Succession planning centers on the strategic transfer of leadership and management within a family business or organization to ensure continuity and preserve wealth across generations. Estate planning involves organizing and managing an individual's assets during their lifetime and distributing them after death according to legal and financial goals. Both are crucial components of comprehensive wealth management, with succession planning focusing on business sustainability and estate planning addressing asset protection and inheritance.
Table of Comparison
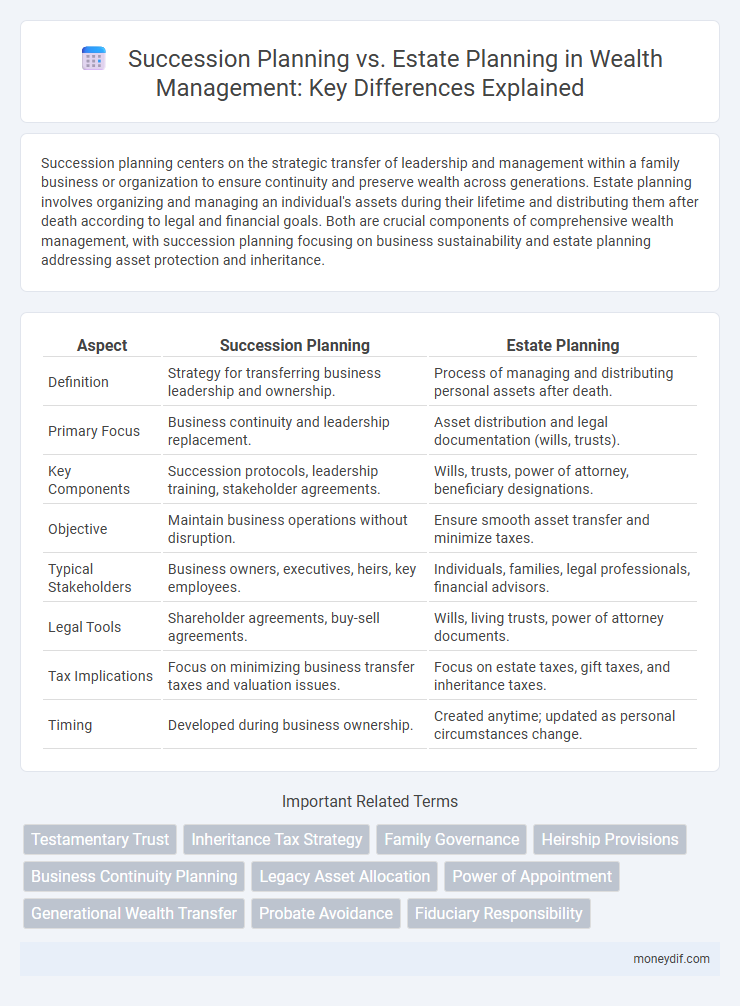
| Aspect | Succession Planning | Estate Planning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Strategy for transferring business leadership and ownership. | Process of managing and distributing personal assets after death. |
| Primary Focus | Business continuity and leadership replacement. | Asset distribution and legal documentation (wills, trusts). |
| Key Components | Succession protocols, leadership training, stakeholder agreements. | Wills, trusts, power of attorney, beneficiary designations. |
| Objective | Maintain business operations without disruption. | Ensure smooth asset transfer and minimize taxes. |
| Typical Stakeholders | Business owners, executives, heirs, key employees. | Individuals, families, legal professionals, financial advisors. |
| Legal Tools | Shareholder agreements, buy-sell agreements. | Wills, living trusts, power of attorney documents. |
| Tax Implications | Focus on minimizing business transfer taxes and valuation issues. | Focus on estate taxes, gift taxes, and inheritance taxes. |
| Timing | Developed during business ownership. | Created anytime; updated as personal circumstances change. |
Understanding Succession Planning in Wealth Management
Succession planning in wealth management ensures the strategic transfer of assets and leadership within family businesses or investment portfolios to preserve long-term wealth and support legacy goals. It involves identifying potential successors, developing their skills, and establishing clear protocols for ownership transition, minimizing conflicts and tax liabilities. Effective succession planning enhances financial security across generations while aligning wealth distribution with the benefactor's intentions.
Estate Planning: Securing Your Legacy
Estate planning involves creating a comprehensive strategy to manage and distribute your assets efficiently, minimizing taxes and legal complications for your heirs. Key components include drafting wills, establishing trusts, and outlining healthcare directives to ensure your wishes are honored. Proper estate planning safeguards your legacy, providing financial security and clarity for your beneficiaries.
Key Differences Between Succession and Estate Planning
Succession planning primarily focuses on the strategic transfer of business leadership and ownership to ensure organizational continuity, while estate planning centers on managing and distributing an individual's personal assets after death. Succession planning involves identifying and developing future leaders and establishing protocols for business transition, whereas estate planning includes wills, trusts, and tax strategies to protect family wealth. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for comprehensive wealth management, as merging both ensures smooth business operations and asset preservation across generations.
The Role of Succession Planning in Family Businesses
Succession planning in family businesses ensures the seamless transfer of leadership and ownership to the next generation, preserving business continuity and family legacy. It addresses potential conflicts by clearly defining roles, responsibilities, and timelines for heirs and key stakeholders. Effective succession planning enhances long-term wealth preservation by aligning business goals with family interests and legal considerations.
Estate Planning Tools: Trusts, Wills, and More
Estate planning tools such as trusts and wills play a critical role in managing and distributing wealth effectively, minimizing taxes, and avoiding probate. Trusts provide flexibility and privacy by allowing assets to be managed according to specific terms, while wills ensure clear instructions for asset allocation upon death. Other instruments like power of attorney and healthcare directives complement these tools by safeguarding financial and medical decisions.
Who Needs Succession Planning?
Succession planning is essential for business owners, family enterprises, and high-net-worth individuals aiming to ensure smooth leadership transitions and preserve wealth across generations. It addresses the transfer of management roles and decision-making authority, making it critical for entities where operational continuity impacts financial stability. Unlike estate planning, which focuses on asset distribution after death, succession planning proactively secures business longevity and governance succession.
Combining Succession and Estate Planning Strategies
Combining succession and estate planning strategies ensures a comprehensive approach to wealth transfer, protecting assets while providing clear directives for business continuity. Integrating these plans aligns family goals with tax efficiency, minimizing estate taxes and avoiding probate delays. Effective coordination between business succession plans and estate documents guarantees a seamless transition of wealth across generations.
Common Mistakes in Wealth Transfer
Common mistakes in wealth transfer often stem from confusing succession planning with estate planning, leading to gaps in asset protection and distribution clarity. Failing to update beneficiary designations, ignoring tax implications, and overlooking family dynamics can result in unintended financial burdens or legal disputes. Effective wealth transfer requires coordinated strategies that address both the management of assets during one's lifetime and the seamless transition after death.
Tax Implications of Succession and Estate Planning
Succession planning and estate planning significantly impact tax liabilities, with succession planning often focusing on minimizing estate and gift taxes during the transfer of business ownership. Estate planning addresses estate taxes and potential generation-skipping transfer taxes that may arise after an individual's death. Strategically structuring these plans can optimize tax efficiency, ensuring wealth preservation and seamless transition to heirs.
Choosing the Right Advisors for Your Wealth Plan
Selecting the right advisors for your wealth plan involves evaluating expertise in both succession and estate planning to ensure seamless asset transition and legal compliance. An interdisciplinary team including estate attorneys, financial planners, and tax specialists can tailor strategies that align with your long-term financial goals and family legacy. Prioritizing advisors with proven experience in wealth preservation helps mitigate risks and optimize tax efficiencies during wealth transfer.
Important Terms
Testamentary Trust
Testamentary trusts are specialized legal arrangements created within a will to manage and distribute assets upon death, playing a crucial role in both succession planning and estate planning by ensuring controlled asset transfer and protection for beneficiaries. Succession planning focuses on the strategic allocation of business and personal assets to heirs and successors, whereas estate planning encompasses broader financial and asset management strategies, including wills, trusts, and tax considerations.
Inheritance Tax Strategy
Inheritance tax strategy focuses on minimizing tax liabilities through effective succession planning, which ensures smooth asset transfer to heirs while preserving wealth. Estate planning complements this by organizing assets, trusts, and legal instruments to reduce estate taxes and protect beneficiaries.
Family Governance
Family governance establishes structured decision-making processes and clear roles to ensure effective succession planning by aligning family values with leadership transition, while estate planning focuses on legal and financial mechanisms to transfer wealth and assets across generations. Integrating both frameworks enables families to maintain harmony, preserve legacy, and mitigate conflicts during ownership and estate transitions.
Heirship Provisions
Heirship provisions in succession planning ensure the smooth transfer of leadership roles within a family business, preserving operational continuity by clearly defining successors. In estate planning, heirship provisions focus on the equitable distribution of assets among beneficiaries, minimizing disputes and aligning with legal requirements for inheritance.
Business Continuity Planning
Business Continuity Planning ensures operational resilience by preparing for leadership transitions through Succession Planning, which focuses on identifying and developing internal talent to maintain business functions. Estate Planning complements this by managing asset distribution and legal considerations, safeguarding the company's long-term financial stability and ownership structure.
Legacy Asset Allocation
Legacy asset allocation focuses on strategically distributing assets to heirs and beneficiaries in alignment with long-term succession planning goals, ensuring the preservation of wealth across generations. Estate planning complements this process by establishing legal frameworks such as wills, trusts, and tax strategies to facilitate the seamless transfer of legacy assets while minimizing probate and estate taxes.
Power of Appointment
Power of Appointment is a critical tool in succession planning, allowing grantors to designate individuals who can control asset distribution and adapt transfers to changing circumstances. Unlike traditional estate planning, which establishes fixed asset allocations, incorporating Power of Appointment provides flexibility in managing wealth transition and optimizing tax strategies across generations.
Generational Wealth Transfer
Generational wealth transfer focuses on preserving and strategically passing assets across multiple family generations to ensure long-term financial security. Succession planning prioritizes leadership and business continuity within families or organizations, while estate planning concentrates on the distribution of personal assets and minimizing tax liabilities after death.
Probate Avoidance
Probate avoidance techniques minimize court involvement, ensuring faster transfer of assets and reduced legal fees during succession planning, which focuses on designating successors for business or family leadership. Estate planning involves comprehensive strategies, including wills, trusts, and powers of attorney, to manage and distribute assets efficiently while minimizing probate and tax liabilities.
Fiduciary Responsibility
Fiduciary responsibility plays a crucial role in succession planning by ensuring that appointed trustees or executors act in the best interest of beneficiaries during the transfer of business ownership or assets. In estate planning, fiduciary duties involve managing and distributing assets according to the decedent's wishes while minimizing tax liabilities and legal disputes.
Succession Planning vs Estate Planning Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com