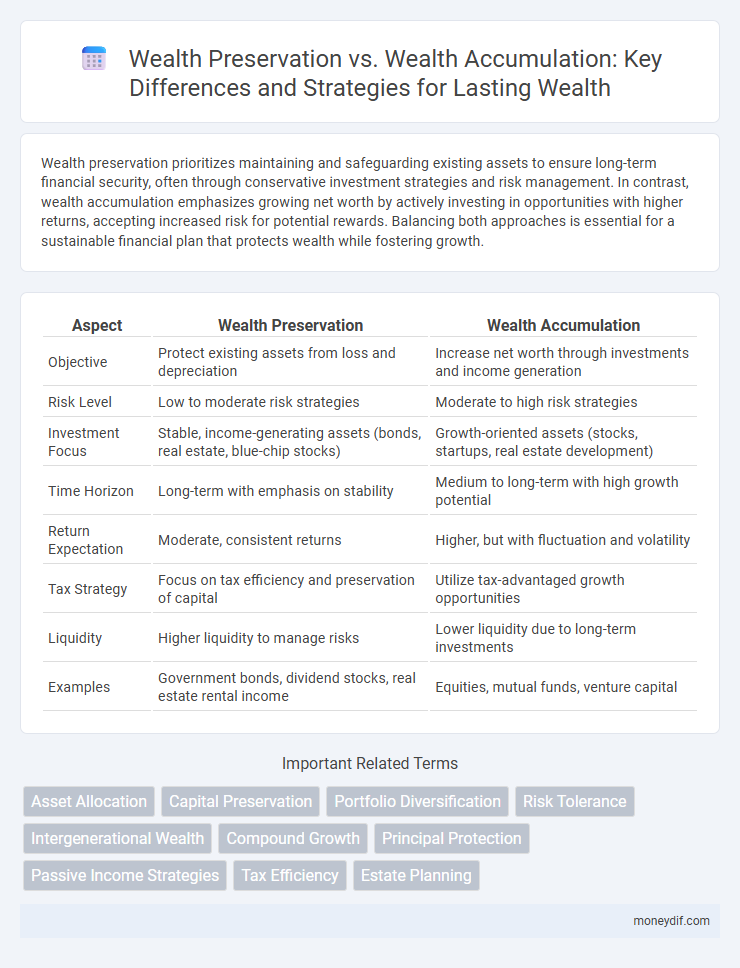
Wealth preservation prioritizes maintaining and safeguarding existing assets to ensure long-term financial security, often through conservative investment strategies and risk management. In contrast, wealth accumulation emphasizes growing net worth by actively investing in opportunities with higher returns, accepting increased risk for potential rewards. Balancing both approaches is essential for a sustainable financial plan that protects wealth while fostering growth.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Wealth Preservation | Wealth Accumulation |
|---|---|---|
| Objective | Protect existing assets from loss and depreciation | Increase net worth through investments and income generation |
| Risk Level | Low to moderate risk strategies | Moderate to high risk strategies |
| Investment Focus | Stable, income-generating assets (bonds, real estate, blue-chip stocks) | Growth-oriented assets (stocks, startups, real estate development) |
| Time Horizon | Long-term with emphasis on stability | Medium to long-term with high growth potential |
| Return Expectation | Moderate, consistent returns | Higher, but with fluctuation and volatility |
| Tax Strategy | Focus on tax efficiency and preservation of capital | Utilize tax-advantaged growth opportunities |
| Liquidity | Higher liquidity to manage risks | Lower liquidity due to long-term investments |
| Examples | Government bonds, dividend stocks, real estate rental income | Equities, mutual funds, venture capital |
Understanding Wealth Preservation and Accumulation
Wealth preservation focuses on protecting existing assets through strategies like diversification, risk management, and maintaining liquidity to ensure long-term financial stability. Wealth accumulation emphasizes actively growing net worth by investing in growth-oriented assets, increasing income streams, and reinvesting returns. Balancing preservation with accumulation is essential for sustainable financial health, allowing individuals to safeguard their wealth while pursuing future growth opportunities.
Key Differences Between Preserving and Accumulating Wealth
Preserving wealth emphasizes safeguarding assets against inflation, market volatility, and unforeseen expenses through conservative investments and risk management strategies. Accumulating wealth focuses on increasing net worth by leveraging higher-risk, growth-oriented opportunities such as stocks, real estate, and entrepreneurship. Key differences lie in the approach to risk tolerance, time horizon, and financial goals, where preservation targets stability and accumulation targets expansion.
Importance of Wealth Preservation Strategies
Wealth preservation strategies are essential for maintaining and protecting existing assets from inflation, market volatility, and unexpected financial downturns. Effective preservation tactics include diversifying investments, utilizing tax-efficient vehicles, and implementing estate planning to safeguard wealth across generations. Prioritizing preservation over accumulation ensures long-term financial stability and the ability to meet future obligations and goals.
Strategies for Effective Wealth Accumulation
Effective wealth accumulation strategies prioritize diversified investments across stocks, real estate, and alternative assets to maximize growth potential and mitigate risk. Regular contributions to retirement accounts, tax-advantaged savings plans, and reinvestment of earnings compound wealth over time. Utilizing financial planning tools and maintaining disciplined budgeting ensure consistent asset growth aligned with long-term financial goals.
Balancing Wealth Accumulation with Preservation
Balancing wealth accumulation with preservation requires a strategic approach that ensures growth without exposing assets to excessive risk, safeguarding financial stability over the long term. Diversifying investment portfolios across asset classes such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and alternative investments helps mitigate volatility while fostering steady appreciation. Implementing estate planning, insurance, and tax-efficient strategies further protects accumulated wealth and facilitates intergenerational transfer.
Risks in Wealth Accumulation vs Preservation
Wealth accumulation involves higher exposure to market volatility, inflation risk, and economic downturns, which can erode asset value and growth potential. Wealth preservation emphasizes capital protection through diversification, low-risk investments, and inflation hedging strategies to maintain purchasing power. Balancing accumulation and preservation requires managing liquidity risks and tax implications to ensure long-term financial stability.
Generational Wealth: Preservation or Growth?
Generational wealth demands a strategic balance between preservation and growth to ensure long-term family prosperity. Wealth preservation involves safeguarding assets through diversification, trust structures, and estate planning to protect against market volatility and taxes. Simultaneously, targeted wealth accumulation through investments in equities, real estate, and business ventures fuels capital appreciation, securing financial stability for future generations.
Tax Implications in Wealth Preservation and Accumulation
Tax implications significantly influence strategies for wealth preservation and accumulation, as accumulation phases often attract higher capital gains and income taxes on investment returns. Wealth preservation prioritizes tax-efficient vehicles such as trusts, municipal bonds, and tax-deferred accounts to minimize tax liabilities and protect assets. Understanding the differential impact of income tax rates, estate taxes, and gift taxes is crucial for optimizing long-term financial planning and ensuring intergenerational wealth transfer.
Common Mistakes in Managing Wealth
Common mistakes in managing wealth include prioritizing rapid wealth accumulation over long-term preservation, leading to high-risk investments that jeopardize financial stability. Ignoring diversification and failing to create a comprehensive estate plan can result in significant losses and wealth erosion through taxes and legal complications. Overlooking the impact of inflation and lifestyle inflation often diminishes the real value of accumulated assets, undermining sustainable wealth growth.
When to Shift Focus: Accumulation to Preservation
Wealth accumulation should transition to preservation typically during late career stages or as retirement approaches, when prioritizing capital protection becomes essential. Focusing on wealth preservation involves reducing exposure to high-risk assets while ensuring steady income streams through dividends, bonds, or annuities. Shifting this focus minimizes volatility and secures long-term financial stability against market downturns and unexpected expenses.
Important Terms
Asset Allocation
Asset allocation balances wealth preservation by prioritizing low-risk, stable investments like bonds and cash equivalents, while wealth accumulation focuses on higher-risk assets such as equities and growth-oriented mutual funds to maximize returns over time. Strategic diversification across asset classes optimizes portfolio stability and growth potential, aligning with individual financial goals and risk tolerance.
Capital Preservation
Capital preservation focuses on safeguarding existing wealth to minimize risk and avoid losses, whereas wealth accumulation emphasizes growth through strategic investments and higher-risk opportunities.
Portfolio Diversification
Effective portfolio diversification balances wealth preservation by reducing risk and wealth accumulation by optimizing asset growth across multiple sectors.
Risk Tolerance
Risk tolerance influences the balance between wealth preservation strategies that prioritize capital protection and wealth accumulation approaches that target higher returns with increased volatility.
Intergenerational Wealth
Intergenerational wealth focuses on preserving assets across generations by prioritizing strategic wealth management and risk mitigation over aggressive wealth accumulation.
Compound Growth
Compound growth accelerates wealth accumulation by reinvesting earnings over time, while wealth preservation focuses on maintaining existing assets with minimal risk to secure financial stability.
Principal Protection
Principal protection ensures the preservation of initial investment capital by minimizing risk, while wealth accumulation focuses on generating higher returns through increased exposure to market fluctuations.
Passive Income Strategies
Passive income strategies prioritize wealth preservation by generating steady cash flow with low risk, while wealth accumulation focuses on higher-risk investments aiming for significant capital growth.
Tax Efficiency
Tax efficiency maximizes wealth preservation by minimizing tax liabilities, enabling greater sustained growth compared to aggressive wealth accumulation strategies.
Estate Planning
Estate planning strategically focuses on wealth preservation by ensuring assets are transferred efficiently across generations while balancing wealth accumulation through tax optimization and risk management.
wealth preservation vs wealth accumulation Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com