Hidden assets are valuable resources not recorded on a company's balance sheet due to accounting limitations or oversight, often including intellectual property or brand reputation. Off-balance sheet assets, on the other hand, are intentionally excluded from the balance sheet through specific financial arrangements like leasing or joint ventures, designed to keep liabilities and associated assets off the main financial statements. Understanding the distinction between hidden and off-balance sheet assets is crucial for accurate financial analysis and risk assessment.
Table of Comparison
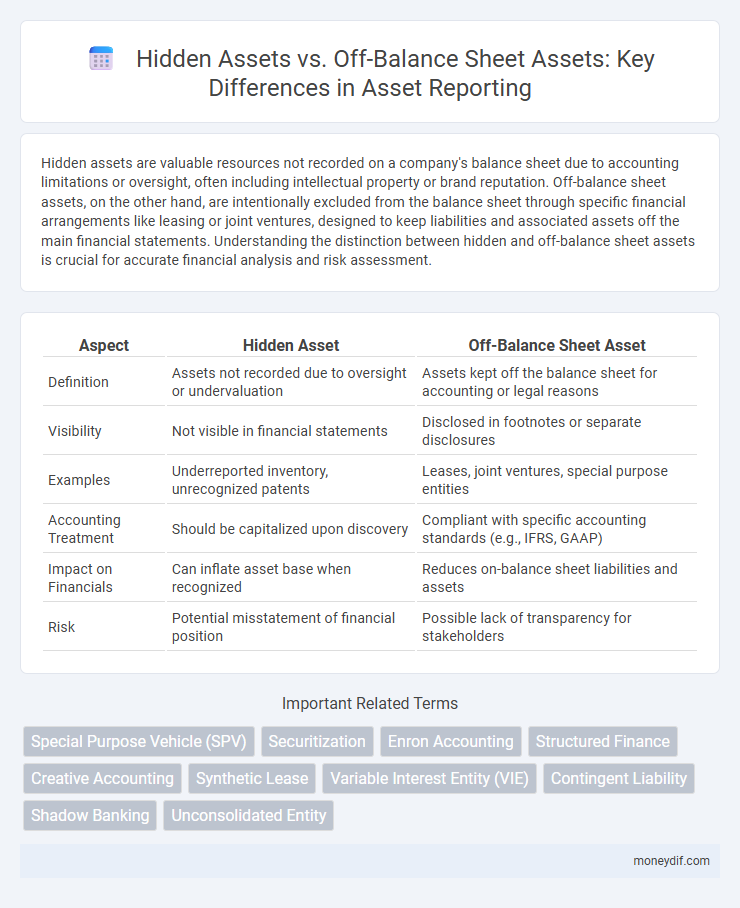
| Aspect | Hidden Asset | Off-Balance Sheet Asset |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Assets not recorded due to oversight or undervaluation | Assets kept off the balance sheet for accounting or legal reasons |
| Visibility | Not visible in financial statements | Disclosed in footnotes or separate disclosures |
| Examples | Underreported inventory, unrecognized patents | Leases, joint ventures, special purpose entities |
| Accounting Treatment | Should be capitalized upon discovery | Compliant with specific accounting standards (e.g., IFRS, GAAP) |
| Impact on Financials | Can inflate asset base when recognized | Reduces on-balance sheet liabilities and assets |
| Risk | Potential misstatement of financial position | Possible lack of transparency for stakeholders |
Understanding Hidden Assets: A Semantic Perspective
Hidden assets refer to valuable resources or properties not explicitly recorded on a company's balance sheet, often due to conservative accounting practices or intangible nature, whereas off-balance sheet assets are assets that a company controls but intentionally excludes from the balance sheet to manage financial ratios. Understanding hidden assets requires semantic analysis of financial statements, footnotes, and qualitative disclosures to uncover embedded value not immediately visible. Leveraging natural language processing and data extraction techniques enhances the identification and valuation of such hidden assets, providing deeper insights into a company's true financial position.
What Are Off-Balance Sheet Assets? Key Definitions
Off-balance sheet assets refer to items not recorded on a company's balance sheet, often to keep liabilities or risks hidden from stakeholders. These assets include operating leases, joint ventures, and certain types of receivables or contingencies that do not meet the criteria for formal recognition under accounting standards. Unlike hidden assets, which are often unrecorded or undervalued tangible or intangible resources, off-balance sheet assets are deliberately excluded to enhance financial appearance or comply with regulatory frameworks.
Hidden Assets vs Off-Balance Sheet Assets: Core Differences
Hidden assets refer to valuable resources or investments not explicitly listed on a company's balance sheet due to limitations in accounting standards or oversight, often including internally developed intellectual property or brand reputation. Off-balance sheet assets are financial arrangements or obligations, such as operating leases or joint ventures, intentionally kept off the balance sheet to improve financial ratios or meet regulatory requirements. The core difference lies in transparency and intent: hidden assets are unreported due to valuation challenges or omissions, while off-balance sheet assets are deliberately excluded for strategic financial presentation.
Examples of Hidden Assets in Corporate Finance
Hidden assets in corporate finance often include undervalued intellectual property, such as patents and trademarks not fully recognized on the balance sheet, proprietary technology, and internally developed goodwill. These assets remain undisclosed or underreported due to conservative accounting practices or difficulties in precise valuation, contrasting with off-balance sheet assets like operating leases or special purpose entities used to manage risk and leverage. Identifying hidden assets can provide a more accurate assessment of a company's intrinsic value and potential for growth.
Common Types of Off-Balance Sheet Assets
Common types of off-balance sheet assets include operating leases, joint ventures, and certain receivables managed through securitization. These assets do not appear directly on the balance sheet but still represent economic value and potential future benefits for the company. Off-balance sheet arrangements often enhance financial flexibility and risk management without increasing reported liabilities.
Risks and Implications of Hidden Asset Reporting
Hidden assets, often unreported due to poor valuation or intentional omission, pose significant risks by misleading stakeholders about a company's true financial health and potentially inflating asset values. Off-balance sheet assets involve legitimate accounting techniques to exclude certain assets from the balance sheet, but they carry transparency risks that can obscure real liabilities and distort financial analysis. Failure to accurately report hidden assets can lead to regulatory penalties, loss of investor trust, and increased volatility in stock prices due to unexpected financial disclosures.
Regulatory Views on Off-Balance Sheet Assets
Regulatory views on off-balance sheet assets emphasize transparency and risk disclosure due to their potential to obscure an entity's true financial position. These assets, which include contingencies, leases, and special purpose entities, are subject to stricter reporting requirements under frameworks like IFRS 16 and US GAAP ASC 842 to enhance investor protection and market stability. Regulators mandate detailed disclosure to prevent hidden liabilities from undermining capital adequacy and financial solvency assessments.
Detecting Hidden Assets: Tools and Techniques
Detecting hidden assets requires advanced forensic accounting techniques, including detailed financial statement analysis and data triangulation from multiple sources such as bank records and property registries. Utilizing digital forensic tools and blockchain analytics enhances the identification of off-balance sheet assets often concealed through complex corporate structures or special purpose vehicles (SPVs). Employing asset tracing software and leveraging artificial intelligence algorithms further improves the accuracy and efficiency of uncovering hidden financial interests crucial for comprehensive asset evaluation.
Transparency and Disclosure in Off-Balance Sheet Accounting
Off-balance sheet assets are intentionally excluded from a company's balance sheet to enhance financial transparency by segregating certain liabilities and risks, whereas hidden assets are undisclosed resources not reported publicly, potentially obscuring true financial health. Transparency in off-balance sheet accounting requires detailed disclosure notes to ensure stakeholders understand the nature and risks of these assets without inflating the balance sheet figures. Proper disclosure practices improve investor confidence and regulatory compliance by clarifying the economic reality behind off-balance sheet arrangements.
Best Practices for Managing Hidden and Off-Balance Sheet Assets
Best practices for managing hidden and off-balance sheet assets include thorough identification through advanced auditing techniques and continuous monitoring using automated asset tracking systems. Implementing robust internal controls and transparent reporting frameworks ensures compliance with accounting standards like IFRS and GAAP, reducing financial risk and enhancing corporate governance. Regular training for finance teams on recognizing and disclosing these assets optimizes asset management and supports accurate financial statement presentation.
Important Terms
Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV)
A Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) is often used to hold hidden assets, enabling companies to keep liabilities or assets off-balance-sheet and improve financial ratios without direct disclosure.
Securitization
Securitization transforms hidden assets, often off-balance sheet assets like receivables, into tradable financial instruments to improve liquidity and manage risk.
Enron Accounting
Enron used off-balance sheet assets to hide liabilities and inflate financial statements, obscuring the true value of hidden assets from investors and regulators.
Structured Finance
Structured finance involves complex financial instruments designed to transfer risk and create liquidity, often utilizing off-balance sheet assets to improve balance sheet appearance while hidden assets represent unrecorded or undervalued resources that may not be disclosed in financial statements. The strategic use of off-balance sheet assets in structured finance enhances capital efficiency, whereas hidden assets pose challenges for accurate valuation and risk assessment in corporate finance.
Creative Accounting
Creative accounting involves manipulating financial statements to present a more favorable image, often by hiding assets or using off-balance sheet assets to keep liabilities and risks undisclosed. Hidden assets refer to valuable resources not reported on the balance sheet, while off-balance sheet assets are structured to remain outside formal financial disclosures, both techniques masking true financial health.
Synthetic Lease
A synthetic lease structures an off-balance sheet asset by keeping leased property off the lessee's balance sheet, effectively creating a hidden asset representation.
Variable Interest Entity (VIE)
A Variable Interest Entity (VIE) often holds hidden assets off-balance sheet, obscuring true financial exposure and complicating risk assessment for investors and regulators.
Contingent Liability
Contingent liabilities represent potential obligations dependent on future events and differ from hidden assets, which are unrecorded resources, and off-balance sheet assets, which exist but are excluded from the balance sheet to manage financial appearance.
Shadow Banking
Shadow banking involves financial activities and entities that operate outside traditional banking regulations, often utilizing off-balance sheet assets to obscure hidden risks and liabilities from standard financial statements.
Unconsolidated Entity
Unconsolidated entities often hold hidden assets that remain undisclosed as off-balance sheet assets, impacting financial transparency and risk assessment.
Hidden asset vs Off-balance sheet asset Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com