AML (Anti-Money Laundering) encompasses a set of policies and procedures designed to prevent, detect, and report suspicious financial activities linked to money laundering and terrorism financing. KYC (Know Your Customer) is a critical component of AML, focusing on verifying the identity of clients to assess potential risks and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. Both AML and KYC processes work together to protect banks from financial crimes and maintain the integrity of the financial system.
Table of Comparison
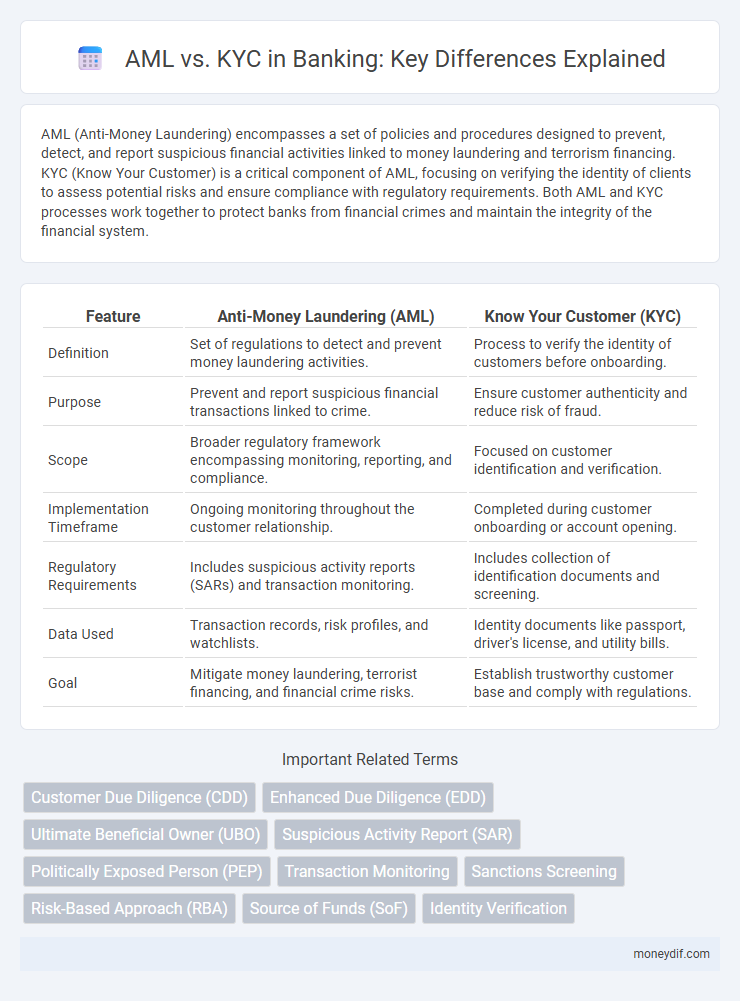
| Feature | Anti-Money Laundering (AML) | Know Your Customer (KYC) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Set of regulations to detect and prevent money laundering activities. | Process to verify the identity of customers before onboarding. |
| Purpose | Prevent and report suspicious financial transactions linked to crime. | Ensure customer authenticity and reduce risk of fraud. |
| Scope | Broader regulatory framework encompassing monitoring, reporting, and compliance. | Focused on customer identification and verification. |
| Implementation Timeframe | Ongoing monitoring throughout the customer relationship. | Completed during customer onboarding or account opening. |
| Regulatory Requirements | Includes suspicious activity reports (SARs) and transaction monitoring. | Includes collection of identification documents and screening. |
| Data Used | Transaction records, risk profiles, and watchlists. | Identity documents like passport, driver's license, and utility bills. |
| Goal | Mitigate money laundering, terrorist financing, and financial crime risks. | Establish trustworthy customer base and comply with regulations. |
Understanding the Fundamentals: AML and KYC in Banking
AML (Anti-Money Laundering) involves comprehensive regulatory measures and monitoring systems designed to detect and prevent money laundering activities within financial institutions. KYC (Know Your Customer) refers to the verification processes that banks implement to identify the identity of their clients, assess risks, and ensure compliance with AML regulations. Both AML and KYC are critical in maintaining the integrity of the banking system by reducing fraudulent transactions and enhancing customer due diligence.
Key Differences Between AML and KYC
AML (Anti-Money Laundering) refers to the comprehensive regulatory framework designed to detect, prevent, and report suspicious financial activities that may involve money laundering or terrorist financing. KYC (Know Your Customer) is a specific process within AML that involves verifying the identity and assessing the risk profile of customers to ensure compliance and prevent fraud. While AML encompasses broader policies and monitoring systems, KYC focuses primarily on customer identification and due diligence at the onboarding stage.
Regulatory Frameworks Governing AML and KYC
AML (Anti-Money Laundering) and KYC (Know Your Customer) are governed by stringent regulatory frameworks including the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) recommendations, USA PATRIOT Act, and the European Union's AML Directives. These frameworks mandate comprehensive customer due diligence, ongoing transaction monitoring, and reporting suspicious activities to combat financial crimes and terrorism financing. Financial institutions must ensure compliance with these laws to mitigate legal risks and enhance the integrity of the banking sector.
The Role of AML in Preventing Financial Crimes
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) plays a critical role in preventing financial crimes by detecting and reporting suspicious activities to authorities, thereby reducing the risk of illicit funds entering the financial system. AML frameworks encompass comprehensive monitoring, transaction analysis, and customer due diligence to identify patterns indicative of money laundering, terrorist financing, and fraud. Effective AML programs complement Know Your Customer (KYC) processes by continuously verifying client information and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards to safeguard the integrity of banking institutions.
KYC Processes: Customer Identification and Verification
Know Your Customer (KYC) processes are critical in banking for customer identification and verification to prevent fraud and comply with Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations. KYC involves collecting government-issued identification, proof of address, and biometric data to authenticate customer identities and assess risk levels. Robust KYC procedures enhance regulatory compliance and strengthen financial institutions' defenses against money laundering and terrorism financing.
Technological Innovations in AML and KYC Compliance
Technological innovations in AML and KYC compliance have revolutionized risk management in banking by leveraging artificial intelligence, machine learning, and blockchain technologies to enhance transaction monitoring and customer verification processes. Advanced analytics and biometric authentication enable faster, more accurate detection of suspicious activities while reducing false positives and improving customer onboarding experience. Integration of real-time data sharing and automated reporting systems ensures regulatory adherence and strengthens financial institutions' defenses against money laundering and fraud.
Challenges Faced by Banks in Implementing AML and KYC
Banks face significant challenges in implementing AML (Anti-Money Laundering) and KYC (Know Your Customer) regulations due to the complexity of continuously updating compliance frameworks to match evolving legal requirements and sophisticated financial crimes. High costs linked to advanced technology integration, skilled personnel training, and the management of vast volumes of customer data impact operational efficiency. Furthermore, there is a delicate balance between rigorous due diligence processes and maintaining customer experience, complicated by regulatory inconsistencies across jurisdictions.
The Impact of AML and KYC on Customer Experience
AML and KYC regulations play a critical role in preventing financial crimes while shaping customer onboarding processes. Effective AML and KYC frameworks enhance trust and security but can also introduce friction through identity verification and ongoing monitoring. Streamlining these protocols with advanced technologies like biometrics and AI-driven risk assessments improves compliance and significantly elevates the overall customer experience in banking.
Global Trends and Best Practices in AML and KYC
Global trends in Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) practices emphasize the integration of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance customer due diligence and transaction monitoring. Regulatory bodies worldwide are increasingly adopting risk-based approaches and mandating comprehensive data sharing among financial institutions to improve the detection of suspicious activities. Best practices include continuous employee training, leveraging biometrics for identity verification, and implementing real-time monitoring systems to ensure compliance and reduce financial crime risks.
Future Outlook: Evolving Strategies in AML and KYC Compliance
Financial institutions are increasingly adopting advanced AI-driven analytics and blockchain technology to enhance AML and KYC compliance, improving transaction monitoring and identity verification accuracy. Regulatory bodies are expected to enforce stricter guidelines, prioritizing real-time data sharing and cross-border collaboration to combat financial crimes more effectively. The integration of biometric authentication and automated risk assessment tools will play a critical role in shaping future AML and KYC strategies, ensuring faster compliance and reduced operational costs.
Important Terms
Customer Due Diligence (CDD)
Customer Due Diligence (CDD) involves verifying the identity and assessing the risk profile of clients to prevent money laundering, a core requirement under Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations. Unlike Know Your Customer (KYC), which primarily focuses on identity verification, CDD encompasses ongoing monitoring and enhanced scrutiny for higher-risk customers to detect and deter suspicious financial activities.
Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD)
Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) is a rigorous process mandated under Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations to identify, assess, and mitigate risks posed by high-risk customers or transactions, going beyond standard Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures. EDD involves in-depth verification of customer identity, source of funds, and ongoing monitoring to detect suspicious activities and comply with regulatory frameworks such as the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) recommendations.
Ultimate Beneficial Owner (UBO)
Ultimate Beneficial Owner (UBO) identification is crucial in Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) processes to prevent financial crimes by revealing individuals who control or benefit from legal entities. Accurate UBO disclosure enhances regulatory compliance, risk assessment, and transparency, effectively reducing money laundering and terrorist financing risks.
Suspicious Activity Report (SAR)
A Suspicious Activity Report (SAR) is a critical document filed by financial institutions to comply with Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations, identifying potential money laundering or fraud activities. Unlike Know Your Customer (KYC) processes that verify customer identity and assess risk at onboarding, SARs focus on reporting and investigating suspicious behaviors detected during ongoing transactions.
Politically Exposed Person (PEP)
Politically Exposed Persons (PEPs) require enhanced due diligence under Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations due to their higher risk of involvement in bribery and corruption. Know Your Customer (KYC) processes integrate specific identification and monitoring steps for PEPs to prevent illicit financial activities and ensure compliance with global AML standards.
Transaction Monitoring
Transaction monitoring involves continuous analysis of financial transactions to detect suspicious activity, playing a crucial role in Anti-Money Laundering (AML) efforts by identifying potential money laundering risks. Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures complement transaction monitoring by verifying customer identities and assessing risk profiles, enabling more effective detection and prevention of illicit financial activities.
Sanctions Screening
Sanctions screening involves checking individuals and entities against global watchlists to prevent transactions with sanctioned parties, playing a critical role in Anti-Money Laundering (AML) efforts. While Know Your Customer (KYC) focuses on verifying customer identity and risk assessment, sanctions screening specifically targets compliance with international regulations to avoid legal and financial penalties.
Risk-Based Approach (RBA)
Risk-Based Approach (RBA) in Anti-Money Laundering (AML) focuses on identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks based on customer profiles and transaction behaviors, allowing resources to be allocated efficiently to higher-risk areas. Unlike Know Your Customer (KYC), which primarily involves verifying customer identity, RBA integrates continuous risk assessment and monitoring to adapt AML controls dynamically and enhance compliance effectiveness.
Source of Funds (SoF)
Source of Funds (SoF) verification is a critical component in Anti-Money Laundering (AML) compliance, ensuring that the origin of financial resources is legitimate and traceable to prevent illicit activities. In Know Your Customer (KYC) processes, SoF documentation validates customer transactions by confirming income sources, employment status, or business operations, thereby mitigating risks associated with fraud and financial crimes.
Identity Verification
Identity verification in AML (Anti-Money Laundering) focuses on preventing illicit financial activities by confirming customers' identities through document checks and biometric data, while KYC (Know Your Customer) involves ongoing customer risk assessment and behavior monitoring to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. Effective identity verification strengthens AML efforts by enabling accurate KYC profiling, reducing fraud, and enhancing overall financial security.
AML vs KYC Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com