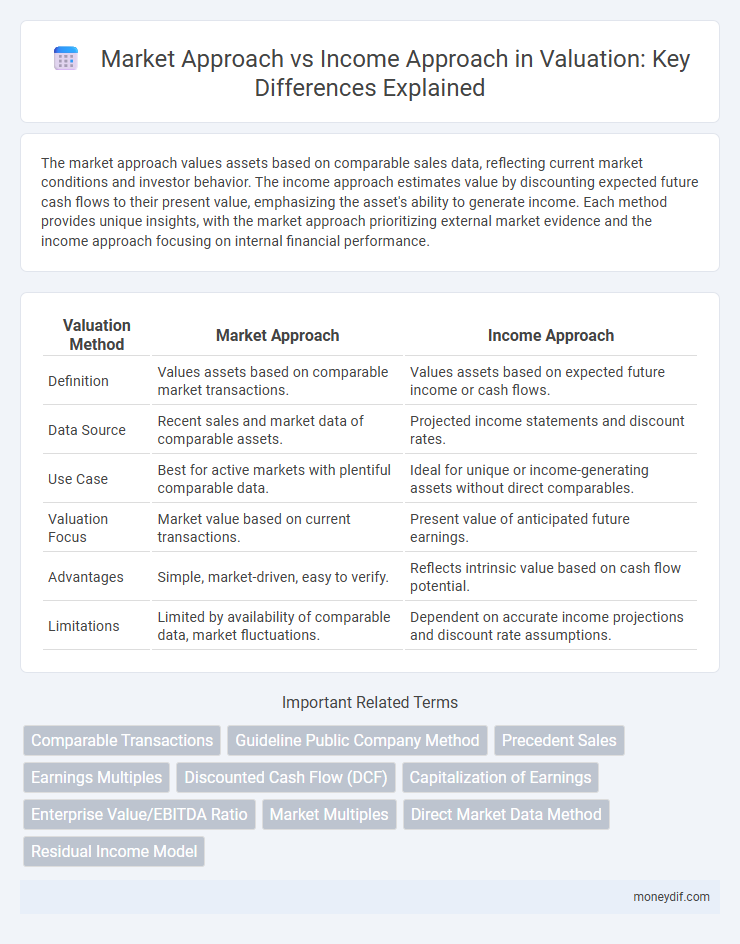
The market approach values assets based on comparable sales data, reflecting current market conditions and investor behavior. The income approach estimates value by discounting expected future cash flows to their present value, emphasizing the asset's ability to generate income. Each method provides unique insights, with the market approach prioritizing external market evidence and the income approach focusing on internal financial performance.
Table of Comparison
| Valuation Method | Market Approach | Income Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Values assets based on comparable market transactions. | Values assets based on expected future income or cash flows. |
| Data Source | Recent sales and market data of comparable assets. | Projected income statements and discount rates. |
| Use Case | Best for active markets with plentiful comparable data. | Ideal for unique or income-generating assets without direct comparables. |
| Valuation Focus | Market value based on current transactions. | Present value of anticipated future earnings. |
| Advantages | Simple, market-driven, easy to verify. | Reflects intrinsic value based on cash flow potential. |
| Limitations | Limited by availability of comparable data, market fluctuations. | Dependent on accurate income projections and discount rate assumptions. |
Understanding the Market Approach in Valuation
The Market Approach in valuation relies on analyzing comparable transactions of similar assets to determine value, emphasizing real-time market data and trends. This method considers factors such as recent sales prices, market demand, and asset condition to establish a fair market value. It is particularly effective in industries with abundant transactional data, providing a straightforward reflection of current market perceptions.
Key Principles of the Income Approach
The Income Approach to valuation centers on the principle that a property's value is directly related to the income it generates, emphasizing future cash flow projections and discounting them to present value through capitalization or discount rates. This approach assumes that an informed investor will pay no more than the property's anticipated income stream, reflecting risk and market conditions. Key valuation metrics include Net Operating Income (NOI), capitalization rate (cap rate), and discount rate, which collectively quantify income potential and investment return expectations.
Core Differences Between Market and Income Approaches
The market approach determines value based on comparing comparable asset sales, emphasizing actual transaction data and market trends, which reflects current market conditions. The income approach calculates value by discounting expected future cash flows, relying on projected income and capitalization rates, focusing on the asset's ability to generate revenue. Core differences lie in the market approach's reliance on external evidences versus the income approach's dependence on internal financial projections and assumptions.
Advantages of the Market Approach
The Market Approach provides a clear advantage by using actual transaction data to determine an asset's value, ensuring relevance and reliability based on comparable sales. It reflects current market conditions, offering timely and easily understandable valuations for investors and stakeholders. This approach is particularly effective in liquid markets where abundant data enhances accuracy and reduces subjectivity compared to the Income Approach.
Limitations of the Income Approach
The Income Approach faces limitations including the challenge of accurately projecting future cash flows due to market volatility and economic uncertainty. It relies heavily on assumptions about discount rates and growth rates, which can introduce subjectivity and estimation errors. Unlike the Market Approach, it may not fully reflect current market conditions or comparable sales data, potentially leading to less reliable valuation outcomes.
When to Use the Market Approach in Valuation
The market approach in valuation is most effective when there is abundant data on comparable assets or businesses with similar characteristics, ensuring reliable benchmarking. It is preferred in industries with frequent transactions and transparent pricing, such as real estate or publicly traded securities. This method provides a straightforward estimate of fair market value by analyzing recent sales and market trends, making it ideal for valuing assets with active and efficient markets.
Suitability of the Income Approach for Different Asset Types
The income approach is particularly suitable for income-generating assets such as commercial real estate, rental properties, and businesses with stable cash flows, as it values assets based on their expected future earnings. This method is less effective for assets without predictable income streams, such as vacant land or unique properties where market comparables are limited. The market approach excels in these cases by relying on comparative sales data to determine value, highlighting the income approach's strengths in assessing assets driven by revenue generation.
Data Requirements: Market vs Income Approach
The market approach to valuation requires comprehensive data on recent comparable sales, including pricing, property characteristics, and market conditions to accurately estimate value. In contrast, the income approach demands detailed financial information such as rental income, operating expenses, vacancy rates, and capitalization rates to forecast future cash flows. The accuracy of each approach hinges on the availability and reliability of respective data sets tailored to market trends or income performance.
Real-World Examples: Market and Income Approaches Compared
The market approach estimates property value by analyzing recent sales of comparable assets, offering clear benchmarks in dynamic sectors like residential real estate. The income approach calculates value based on the present value of expected future cash flows, commonly applied in commercial properties such as office buildings and rental complexes. For instance, a retail center's worth might be determined through income capitalization, while a suburban home is more accurately valued using comparable sales data in the market approach.
Choosing the Right Valuation Method for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate valuation method depends on the asset type, data availability, and purpose of the valuation. The market approach leverages comparable sales and is ideal for assets with active market transactions, while the income approach focuses on future cash flow projections, making it suitable for income-generating assets or businesses. Evaluating liquidity, market conditions, and reliability of financial forecasts ensures alignment with your valuation objectives and enhances decision-making accuracy.
Important Terms
Comparable Transactions
Comparable transactions analysis utilizes market approach data by examining similar asset sales, while income approach relies on projected cash flows and earnings to estimate value.
Guideline Public Company Method
The Guideline Public Company Method estimates business value by comparing market multiples of publicly traded peer companies, aligning with the market approach rather than the income approach's discounted cash flow analysis.
Precedent Sales
Precedent sales analysis uses comparable market transactions to estimate property value, emphasizing the market approach's reliance on actual sales data over the income approach's focus on projected cash flows.
Earnings Multiples
Earnings multiples in the market approach reflect comparable company valuations based on current market prices, whereas the income approach uses discounted future earnings projections to determine intrinsic value.
Discounted Cash Flow (DCF)
Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) analysis, an income approach, values a company by estimating future cash flows and discounting them to present value using a risk-adjusted rate, reflecting intrinsic business performance. In contrast, the market approach derives value from comparable company transactions or market multiples, focusing on external market data rather than the company's projected income streams.
Capitalization of Earnings
Capitalization of earnings uses a market approach by applying a capitalization rate derived from comparable companies, whereas the income approach estimates value based on the present value of projected future earnings or cash flows.
Enterprise Value/EBITDA Ratio
The Enterprise Value/EBITDA ratio is a critical valuation metric that aligns with the market approach by reflecting comparable company multiples, while the income approach focuses on discounted future cash flows, making the EV/EBITDA ratio more relevant for market-based valuations.
Market Multiples
Market multiples provide comparative valuation metrics that enhance the market approach by reflecting real-time trading data, whereas the income approach relies on discounted future cash flows for intrinsic value estimation.
Direct Market Data Method
The Direct Market Data Method evaluates asset value by comparing recent sales of similar properties, emphasizing market approach accuracy over the income approach's focus on projected cash flows.
Residual Income Model
The Residual Income Model calculates a firm's intrinsic value by adding the book value of equity to the present value of future residual incomes, aligning closely with the income approach. Unlike the market approach, which relies on comparable market multiples, the Residual Income Model directly measures economic profit beyond required returns, providing a more intrinsic assessment of value.
Market approach vs income approach Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com