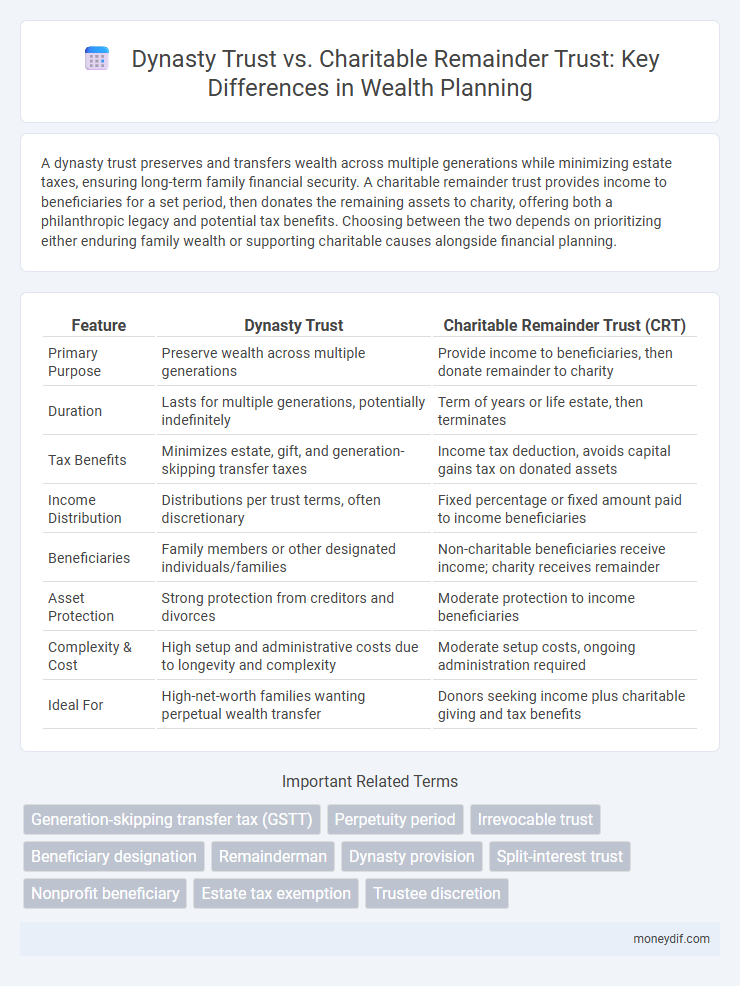
A dynasty trust preserves and transfers wealth across multiple generations while minimizing estate taxes, ensuring long-term family financial security. A charitable remainder trust provides income to beneficiaries for a set period, then donates the remaining assets to charity, offering both a philanthropic legacy and potential tax benefits. Choosing between the two depends on prioritizing either enduring family wealth or supporting charitable causes alongside financial planning.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Dynasty Trust | Charitable Remainder Trust (CRT) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Preserve wealth across multiple generations | Provide income to beneficiaries, then donate remainder to charity |
| Duration | Lasts for multiple generations, potentially indefinitely | Term of years or life estate, then terminates |
| Tax Benefits | Minimizes estate, gift, and generation-skipping transfer taxes | Income tax deduction, avoids capital gains tax on donated assets |
| Income Distribution | Distributions per trust terms, often discretionary | Fixed percentage or fixed amount paid to income beneficiaries |
| Beneficiaries | Family members or other designated individuals/families | Non-charitable beneficiaries receive income; charity receives remainder |
| Asset Protection | Strong protection from creditors and divorces | Moderate protection to income beneficiaries |
| Complexity & Cost | High setup and administrative costs due to longevity and complexity | Moderate setup costs, ongoing administration required |
| Ideal For | High-net-worth families wanting perpetual wealth transfer | Donors seeking income plus charitable giving and tax benefits |
Understanding Dynasty Trusts: Preserving Wealth Across Generations
Dynasty trusts are designed to preserve wealth across multiple generations without incurring estate taxes at each generational level, allowing assets to grow and benefit descendants over long periods. These trusts offer creditor protection and can last indefinitely in states with favorable perpetual trust laws, making them ideal for maintaining family legacy and financial stability. In contrast, charitable remainder trusts provide income tax benefits and support charities, but do not offer the same level of multigenerational wealth preservation as dynasty trusts.
What Is a Charitable Remainder Trust? Key Concepts Explained
A Charitable Remainder Trust (CRT) is an irrevocable trust designed to provide income to designated beneficiaries for a specified term, after which the remaining assets are donated to one or more charities. CRTs offer significant tax benefits by allowing donors to receive income tax deductions based on the estimated remainder value passing to charity and reduce estate taxes by removing assets from the donor's estate. Unlike dynasty trusts, which preserve wealth across multiple generations without charitable distribution, CRTs balance income needs with philanthropic goals, making them a strategic tool for wealth management and legacy planning.
Dynasty Trust vs. Charitable Remainder Trust: Core Differences
Dynasty trusts allow wealth to be preserved and passed down through multiple generations without incurring estate taxes, providing long-term asset protection and control. Charitable remainder trusts generate income for beneficiaries during their lifetime while ultimately transferring assets to a designated charity, offering immediate tax deductions and philanthropic benefits. The core difference lies in dynasty trusts focusing on multigenerational wealth preservation, whereas charitable remainder trusts combine income generation with charitable giving.
Tax Advantages: Comparing Dynasty and Charitable Remainder Trusts
Dynasty trusts offer significant tax advantages by allowing assets to grow free of estate, gift, and generation-skipping transfer taxes for multiple generations, preserving wealth long-term. Charitable remainder trusts provide immediate income tax deductions and help reduce capital gains taxes by donating appreciated assets while retaining income for a period before the remainder goes to charity. Comparing the two, dynasty trusts maximize intergenerational tax savings, whereas charitable remainder trusts combine income tax benefits with philanthropy and eventual tax-efficient wealth transfer.
Asset Protection Strategies for Multigenerational Wealth
Dynasty trusts offer unparalleled asset protection by preserving wealth across multiple generations without being subject to estate taxes or creditor claims, ensuring long-term family financial security. Charitable remainder trusts provide a strategic balance between generating income for beneficiaries and reducing taxable estate value while supporting philanthropic goals. Utilizing these trusts in tandem enhances multigenerational wealth preservation by combining tax efficiency, creditor protection, and legacy planning.
Philanthropic Goals vs. Family Legacy: Choosing the Right Trust
Dynasty trusts preserve family wealth across multiple generations by minimizing estate taxes and protecting assets from creditors, ensuring a lasting family legacy. Charitable remainder trusts provide income to beneficiaries for a set period, with remaining assets directed to designated charities, supporting philanthropic goals while offering tax advantages. Selecting between the two depends on whether the primary focus is on sustaining intergenerational wealth or maximizing charitable impact and tax benefits.
Flexibility and Control: Governance in Trust Structures
Dynasty trusts offer long-term wealth preservation across multiple generations with high control through designated trustees, minimizing estate taxes and protecting assets from creditors. Charitable remainder trusts provide income flexibility and tax benefits by distributing income to beneficiaries for a specified term before transferring the remainder to charities, but they limit control over the ultimate disposition of assets. Governance in dynasty trusts focuses on maintaining family wealth and succession planning, whereas charitable remainder trusts emphasize philanthropic goals combined with income Stream management.
Potential Risks and Legal Considerations for Trust Setups
Dynasty trusts face potential risks such as changes in tax laws that may limit their duration or increase tax liabilities, while charitable remainder trusts carry risks related to fluctuating income from trust assets and strict IRS compliance requirements. Legal considerations for dynasty trusts include ensuring proper state law validation to maintain perpetual duration and avoiding generation-skipping transfer tax pitfalls. Charitable remainder trusts require precise valuation of remainder interests and adherence to payout rates to avoid disqualification under tax-exempt status regulations.
Estate Planning: When to Use Dynasty Trusts or Charitable Remainder Trusts
Dynasty trusts excel in preserving wealth across multiple generations by minimizing estate taxes and protecting assets from creditors, ideal for families seeking long-term legacy planning. Charitable remainder trusts offer significant income tax deductions and provide a stream of income during the grantor's lifetime while benefiting selected charities after death. Selecting between these trusts depends on goals: dynasty trusts for multigenerational wealth transfer and asset protection, charitable remainder trusts for philanthropic objectives combined with income and estate tax advantages.
Case Studies: Real-World Applications of Dynasty and Charitable Remainder Trusts
Case studies reveal dynasty trusts effectively preserve multigenerational wealth by minimizing estate taxes and protecting assets from creditors, as demonstrated by prominent family offices maintaining wealth for over five generations. Charitable remainder trusts (CRTs) are strategically utilized by high-net-worth individuals to generate income streams while supporting philanthropic goals, often leading to significant income tax deductions and eventual charitable gifts, exemplified in numerous donor scenarios. The practical applications highlight dynasty trusts as optimal for legacy planning, whereas CRTs serve those balancing income needs with charitable intentions.
Important Terms
Generation-skipping transfer tax (GSTT)
Generation-skipping transfer tax (GSTT) applies to transfers made to beneficiaries two or more generations below the grantor, significantly impacting dynasty trusts designed to preserve wealth across multiple generations. Charitable remainder trusts (CRTs) offer estate tax benefits and income streams without incurring GSTT, making them effective tools for philanthropic goals while potentially reducing tax liabilities compared to dynasty trusts.
Perpetuity period
The perpetuity period in a Dynasty trust allows assets to grow and pass through generations indefinitely without incurring estate taxes, while a Charitable Remainder Trust (CRT) typically has a finite term limited by the lifetime of beneficiaries or a set number of years, after which the remaining assets are donated to charity. Dynasty trusts maximize long-term wealth preservation across multiple generations, whereas CRTs provide income benefits during the term and eventual charitable contributions.
Irrevocable trust
An irrevocable trust ensures assets are permanently removed from the grantor's estate, providing strong protection and tax benefits, often favored in Dynasty trusts for multigenerational wealth preservation. Charitable remainder trusts, while also irrevocable, focus on generating income for the grantor or beneficiaries with the remainder benefiting a charity, offering distinct income tax deductions and philanthropy advantages compared to Dynasty trusts.
Beneficiary designation
Beneficiary designation in a dynasty trust allows assets to pass through multiple generations without incurring estate taxes, preserving wealth indefinitely within a family lineage. In contrast, a charitable remainder trust designates beneficiaries after a term or lifetime income interest to a charity, providing tax benefits while supporting philanthropic goals.
Remainderman
A remainderman in a dynasty trust benefits from wealth accumulation over multiple generations without estate taxes, preserving assets indefinitely. In contrast, a charitable remainder trust provides income to beneficiaries for a term or life, with remaining assets donated to charity, balancing philanthropy and tax advantages.
Dynasty provision
Dynasty provisions in trusts allow wealth to be preserved and transferred across multiple generations without incurring repeated estate taxes, making dynasty trusts highly effective for long-term family wealth accumulation. Unlike charitable remainder trusts, which provide income to beneficiaries for a specified period before donating assets to charity, dynasty trusts focus on maintaining wealth within the family lineage over an extended duration.
Split-interest trust
A split-interest trust, combining elements of a Dynasty trust and a Charitable Remainder Trust (CRT), allows beneficiaries to receive income for a specified term while the remainder passes to a designated charity, enabling both multi-generational wealth preservation and philanthropic benefits. Unlike a traditional Dynasty trust, which focuses solely on long-term family wealth transfer without charitable distribution, the split-interest trust offers income tax deductions and potential estate tax advantages through its charitable component.
Nonprofit beneficiary
A nonprofit beneficiary in a Dynasty trust can receive perpetual financial support without estate taxes, while a charitable remainder trust provides income to non-charitable beneficiaries before donating the remainder to a nonprofit, enabling both asset growth and philanthropic impact. Selecting between these trusts depends on goals for long-term family wealth preservation versus immediate charitable giving combined with tax benefits.
Estate tax exemption
Estate tax exemption allows individuals to transfer a specific amount of assets tax-free, which is crucial when structuring trusts like Dynasty trusts and Charitable Remainder Trusts (CRTs). Dynasty trusts leverage the exemption to preserve wealth across generations without incurring estate taxes, while CRTs use the exemption in combination with charitable giving to reduce estate taxes by providing income to beneficiaries before donating the remainder to charity.
Trustee discretion
Trustee discretion in a dynasty trust typically allows the trustee broad authority to manage and distribute assets across multiple generations, optimizing wealth preservation and minimizing estate taxes. In contrast, trustee discretion in a charitable remainder trust focuses on balancing income payments to beneficiaries with eventual charitable distribution, requiring careful management to comply with tax-exempt status and payout requirements.
Dynasty trust vs charitable remainder trust Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com