Direct costing allocates only variable manufacturing costs to products, treating fixed manufacturing overhead as a period expense, which aids in short-term decision-making and profit analysis. Absorption costing assigns both variable and fixed manufacturing costs to products, ensuring compliance with GAAP and providing a comprehensive view of total production cost. The choice between these methods affects inventory valuation, cost control, and financial reporting accuracy.
Table of Comparison
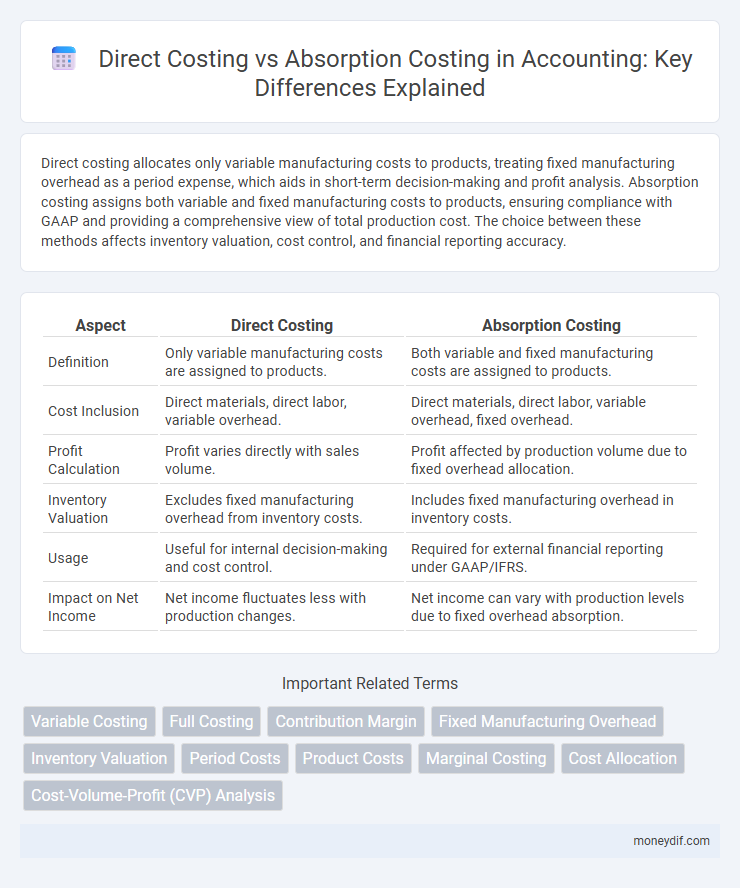
| Aspect | Direct Costing | Absorption Costing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Only variable manufacturing costs are assigned to products. | Both variable and fixed manufacturing costs are assigned to products. |
| Cost Inclusion | Direct materials, direct labor, variable overhead. | Direct materials, direct labor, variable overhead, fixed overhead. |
| Profit Calculation | Profit varies directly with sales volume. | Profit affected by production volume due to fixed overhead allocation. |
| Inventory Valuation | Excludes fixed manufacturing overhead from inventory costs. | Includes fixed manufacturing overhead in inventory costs. |
| Usage | Useful for internal decision-making and cost control. | Required for external financial reporting under GAAP/IFRS. |
| Impact on Net Income | Net income fluctuates less with production changes. | Net income can vary with production levels due to fixed overhead absorption. |
Introduction to Direct Costing vs Absorption Costing
Direct costing assigns only variable manufacturing costs to product costs, treating fixed overhead as a period expense, which enhances cost-volume-profit analysis accuracy. Absorption costing allocates both variable and fixed manufacturing overhead to product costs, aligning with GAAP for external financial reporting but potentially distorting product profitability. Understanding these costing methods is crucial for accurate inventory valuation, decision-making, and financial statement preparation.
Key Definitions and Concepts
Direct costing, also known as variable costing, assigns only variable manufacturing costs to product inventory, excluding fixed overhead from product costs and treating it as a period expense. Absorption costing allocates both variable and fixed manufacturing overhead to product costs, aligning with GAAP requirements for external financial reporting. Understanding the distinction between these methods is crucial for accurate cost behavior analysis and decision-making in managerial accounting.
Components Included in Each Costing Method
Direct costing includes only variable manufacturing costs such as direct materials, direct labor, and variable manufacturing overhead in product costs, while fixed manufacturing overhead is treated as a period expense. Absorption costing incorporates both variable and fixed manufacturing costs, encompassing direct materials, direct labor, variable overhead, and fixed overhead in inventory valuation. This distinction affects inventory valuation and profitability analysis significantly in cost accounting.
Calculation Differences Explained
Direct costing calculates product costs by including only variable manufacturing costs, excluding fixed overhead from inventory valuations, whereas absorption costing allocates both variable and fixed manufacturing overhead to products. This fundamental difference affects cost of goods sold and inventory valuations; under absorption costing, fixed overhead is absorbed into inventory costs, delaying expense recognition. The choice impacts profitability analysis and decision-making, with direct costing providing clearer insight into variable costs and contribution margins.
Impact on Financial Statements
Direct costing treats only variable manufacturing costs as product costs, resulting in fixed manufacturing overhead being expensed in full during the period, which leads to lower inventory values and potentially lower net income on the financial statements. Absorption costing allocates both variable and fixed manufacturing overhead to products, increasing inventory values and net income when production exceeds sales due to fixed costs being deferred in inventory. The choice between these methods significantly affects the balance sheet and income statement, influencing profit margins, tax liabilities, and managerial decision-making.
Effects on Profit Reporting
Direct costing treats only variable production costs as product costs, leading to profit figures that fluctuate with sales volume and provide clearer contribution margin insights. Absorption costing allocates both fixed and variable manufacturing costs to products, often resulting in profit distortion when inventory levels change due to fixed overhead being deferred in inventory valuation. This difference affects managerial decisions, as absorption costing can show higher profits during inventory build-up, while direct costing offers more accurate data for performance evaluation and cost control.
Managerial Decision-Making Implications
Direct costing provides managers with clearer insights into variable costs, facilitating short-term decision-making such as pricing and cost control. Absorption costing allocates fixed manufacturing overheads to products, affecting inventory valuation and potentially influencing profitability assessments. Understanding the difference between these costing methods is crucial for accurately analyzing product profitability and making strategic decisions.
Advantages of Direct Costing
Direct costing provides clearer insight into variable costs and contribution margin, enhancing decision-making related to pricing and production levels. It simplifies cost control by separating fixed and variable expenses, allowing managers to focus on cost behavior and profitability analysis. This method improves short-term financial planning by providing timely information on the impact of changes in sales volume on profitability.
Advantages of Absorption Costing
Absorption costing offers the advantage of compliance with GAAP and IFRS by including all manufacturing costs, both fixed and variable, in product cost, providing a more accurate inventory valuation. This method ensures that fixed manufacturing overhead is allocated to units produced, which aligns product costs with financial reporting and supports better matching of expenses with revenues. Absorption costing aids in decision-making by reflecting the full cost of production, which can enhance pricing strategies and profitability analysis.
Choosing the Right Costing Method for Your Business
Choosing the right costing method depends on your business's financial goals and inventory management needs, with direct costing providing clearer insight into variable costs and absorption costing offering a comprehensive view of product cost by including fixed manufacturing overhead. Businesses aiming for accurate product pricing and inventory valuation often prefer absorption costing, especially in industries with significant fixed production costs. Direct costing is beneficial for internal decision-making and short-term analysis, as it highlights cost behavior and contribution margin without allocating fixed overhead to individual units.
Important Terms
Variable Costing
Variable costing includes only direct materials, direct labor, and variable manufacturing overhead in product costs, whereas absorption costing allocates both variable and fixed manufacturing overhead to products.
Full Costing
Full costing, also known as absorption costing, allocates all manufacturing costs, both fixed and variable, to products, whereas direct costing assigns only variable manufacturing costs to products, treating fixed costs as period expenses.
Contribution Margin
Contribution margin represents the difference between sales revenue and variable costs, highlighting the amount available to cover fixed costs under direct costing. Absorption costing allocates both variable and fixed manufacturing overhead to product costs, which can obscure the true contribution margin by including fixed expenses in inventory valuation.
Fixed Manufacturing Overhead
Fixed manufacturing overhead is treated as a period expense in direct costing, whereas it is allocated to product costs under absorption costing.
Inventory Valuation
Inventory valuation under direct costing includes only variable manufacturing costs, while absorption costing incorporates both variable and fixed manufacturing overheads into product costs.
Period Costs
Period costs under direct costing are expensed immediately, whereas absorption costing allocates period costs between product inventory and expenses.
Product Costs
Product costs under direct costing include only variable manufacturing expenses such as direct materials, direct labor, and variable manufacturing overhead, while absorption costing incorporates both variable and fixed manufacturing overhead as part of product costs. This difference impacts inventory valuation and net income, as absorption costing allocates fixed overhead to units produced, influencing cost of goods sold and profitability analysis.
Marginal Costing
Marginal costing calculates product costs using only variable costs, whereas absorption costing includes both variable and fixed manufacturing overheads in product cost.
Cost Allocation
Cost allocation methods impact financial reporting by assigning direct costs only in direct costing while absorption costing allocates both direct and fixed manufacturing overhead costs to products.
Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) Analysis
Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) Analysis relies on direct costing to focus on variable costs and contribution margin, providing clearer insights into how changes in sales volume affect profit. Absorption costing includes fixed manufacturing overhead in product costs, which can obscure CVP relationships by allocating fixed costs per unit, complicating margin and break-even calculations.
direct costing vs absorption costing Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com