisals.
Importance in Property Valuation
Replacement cost reflects the current expense to construct a property with equivalent utility using modern materials and standards, making it crucial for insurance valuations and depreciation assessments. Reproduction cost measures the expense to replicate the exact original structure with identical materials and craftsmanship, essential for historic property appraisals. Understanding the distinction ensures accurate property valuation by aligning the valuation method with the property's purpose and condition.
Factors Affecting Replacement Cost
Replacement cost is influenced by factors such as current material prices, labor rates, and technological advancements in construction methods. Geographic location and availability of skilled labor also significantly impact the replacement cost, as remote areas often incur higher expenses. Market demand fluctuations and regulatory changes, including building codes and zoning laws, further affect the overall replacement cost calculations.
Factors Influencing Reproduction Cost
Reproduction cost is influenced by factors such as the availability of original materials, labor intensity, and adherence to historical building techniques. Regulatory requirements, including building codes and preservation standards, also significantly affect reproduction expenses. Market conditions and technological advancements further impact the overall valuation of reproduction cost in property appraisal.
Differences Between Replacement and Reproduction Costs
Replacement cost refers to the expense required to construct a building with equivalent utility using modern materials and standards, whereas reproduction cost is the price to duplicate an exact replica of the original structure, including outdated materials and craftsmanship. Replacement cost prioritizes functionality and current building codes, while reproduction cost emphasizes historical accuracy and authenticity. These differences significantly impact valuation methodologies, especially in insurance and historic property assessments.
Practical Scenarios for Each Cost Approach
Replacement cost offers a practical valuation method in scenarios where modern materials or construction techniques improve functionality or reduce expenses, such as upgrading an older home's roofing with more durable synthetic materials. Reproduction cost is essential for historic property appraisals requiring exact replication of original design, materials, and workmanship to preserve authenticity and heritage value. Insurance claims often prioritize replacement cost to expedite repairs and minimize downtime, while museum restorations rely on reproduction cost for accuracy in artifact preservation.
Pros and Cons of Replacement Cost Method
Replacement cost method offers a practical and cost-effective valuation by estimating the expense to replace an asset with a modern equivalent, reflecting current market prices and technology. It avoids the often higher expenses and regulatory challenges of exact duplication required in reproduction cost, but may undervalue historical or unique features that contribute to an asset's original character. While replacement cost provides flexibility and relevance in insurance and financial reporting, its reliance on current standards can lead to discrepancies in asset depreciation and market value assessments.
Pros and Cons of Reproduction Cost Method
The Reproduction Cost method assesses property value based on the expense to construct an exact replica using the same materials and techniques, ensuring historical accuracy for unique or heritage assets. This approach provides high precision in valuation but often results in higher costs due to obsolete materials, craftsmanship, and compliance with outdated construction standards. Limitations include the potential for overvaluation compared to market conditions and longer construction timelines that impact overall feasibility.
Choosing the Right Approach for Accurate Valuation
Replacement cost measures the expense to construct a similar property using modern materials and standards, while reproduction cost calculates the price to duplicate the exact original structure with identical materials and workmanship. Selecting the appropriate approach depends on the purpose of valuation, property type, and age, with replacement cost favored for functional equivalence and reproduction cost applicable for historic or unique properties. Accurate valuation hinges on aligning the cost method with investor goals, insurer requirements, and market conditions to reflect true economic value.
Important Terms
Physical Depreciation
Physical depreciation reduces asset value by reflecting wear and tear, influencing replacement cost assessments differently than reproduction cost, which estimates exact duplication expenses.
Functional Obsolescence
Functional obsolescence reduces replacement cost compared to reproduction cost by accounting for outdated features or design inefficiencies in property valuation.
Historical Cost
Historical cost records the original purchase price of an asset, providing a reliable and objective basis for financial reporting. Replacement cost measures the expense to replace an asset with a similar one at current market prices, while reproduction cost estimates the cost to recreate an exact duplicate of the original asset, often resulting in higher valuation due to unique or obsolete features.
Accrued Depreciation
Accrued depreciation measures the loss in value of an asset based on replacement cost, reflecting wear and obsolescence, rather than reproduction cost, which calculates the value to duplicate the asset exactly.
Incurable Deterioration
Incurable deterioration significantly impacts replacement cost valuation as it reflects the expense to replace an asset with a similar utility, whereas reproduction cost assesses the cost to create an exact duplicate including outdated or obsolete features.
Cost Approach
Cost Approach evaluates property value by comparing Replacement Cost, which estimates expenses to construct a similar utility building with modern materials, against Reproduction Cost, which estimates expenses to create an exact duplicate using original materials and methods.
New Reproduction
New reproduction cost estimates the the expense to build an exact replica of an asset using current materials and standards, while replacement cost calculates the expense to replace the asset with one of similar utility but not necessarily identical specifications.
Market Extraction Method
The Market Extraction Method estimates replacement cost by analyzing comparable market prices, offering a practical alternative to the theoretical calculation of reproduction cost based on duplicating an asset's exact original specifications.
Effective Age
Effective age measures a building's condition relative to its chronological age, reflecting wear and improvements, directly impacting both replacement cost and reproduction cost assessments; replacement cost focuses on modern materials and standards while reproduction cost considers exact historical duplication. Properly accounting for effective age ensures more accurate valuation by adjusting replacement and reproduction costs to realistic depreciation and functional obsolescence levels.
Book Value
Book value represents an asset's net worth on the balance sheet, differing from replacement cost, which is the expense to substitute an asset with a similar one at current prices, and reproduction cost, the expense to replicate an exact asset including its original features and depreciation.
Replacement Cost vs Reproduction Cost Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com