Philanthrocapitalism leverages business strategies and market-based approaches to maximize social impact and drive sustainable change, contrasting traditional philanthropy's reliance on donations and grants. By integrating investment principles and measurable outcomes, philanthroprocapitalism aims to create scalable solutions that address root causes of societal issues. Traditional philanthropy often emphasizes direct aid and charitable activities without necessarily prioritizing financial returns or systemic transformation.
Table of Comparison
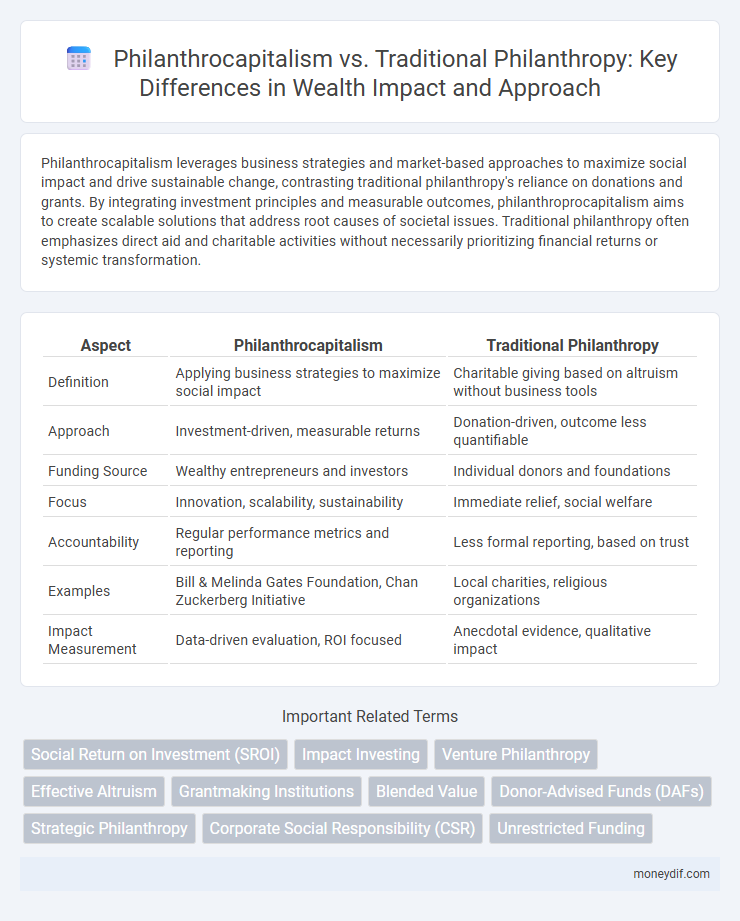
| Aspect | Philanthrocapitalism | Traditional Philanthropy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Applying business strategies to maximize social impact | Charitable giving based on altruism without business tools |
| Approach | Investment-driven, measurable returns | Donation-driven, outcome less quantifiable |
| Funding Source | Wealthy entrepreneurs and investors | Individual donors and foundations |
| Focus | Innovation, scalability, sustainability | Immediate relief, social welfare |
| Accountability | Regular performance metrics and reporting | Less formal reporting, based on trust |
| Examples | Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, Chan Zuckerberg Initiative | Local charities, religious organizations |
| Impact Measurement | Data-driven evaluation, ROI focused | Anecdotal evidence, qualitative impact |
Defining Philanthrocapitalism and Traditional Philanthropy
Philanthrocapitalism applies business strategies and market-based approaches to achieve social impact, leveraging investments for measurable returns alongside societal benefits. Traditional philanthropy typically relies on donations and grants focused on charity and immediate relief without the expectation of financial gain or scalable impact. Both approaches aim to address social issues, but philanthrocapitalism emphasizes sustainability and efficiency through investment principles.
Historical Evolution of Wealth-Driven Giving
Wealth-driven giving has evolved from traditional philanthropy, characterized by altruistic donations and charitable trusts, to philanthrocapitalism, which integrates business strategies and market-based approaches to achieve social impact. Traditional philanthropy's historical roots trace back to religious and community-based giving, while philanthrocapitalism emerged in the late 20th century alongside the rise of billionaire entrepreneurs seeking scalable, innovative solutions to global challenges. This evolution reflects a shift toward leveraging wealth not only for charity but also for systemic change and measurable returns on social investment.
Philosophies Behind Charitable Giving
Philanthrocapitalism emphasizes strategic investments and measurable social impact by leveraging business principles and market-based solutions to address global challenges. Traditional philanthropy prioritizes altruism and direct charitable donations, often focusing on immediate relief and community-based initiatives without expectations of financial returns. Both approaches are driven by a commitment to social good but differ fundamentally in motivation, methods, and evaluation of success.
Key Players and Motivations in Modern Philanthropy
Key players in modern philanthropy include tech billionaires like Bill Gates and Mark Zuckerberg, who emphasize measurable impact and scalable solutions, reflecting philantrocapitalism's data-driven approach. Traditional philanthropy, led by families such as the Rockefellers and Carnegies, often focuses on legacy-building and long-term community support through established charitable institutions. Motivations in philantrocapitalism revolve around leveraging business strategies for social change, while traditional philanthropy prioritizes altruism and sustaining cultural or social values.
Measuring Impact: Outcomes and Metrics
Philanthrocapitalism emphasizes data-driven strategies and rigorous impact measurement using metrics such as social return on investment (SROI) and key performance indicators (KPIs) to maximize efficiency and scalability. Traditional philanthropy often relies on qualitative assessments and anecdotal evidence, focusing more on charitable intent and community relationships. Advancements in technology and analytics enable philanthroprocapitalists to track real-time outcomes, driving accountability and informed decision-making.
Transparency and Accountability in Wealth Distribution
Philanthrocapitalism integrates business principles into charitable giving, emphasizing measurable outcomes and transparent reporting of wealth distribution. Traditional philanthropy often relies on established nonprofit structures with varying degrees of accountability, sometimes resulting in less clear tracking of funds. Transparency and accountability in wealth distribution are enhanced in philanthrocapitalism through data-driven metrics and continuous performance evaluation, promoting more efficient and impactful use of resources.
Power Dynamics and Social Influence
Philanthrocapitalism leverages market-based strategies and investor principles to drive social change, often concentrating power in the hands of wealthy entrepreneurs who shape agendas through large-scale funding and venture philanthropy models. Traditional philanthropy tends to rely on grant-making and charity, preserving established power hierarchies by distributing resources through nonprofits and community organizations with less direct influence on systemic change. The shift toward philanthrocapitalism raises critical questions about accountability, as influential donors increasingly dictate social priorities and methods, potentially sidelining grassroots voices and democratic decision-making processes.
Criticisms and Ethical Considerations
Philanthrocapitalism faces criticism for prioritizing market-based solutions that may reinforce existing inequalities rather than addressing root causes of social issues. Traditional philanthropy is often questioned for inefficiency and lack of measurable impact but is praised for its community-based, empathetic approach. Ethical concerns arise around power dynamics, with philanthroprocapitalists potentially exerting undue influence over public policies and priorities through their wealth.
Case Studies: Successes and Controversies
Philanthrocapitalism, exemplified by initiatives like the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, leverages market-driven strategies and data analytics to maximize social impact, achieving significant successes in global health and education. Contrastingly, traditional philanthropy, as seen in longstanding institutions such as the Rockefeller Foundation, emphasizes grant-making and community engagement but faces criticism for slower scalability and less measurable outcomes. Both models encounter controversies: philanthroprocapitalism is challenged over potential conflicts of interest and top-down approaches, while traditional philanthropy grapples with sustainability and adapting to modern social complexities.
The Future of Philanthropy: Collaboration or Conflict?
Philanthrocapitalism leverages market-driven strategies to amplify impact, emphasizing scalable solutions and measurable results, contrasting with traditional philanthropy's grant-based, relationship-focused approach. The future of philanthropy hinges on finding synergy between these models, fostering collaborative frameworks that combine innovative investment with grassroots engagement to address complex social challenges effectively. Emerging trends show increased partnerships between corporates and nonprofits, signaling a shift toward integration rather than conflict in wealth-driven social change efforts.
Important Terms
Social Return on Investment (SROI)
Social Return on Investment (SROI) measures the social, environmental, and economic value generated by investments, emphasizing outcomes beyond financial profits. Philanthrocapitalism leverages SROI by applying business metrics and market-driven strategies to maximize impact, contrasting with traditional philanthropy's focus on grant-making and charitable donations without rigorous impact quantification.
Impact Investing
Impact investing integrates financial returns with measurable social and environmental outcomes, contrasting with traditional philanthropy's primarily grant-based, no-return approach. Philanthrocapitalism leverages business principles and market-driven strategies within impact investing to scale solutions, whereas traditional philanthropy focuses on charitable giving without an expectation of financial profit.
Venture Philanthropy
Venture philanthropy blends strategic investment approaches with philanthropic goals, focusing on measurable impact and scalability, distinguishing itself from traditional philanthropy, which often emphasizes grant-giving without direct operational involvement. Philanthrocapitalism merges profit-driven techniques with social causes, prioritizing returns and innovation, whereas venture philanthropy applies venture capital methods for long-term social change, contrasting with traditional philanthropy's grant-based and donor-driven model.
Effective Altruism
Effective Altruism prioritizes measurable outcomes and evidence-based strategies to maximize social impact, contrasting with traditional philanthropy's often intuition-driven approach. Philanthrocapitalism integrates market-based principles and scalability from for-profit models, aiming to optimize resource allocation more efficiently than conventional charitable methods.
Grantmaking Institutions
Grantmaking institutions increasingly adopt philanthropocapitalism by leveraging venture capital strategies and impact investing to maximize social returns, contrasting with traditional philanthropy's reliance on grants and donations focused on immediate relief. This shift enhances scalability and sustainability of social projects, integrating business efficiency with altruistic goals to address systemic issues more effectively.
Blended Value
Blended Value integrates social, environmental, and financial returns into a single framework, bridging the gap between philanthrocapitalism's market-driven investments and traditional philanthropy's grant-based giving. This approach prioritizes measurable impact and sustainability, aligning with philanthrocapitalism's emphasis on leveraging business strategies for social change while maintaining traditional philanthropy's commitment to social good.
Donor-Advised Funds (DAFs)
Donor-Advised Funds (DAFs) facilitate strategic, tax-efficient giving by allowing donors to recommend grants over time, aligning with philanthropocapitalism's focus on measurable impact and sustainable investments. Traditional philanthropy often emphasizes direct donations and grantmaking without leveraging financial instruments or business principles to maximize long-term social returns.
Strategic Philanthropy
Strategic philanthropy leverages business principles and market-driven strategies to maximize social impact, closely aligning with philanthroprocapitalism's emphasis on measurable returns and scalable solutions, contrasting with traditional philanthropy's focus on charity and immediate relief without a systematic impact framework. By integrating investment mindsets and performance metrics, strategic philanthropy redefines philanthropic efforts to drive sustainable change and long-term value creation.
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) increasingly integrates Philanthrocapitalism by leveraging business strategies and market-based approaches to address social issues, contrasting with Traditional Philanthropy's donation-focused model. Philanthrocapitalism emphasizes measurable impact and sustainability through innovation and investment, while Traditional Philanthropy primarily relies on charitable giving and grant-making for social support.
Unrestricted Funding
Unrestricted funding enables nonprofits to allocate resources flexibly, fostering innovation and long-term sustainability, a principle embraced by philanthropocapitalism through strategic, impact-driven investments. Traditional philanthropy often relies on restricted grants earmarked for specific projects, limiting organizational adaptability and comprehensive problem-solving capacity.
Philanthrocapitalism vs Traditional Philanthropy Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com