Tax harvesting involves strategically selling investments at a loss to offset gains and reduce taxable income, enhancing after-tax returns. In contrast, tax deferral postpones tax obligations by delaying the recognition of income or gains, allowing investment growth to compound tax-free until withdrawal. Choosing between these strategies depends on individual goals, risk tolerance, and long-term financial planning.
Table of Comparison
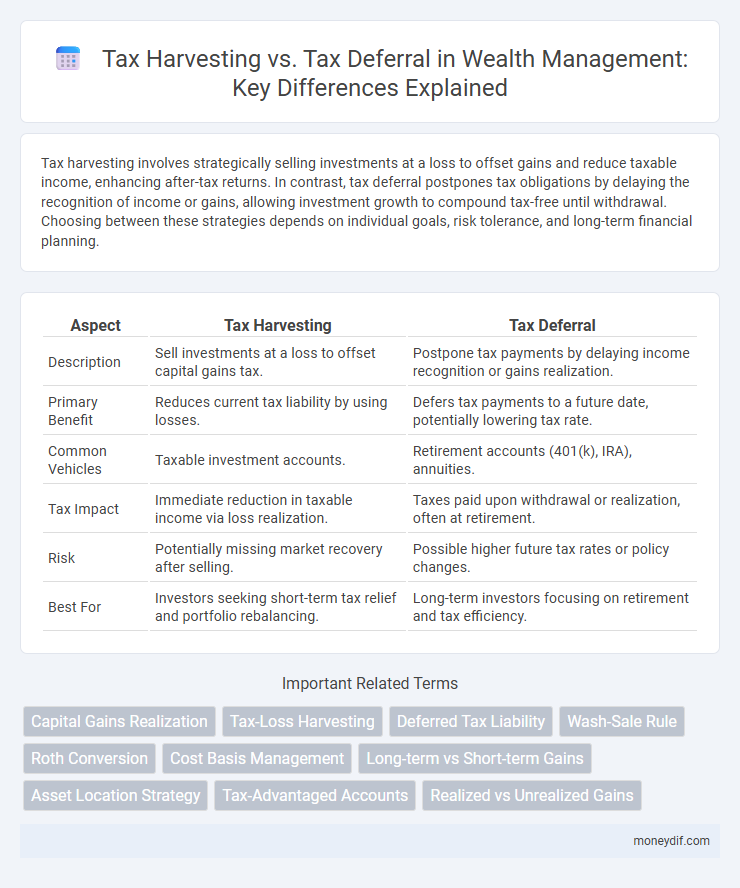
| Aspect | Tax Harvesting | Tax Deferral |
|---|---|---|
| Description | Sell investments at a loss to offset capital gains tax. | Postpone tax payments by delaying income recognition or gains realization. |
| Primary Benefit | Reduces current tax liability by using losses. | Defers tax payments to a future date, potentially lowering tax rate. |
| Common Vehicles | Taxable investment accounts. | Retirement accounts (401(k), IRA), annuities. |
| Tax Impact | Immediate reduction in taxable income via loss realization. | Taxes paid upon withdrawal or realization, often at retirement. |
| Risk | Potentially missing market recovery after selling. | Possible higher future tax rates or policy changes. |
| Best For | Investors seeking short-term tax relief and portfolio rebalancing. | Long-term investors focusing on retirement and tax efficiency. |
Understanding Tax Harvesting: An Overview
Tax harvesting involves strategically selling investments at a loss to offset taxable gains, reducing overall tax liability within a given year. This technique contrasts with tax deferral, which postpones taxes by holding investments longer, allowing capital growth to accumulate tax-free until withdrawal. Effectively understanding tax harvesting requires analyzing portfolio losses and gains to optimize tax outcomes while maintaining desired asset allocation.
What Is Tax Deferral? Key Concepts Explained
Tax deferral allows investors to postpone paying taxes on investment gains until a later date, typically during retirement when their income and tax rates may be lower. This strategy harnesses the power of compounding, as the funds that would have been paid in taxes remain invested and continue to grow tax-deferred. Understanding tax deferral is essential for optimizing long-term wealth accumulation and retirement planning.
Tax Harvesting vs Tax Deferral: Core Differences
Tax harvesting involves strategically selling investments at a loss to offset capital gains taxes, actively reducing tax liability within the current year. Tax deferral postpones the payment of taxes by delaying income recognition or capital gains realization, allowing investments to grow tax-deferred over time. The core difference lies in tax harvesting's immediate use of realized losses versus tax deferral's focus on long-term growth through postponed taxation.
When to Choose Tax Harvesting for Wealth Growth
Tax harvesting is ideal when investors realize capital losses to offset gains, reducing current tax liability and freeing up capital for reinvestment, which accelerates wealth growth. This strategy is particularly beneficial during market downturns or portfolio rebalancing when losses can be strategically recognized without disrupting long-term investment goals. Choosing tax harvesting over tax deferral maximizes after-tax returns by optimizing tax efficiency in volatile markets and periods of high income.
Situations Favoring Tax Deferral Strategies
Tax deferral strategies are advantageous when investors anticipate higher income or tax rates in the future, allowing for the postponement of tax liabilities until a potentially lower tax period. These strategies are particularly beneficial in retirement accounts such as 401(k)s or IRAs, where earnings grow tax-deferred until withdrawal. Investors expecting to be in a lower tax bracket after retirement gain maximum benefit by deferring taxes, preserving more capital for growth and future distributions.
Wealth Optimization: Combining Harvesting and Deferral
Tax harvesting reduces taxable income by realizing losses to offset gains, directly lowering current tax liabilities and optimizing wealth accumulation. Tax deferral delays tax payments on income, enabling investments to grow uninterrupted, enhancing compound growth over time. Combining tax harvesting and deferral strategies maximizes after-tax returns by strategically managing both current and future tax burdens within a comprehensive wealth optimization plan.
Tax Harvesting: Benefits and Potential Pitfalls
Tax harvesting involves selling investments at a loss to offset gains and reduce taxable income, potentially lowering immediate tax liabilities. This strategy enhances after-tax returns by optimizing capital gains and losses but requires careful timing to avoid wash sale rules, which disallow repurchasing the same asset within 30 days. Investors must weigh short-term tax savings against the risk of missing market rebounds, ensuring tax harvesting aligns with overall portfolio goals.
Tax Deferral: Advantages and Drawbacks for Investors
Tax deferral allows investors to postpone tax payments on investment gains, enhancing compounding potential and enabling larger portfolio growth over time. It offers flexibility in managing taxable income by deferring capital gains and dividend taxes until withdrawal, often during retirement when tax rates may be lower. However, tax deferral carries risks such as potential future tax rate increases and mandatory withdrawal requirements that can reduce long-term wealth accumulation.
Real-Life Scenarios: Tax Harvesting vs Tax Deferral
Tax harvesting involves selling investments at a loss to offset taxable gains, effectively reducing current tax liability and enhancing after-tax returns. In contrast, tax deferral postpones tax payments by retaining investments in tax-advantaged accounts like IRAs or 401(k)s, allowing assets to grow tax-free until withdrawal. For example, an investor might harvest losses in a brokerage account to balance gains while deferring tax on retirement account earnings, optimizing overall tax efficiency in their wealth management strategy.
Expert Tips: Maximizing Wealth Through Smart Tax Strategies
Tax harvesting involves selling investments at a loss to offset gains, effectively reducing taxable income and boosting wealth retention. Tax deferral strategies, such as contributing to retirement accounts, delay tax liabilities, allowing investments to grow tax-free or tax-deferred, enhancing compound growth. Expert tips emphasize balancing both methods to optimize after-tax returns, manage cash flow, and align with long-term financial goals.
Important Terms
Capital Gains Realization
Capital gains realization through tax harvesting involves selling assets to capture losses and offset gains for immediate tax benefits, whereas tax deferral postpones capital gains taxes by retaining investments without triggering a taxable event.
Tax-Loss Harvesting
Tax-loss harvesting reduces current taxable income by selling depreciated assets to offset gains, while tax deferral postpones tax liability by delaying asset sales or income recognition.
Deferred Tax Liability
Deferred tax liability arises when tax harvesting accelerates income recognition, creating timing differences that defer tax payments to future periods.
Wash-Sale Rule
The Wash-Sale Rule prevents investors from claiming a tax loss on a security sold at a loss if the same or substantially identical security is purchased within 30 days before or after the sale, limiting benefits in tax loss harvesting strategies. Tax deferral involves postponing taxes by holding investments longer, whereas tax harvesting exploits realized losses to offset gains, but the Wash-Sale Rule restricts harvesting by disallowing immediate repurchase of the same asset.
Roth Conversion
Roth conversion allows taxpayers to pay taxes upfront at their current rate to enable tax-free growth and withdrawals, contrasting with traditional tax deferral strategies that delay tax payments until retirement. Strategic tax harvesting can complement Roth conversion by realizing capital losses to offset taxable income generated during the conversion, optimizing overall tax efficiency.
Cost Basis Management
Cost basis management optimizes capital gains tax impact by accurately tracking investments' original value, enabling strategic tax harvesting to realize losses and tax deferral to postpone gains.
Long-term vs Short-term Gains
Tax-loss harvesting maximizes short-term tax benefits by offsetting gains immediately, while tax deferral strategies prioritize long-term gains to reduce taxable income over time through delayed realization.
Asset Location Strategy
Optimizing asset location strategy involves balancing tax harvesting opportunities in taxable accounts with tax deferral benefits in retirement accounts to maximize after-tax investment returns.
Tax-Advantaged Accounts
Tax-advantaged accounts enable tax harvesting by offsetting capital gains with losses for immediate tax benefits, while tax deferral strategies postpone tax liabilities by allowing investments to grow tax-free until withdrawal.
Realized vs Unrealized Gains
Realized gains from tax harvesting trigger taxable events by selling assets at a profit, while unrealized gains involved in tax deferral strategies postpone taxes by holding assets without selling.
tax harvesting vs tax deferral Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com