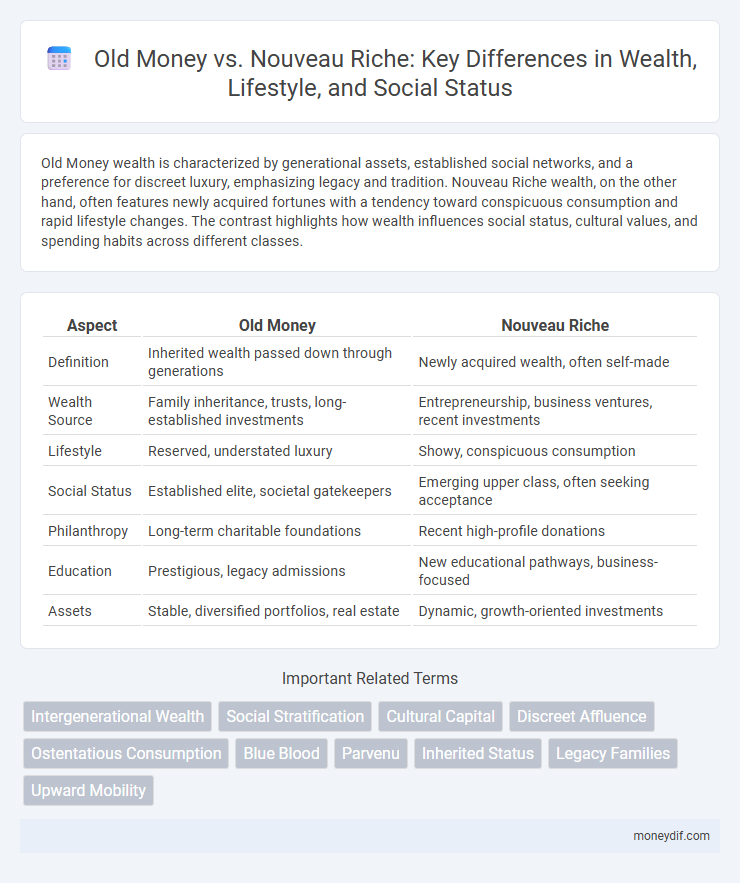
Old Money wealth is characterized by generational assets, established social networks, and a preference for discreet luxury, emphasizing legacy and tradition. Nouveau Riche wealth, on the other hand, often features newly acquired fortunes with a tendency toward conspicuous consumption and rapid lifestyle changes. The contrast highlights how wealth influences social status, cultural values, and spending habits across different classes.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Old Money | Nouveau Riche |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inherited wealth passed down through generations | Newly acquired wealth, often self-made |
| Wealth Source | Family inheritance, trusts, long-established investments | Entrepreneurship, business ventures, recent investments |
| Lifestyle | Reserved, understated luxury | Showy, conspicuous consumption |
| Social Status | Established elite, societal gatekeepers | Emerging upper class, often seeking acceptance |
| Philanthropy | Long-term charitable foundations | Recent high-profile donations |
| Education | Prestigious, legacy admissions | New educational pathways, business-focused |
| Assets | Stable, diversified portfolios, real estate | Dynamic, growth-oriented investments |
Defining Old Money and Nouveau Riche
Old Money refers to families that have preserved generational wealth through inheritance, often associated with established social status, refined cultural values, and traditional investments. Nouveau Riche describes individuals or families who have recently acquired significant wealth, typically through entrepreneurship or new industries, and are characterized by their display of luxury and rapid lifestyle changes. The distinction between Old Money and Nouveau Riche highlights differences in wealth origin, social integration, and cultural attitudes towards money management.
Historical Origins of Wealth
Old Money wealth originates from longstanding family fortunes accumulated through inheritance, land ownership, and established industries dating back centuries, often associated with aristocracy and stable economic foundations. Nouveau Riche wealth emerges from recent, rapid financial success typically in modern sectors like technology, entertainment, and entrepreneurship, reflecting social mobility and dynamic market opportunities. The historical origin of wealth shapes cultural attitudes, social networks, and prestige, influencing how each group navigates economic power and societal influence.
Social Status and Class Distinctions
Old Money families often maintain their social status through generational wealth, established cultural capital, and exclusive networks, reinforcing traditional class distinctions. Nouveau Riche individuals, despite newfound financial success, frequently face social scrutiny and challenges in gaining acceptance within elite circles due to differences in social etiquette and historical legacy. These dynamics highlight persistent class divisions rooted in heritage and social perception rather than just financial wealth.
Cultural Values and Lifestyle
Old Money families emphasize heritage, discretion, and long-standing social traditions, often valuing philanthropy and exclusive educational backgrounds. Nouveau Riche typically showcase wealth through conspicuous consumption, luxury goods, and investment in modern experiences, reflecting a more flamboyant lifestyle. Cultural values between the two diverge significantly, with Old Money prioritizing legacy and restraint, while Nouveau Riche focus on status symbols and rapid wealth display.
Approaches to Wealth Management
Old Money families prioritize preservation and intergenerational wealth transfer through conservative investment strategies and diversified portfolios that emphasize blue-chip stocks, real estate, and trusts. Nouveau Riche often adopt aggressive wealth management approaches, seeking high-risk, high-reward opportunities such as startups, cryptocurrencies, and luxury asset acquisitions to rapidly increase their net worth. Both groups use financial advisors, but Old Money favors legacy planning and philanthropy, while Nouveau Riche emphasizes personal branding and lifestyle investments.
Philanthropy and Social Responsibility
Old money families often emphasize philanthropy as a long-standing tradition, supporting established institutions and prioritizing social responsibility through sustained charitable giving. Nouveau riche individuals tend to engage in philanthropy with a focus on high-impact, visible projects, leveraging wealth to create immediate social change and build public reputation. Both groups contribute significantly to charitable causes but differ in approach, with old money stressing legacy and new wealth prioritizing innovation and visibility.
Fashion and Taste: Subtlety vs. Display
Old Money fashion embodies timeless elegance with subdued colors, high-quality fabrics, and classic tailoring that emphasize refinement and restraint. In contrast, Nouveau Riche often favor bold, ostentatious styles featuring bright hues, flashy logos, and trendy designs aimed at displaying wealth conspicuously. This distinction highlights subtlety versus display in taste, where Old Money prioritizes understated sophistication and Nouveau Riche embraces conspicuous consumption.
Legacy and Family Traditions
Old Money emphasizes preserving legacy through generational wealth and established family traditions that reinforce social status and values. Nouveau Riche often prioritize rapid asset accumulation and modern lifestyle choices, sometimes lacking the deeply rooted customs of inherited wealth. Legacy in Old Money encompasses philanthropy, education, and maintaining historic estates, contrasting with Nouveau Riche's focus on innovation and contemporary cultural influence.
Reputation and Social Networks
Old Money families maintain long-standing reputations built on generations of wealth, often enjoying exclusive social networks that reinforce their status and influence in elite circles. Nouveau Riche individuals acquire wealth rapidly, facing challenges gaining the same level of social acceptance and prestige despite their financial power. Social networks of Old Money emphasize legacy and tradition, while Nouveau Riche leverage modern platforms and entrepreneurial connections to establish their social standing.
The Influence on Modern Society
Old Money, characterized by inherited wealth and established social status, shapes modern society through longstanding cultural traditions, exclusive educational institutions, and entrenched political influence. Nouveau Riche, defined by newly acquired wealth often from entrepreneurship or technology, drives innovation, consumer trends, and the democratization of luxury goods. The dynamic tension between these groups influences social mobility, economic policies, and perceptions of success in contemporary culture.
Important Terms
Intergenerational Wealth
Intergenerational wealth shapes financial stability and social status, distinguishing Old Money families with generational assets and cultural capital from Nouveau Riche who often acquire wealth rapidly without inherited legacy. The preservation of Old Money relies on longstanding institutions, trusts, and values, whereas Nouveau Riche tends to emphasize entrepreneurial ventures and conspicuous consumption.
Social Stratification
Social stratification distinguishes Old Money, families with inherited wealth and established social status, from Nouveau Riche, individuals who have recently acquired wealth often through entrepreneurship or innovation. This divide influences social mobility, cultural capital, and access to exclusive networks, perpetuating class distinctions within society.
Cultural Capital
Cultural capital embodies the non-financial social assets such as education, style, and manners that distinguish Old Money families from the Nouveau Riche, with the former traditionally possessing inherited cultural sophistication and exclusive social networks. Nouveau Riche often invest in acquiring cultural capital to gain legitimacy and social acceptance, but their lack of generational heritage can limit their integration into elite circles.
Discreet Affluence
Discreet affluence often characterizes Old Money, where wealth is inherited and displayed through understated elegance and generational legacy, contrasting with the Nouveau Riche's penchant for overt luxury and conspicuous consumption. This subtlety in Old Money reflects deep-rooted social norms and long-standing cultural capital, emphasizing exclusivity over extravagance.
Ostentatious Consumption
Ostentatious consumption, characterized by the lavish display of wealth through luxury goods and experiences, often distinguishes Nouveau Riche from Old Money, who typically favor understated elegance and discreet spending habits. This contrast reflects deeper social values, where Old Money emphasizes heritage and subtlety, while Nouveau Riche seeks social recognition and status through conspicuous consumption.
Blue Blood
Blue Blood represents established aristocracy often associated with Old Money, signifying hereditary wealth, refined social status, and long-standing family lineage. In contrast, Nouveau Riche refers to individuals or families who have recently acquired significant wealth, frequently lacking traditional social pedigree but asserting new economic influence.
Parvenu
The term "parvenu" describes individuals who have recently acquired wealth and social status, often associated with the "nouveau riche," contrasting sharply with "old money" families who inherit wealth and exhibit established social refinement. Parvenus are frequently perceived as lacking the cultural sophistication and social graces that characterize old money, highlighting the social tensions between inherited privilege and newly acquired affluence.
Inherited Status
Inherited status signifies wealth and social prestige passed down through generations, often associated with Old Money families who value tradition, discretion, and long-standing societal influence. In contrast, Nouveau Riche individuals acquire wealth rapidly, emphasizing ostentatious displays and contemporary luxury to assert their newfound economic power and social standing.
Legacy Families
Legacy families, often associated with old money, possess generational wealth and social status passed down through decades, emphasizing tradition and established influence. Nouveau riche individuals, by contrast, have recently acquired wealth and may display their affluence more conspicuously, reflecting a shift in cultural and economic dynamics.
Upward Mobility
Upward mobility often faces unique challenges when comparing Old Money and Nouveau Riche, as Old Money benefits from generational wealth, established social networks, and cultural capital that facilitate access to exclusive opportunities. Nouveau Riche individuals might acquire substantial wealth quickly but frequently lack the inherited social prestige and insider connections, complicating their long-term social integration and acceptance into elite circles.
Old Money vs Nouveau Riche Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com