Callable deposits allow banks to redeem the deposit before maturity, offering flexibility to manage interest rate risks, while non-callable deposits lock funds for a fixed term ensuring stable returns for depositors. Callable deposit holders may face reinvestment risk if the bank exercises the call option, whereas non-callable deposit holders benefit from guaranteed interest payments and principal security throughout the term. Choosing between callable and non-callable deposits depends on the depositor's preference for liquidity versus fixed income stability.
Table of Comparison
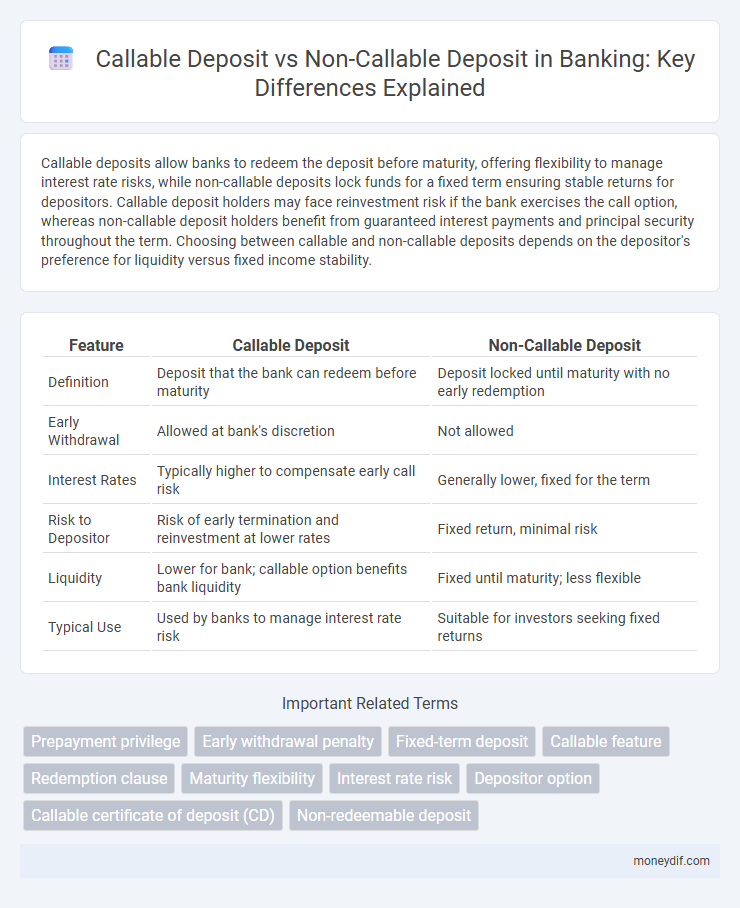
| Feature | Callable Deposit | Non-Callable Deposit |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Deposit that the bank can redeem before maturity | Deposit locked until maturity with no early redemption |
| Early Withdrawal | Allowed at bank's discretion | Not allowed |
| Interest Rates | Typically higher to compensate early call risk | Generally lower, fixed for the term |
| Risk to Depositor | Risk of early termination and reinvestment at lower rates | Fixed return, minimal risk |
| Liquidity | Lower for bank; callable option benefits bank liquidity | Fixed until maturity; less flexible |
| Typical Use | Used by banks to manage interest rate risk | Suitable for investors seeking fixed returns |
Understanding Callable Deposits
Callable deposits provide banks with the flexibility to withdraw funds before maturity, typically offering higher interest rates compared to non-callable deposits. These deposits come with a predefined call period during which the bank can decide to recall the funds, helping manage liquidity risks more effectively. Investors benefit from better returns but must accept potential early withdrawal by the bank, which impacts investment planning.
What Are Non-Callable Deposits?
Non-callable deposits are fixed-term banking products where the depositor cannot withdraw funds before the maturity date without incurring penalties. These deposits offer higher interest rates compared to callable deposits due to the locked-in investment period, providing predictable returns for both banks and customers. Common examples include certificates of deposit (CDs) and fixed deposits with specified terms ranging from months to years.
Key Differences: Callable vs Non-Callable Deposits
Callable deposits allow banks to redeem the deposit before maturity, providing greater liquidity and flexibility in managing interest rates, unlike non-callable deposits which lock funds for a fixed term with guaranteed interest. Callable deposits typically offer lower interest rates due to their redeemable feature, whereas non-callable deposits often yield higher returns as they prevent early withdrawal risk. Understanding these key differences helps depositors choose between flexible cash access and potentially higher earnings based on their investment priorities.
Interest Rate Implications
Callable deposits generally offer higher interest rates compared to non-callable deposits due to the issuer's right to terminate the deposit before maturity, which introduces reinvestment risk for the investor. Non-callable deposits provide more stable and predictable returns with fixed interest rates throughout the term, appealing to risk-averse investors seeking guaranteed income. Interest rate fluctuations significantly impact callable deposits, as early call features tend to activate when rates decline, limiting potential earnings, whereas non-callable deposits lock in the agreed interest rate regardless of market changes.
Flexibility for Banks and Depositors
Callable deposits offer banks enhanced liquidity management by allowing them to redeem funds before maturity, providing greater flexibility in adjusting to interest rate changes and liquidity needs. Depositors in callable deposits accept potential early withdrawal but may benefit from higher interest rates as compensation for reduced certainty. Non-callable deposits, in contrast, provide depositors with fixed-term security and predictable returns, while limiting the bank's ability to reallocate funds before maturity, potentially reducing financial adaptability.
Risk Assessment: Callable vs Non-Callable
Callable deposits pose higher risk for depositors due to the bank's right to redeem the principal before maturity, potentially causing reinvestment risk at lower interest rates. Non-callable deposits offer predictable returns and lower liquidity risk, as funds cannot be withdrawn prematurely by the bank. Financial institutions assess callable deposits as higher risk liabilities, requiring careful management of interest rate exposure and liquidity reserves.
Suitability for Different Investors
Callable deposits suit investors seeking higher interest rates with the flexibility to allow banks to redeem the deposit early, ideal for risk-tolerant individuals or institutions expecting interest rate fluctuations. Non-callable deposits provide fixed maturity and guaranteed returns, appealing to conservative investors prioritizing capital preservation and predictable income streams. The choice depends on an investor's risk tolerance, need for liquidity, and interest rate outlook.
Liquidity Considerations
Callable deposits offer enhanced liquidity as the bank can redeem the deposit before maturity, providing flexibility for both the institution and the depositor. Non-callable deposits generally lock funds until maturity, restricting access and potentially impacting cash flow management. Understanding liquidity needs is crucial when choosing between callable and non-callable deposits to optimize short-term financial planning.
Impact on Banking Strategies
Callable deposits allow banks to manage liquidity more flexibly by redeeming funds before maturity, enabling rapid response to interest rate fluctuations and funding needs. Non-callable deposits offer stability in funding sources, supporting long-term asset-liability management and reducing refinancing risk. The strategic choice between these deposit types influences interest expense optimization and balance sheet risk profiles.
Making the Right Choice: Factors to Consider
When selecting between callable and non-callable deposits, consider the flexibility needs and interest rate environment. Callable deposits offer banks the option to redeem the deposit early, typically yielding higher interest rates but carrying the risk of early termination for depositors. Non-callable deposits provide fixed terms and guaranteed returns, making them suitable for investors prioritizing stability and predictable income.
Important Terms
Prepayment privilege
Prepayment privilege in callable deposits allows investors to withdraw funds before maturity without penalty, enhancing liquidity compared to non-callable deposits, which restrict access until the fixed term ends. Callable deposits often feature higher interest rates as compensation for this flexibility, whereas non-callable deposits typically offer lower yields but greater interest rate stability.
Early withdrawal penalty
Callable deposits often impose early withdrawal penalties allowing the bank to call the deposit before maturity, whereas non-callable deposits typically do not permit early withdrawal, thereby avoiding such penalties. Penalties on callable deposits can include loss of interest earned or fees, impacting the effective return compared to the fixed terms of non-callable deposits.
Fixed-term deposit
Fixed-term deposits offer guaranteed interest rates over a specified period, with callable deposits allowing the bank to redeem the funds before maturity, often at a premium, while non-callable deposits provide stability by locking in the investment until the agreed term ends. Callable deposits typically yield higher returns due to the issuer's option to call, whereas non-callable deposits minimize reinvestment risk by ensuring full-term investment.
Callable feature
Callable deposits offer financial institutions the flexibility to redeem the deposit before maturity, usually after a lock-in period, enabling them to manage interest rate risks effectively. In contrast, non-callable deposits provide fixed-term investment security to depositors, ensuring guaranteed access to funds only at maturity without early withdrawal options.
Redemption clause
Redemption clause in callable deposits allows the issuer to redeem the deposit before maturity, offering flexibility to manage interest rate risks, unlike non-callable deposits which lack early redemption options, ensuring fixed returns for investors. Callable deposits typically have higher interest rates to compensate for redemption risk, whereas non-callable deposits provide stable, predictable income without early termination possibilities.
Maturity flexibility
Callable deposits offer maturity flexibility by allowing the bank to redeem the deposit before its scheduled maturity date, providing adaptability to changing interest rates, while non-callable deposits lock the funds until the end of the agreed term, ensuring fixed maturity but less flexibility for either party. Investors in callable deposits often face reinvestment risk if the deposit is called early, whereas non-callable deposits provide predictable returns over a fixed maturity period.
Interest rate risk
Interest rate risk affects callable deposits more significantly because issuers can redeem these deposits before maturity when interest rates decline, forcing investors to reinvest at lower rates. Non-callable deposits, lacking early redemption options, provide more stability against interest rate fluctuations by maintaining a fixed return until maturity.
Depositor option
Callable deposits provide depositors the option to withdraw funds before maturity with potential penalties, offering flexibility but typically lower interest rates. Non-callable deposits restrict early withdrawal, ensuring fixed returns and higher interest rates, appealing to investors prioritizing guaranteed earnings and term stability.
Callable certificate of deposit (CD)
Callable certificates of deposit (CDs) allow issuers to redeem the CD before maturity, typically offering higher interest rates compared to non-callable deposits, which lock in the rate for the entire term. Investors in callable CDs face reinvestment risk due to the issuer's right to call the CD, while non-callable deposits provide fixed returns and greater predictability.
Non-redeemable deposit
Non-redeemable deposits, unlike callable deposits, do not allow early withdrawal before maturity, ensuring fixed tenure investment and stable returns without liquidity flexibility; non-callable deposits similarly restrict premature redemption but differ from callable deposits, which grant issuers the right to redeem the deposit early, often influenced by interest rate changes or financial strategy. This distinction impacts investor risk profiles, with non-redeemable and non-callable deposits favoring investors seeking predictable income over access to funds, contrasting the callability feature that introduces potential reinvestment risk.
Callable deposit vs Non-callable deposit Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com