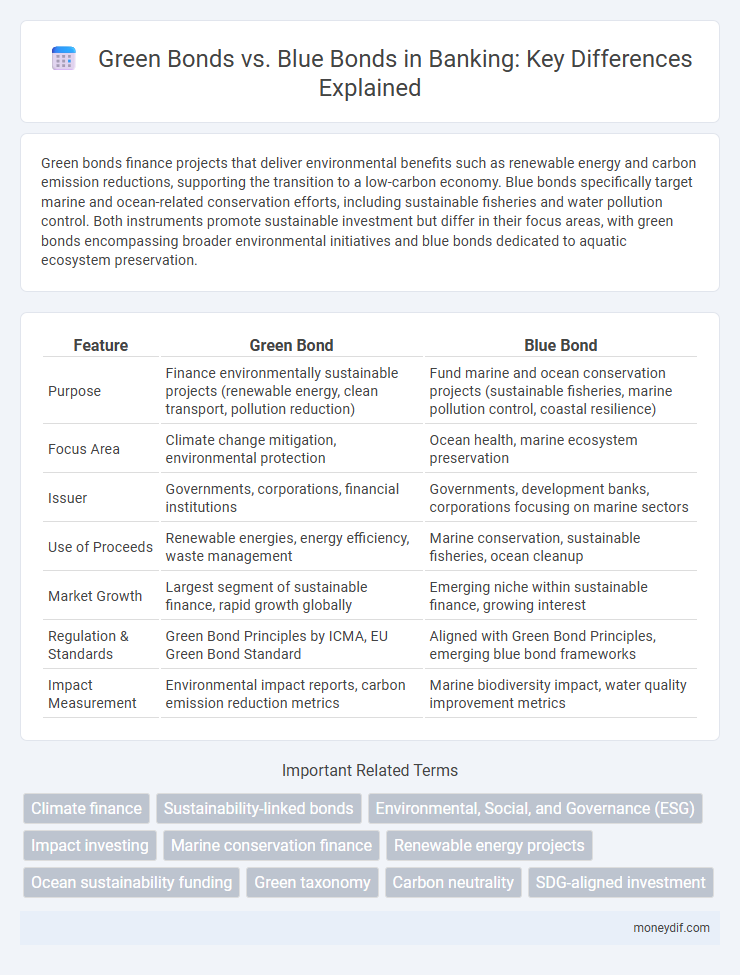
Green bonds finance projects that deliver environmental benefits such as renewable energy and carbon emission reductions, supporting the transition to a low-carbon economy. Blue bonds specifically target marine and ocean-related conservation efforts, including sustainable fisheries and water pollution control. Both instruments promote sustainable investment but differ in their focus areas, with green bonds encompassing broader environmental initiatives and blue bonds dedicated to aquatic ecosystem preservation.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Green Bond | Blue Bond |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Finance environmentally sustainable projects (renewable energy, clean transport, pollution reduction) | Fund marine and ocean conservation projects (sustainable fisheries, marine pollution control, coastal resilience) |
| Focus Area | Climate change mitigation, environmental protection | Ocean health, marine ecosystem preservation |
| Issuer | Governments, corporations, financial institutions | Governments, development banks, corporations focusing on marine sectors |
| Use of Proceeds | Renewable energies, energy efficiency, waste management | Marine conservation, sustainable fisheries, ocean cleanup |
| Market Growth | Largest segment of sustainable finance, rapid growth globally | Emerging niche within sustainable finance, growing interest |
| Regulation & Standards | Green Bond Principles by ICMA, EU Green Bond Standard | Aligned with Green Bond Principles, emerging blue bond frameworks |
| Impact Measurement | Environmental impact reports, carbon emission reduction metrics | Marine biodiversity impact, water quality improvement metrics |
Introduction to Green Bonds and Blue Bonds
Green bonds finance projects that generate positive environmental benefits, primarily targeting renewable energy, energy efficiency, and pollution reduction. Blue bonds specifically support marine and water-related initiatives, including ocean conservation, sustainable fisheries, and water resource management. Both bond types attract socially responsible investors aiming to fund sustainable development and environmental protection efforts.
Defining Green Bonds: Purpose and Scope
Green bonds are debt instruments specifically issued to finance projects that generate positive environmental benefits, such as renewable energy, energy efficiency, and sustainable waste management. Their primary purpose is to support climate change mitigation and environmental sustainability within sectors like clean transportation and green infrastructure. Unlike blue bonds, which target marine and water resource conservation, green bonds cover a broader scope encompassing diverse ecosystems and carbon reduction initiatives.
What Are Blue Bonds? Key Characteristics
Blue bonds are debt instruments specifically designed to finance ocean and water-related projects, such as marine conservation, sustainable fisheries, and coastal resilience initiatives. These bonds prioritize environmental impact by supporting activities that protect marine ecosystems and ensure the sustainable use of aquatic resources. Key characteristics include targeted use of proceeds for blue economy projects, alignment with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria, and strong investor interest driven by growing awareness of water resource challenges.
Environmental Objectives: Green vs Blue Financing
Green bonds primarily finance projects that promote renewable energy, energy efficiency, and pollution reduction to combat climate change and foster sustainable development. Blue bonds specifically target marine and water-related initiatives, including ocean conservation, sustainable fisheries, and clean water infrastructure to protect aquatic ecosystems. Both financing mechanisms support environmental objectives but differ in focus, with green bonds addressing broader environmental sustainability and blue bonds concentrating on marine and freshwater resource preservation.
Sectors Funded by Green and Blue Bonds
Green bonds primarily fund renewable energy, energy efficiency, sustainable agriculture, and pollution prevention projects, targeting environmental benefits and climate change mitigation. Blue bonds focus specifically on ocean and water-related sectors such as marine conservation, sustainable fisheries, and clean water infrastructure, addressing marine ecosystem protection and water resource management. Both bond types support sustainable development but differ in their sector-specific impact areas.
Impact Measurement: Green Bond vs Blue Bond Metrics
Green bonds primarily measure impact through reductions in carbon emissions and investments in renewable energy projects, tracking metrics such as CO2 avoided and energy generated. Blue bonds focus on ocean-related outcomes, emphasizing metrics like improvements in marine biodiversity, water quality, and sustainable fisheries management. Both bond types increasingly integrate third-party verifications and standardized reporting frameworks to ensure transparency and accountability in environmental impact assessments.
Regulatory Frameworks and Standards
Green bonds adhere to established regulatory frameworks such as the Climate Bonds Initiative standards and EU Green Bond Standard, promoting transparency and environmental impact reporting. Blue bonds, while emerging, follow similar regulatory principles but focus specifically on ocean and marine conservation projects, with evolving guidelines like the Blue Bond Principles set by the International Capital Market Association. Both bond types require rigorous verification processes to ensure compliance with sustainability criteria and investor confidence.
Investor Perspectives on Green and Blue Bonds
Investors view green bonds as instruments dedicated to financing projects with environmental benefits like renewable energy and pollution reduction, offering stable returns aligned with sustainability goals. Blue bonds specifically target ocean-related initiatives, such as marine conservation and sustainable fisheries, attracting investors focused on aquatic ecosystem preservation and climate resilience. Both bond types provide opportunities for impact investing, with blue bonds appealing to a niche market prioritizing ocean health within the broader ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) investment framework.
Challenges and Opportunities in Green and Blue Bond Markets
Green and blue bond markets face challenges including limited investor awareness, regulatory uncertainties, and difficulty in measuring environmental impact. Opportunities arise from increasing global demand for sustainable finance, growing government support, and advancements in impact assessment technologies. Effective risk management and transparent reporting can enhance market confidence and drive capital flow toward environmentally beneficial projects.
Future Trends: The Outlook for Green and Blue Bonds in Banking
Green bonds are projected to dominate sustainable finance due to increasing regulatory support and growing investor demand for environmental projects. Blue bonds, targeting marine and water-related initiatives, are gaining traction as climate resilience and ocean conservation become critical global priorities. Integration of advanced ESG metrics and digital platforms will enhance transparency and investor confidence, driving future growth in both green and blue bond markets within banking.
Important Terms
Climate finance
Climate finance channels investments into sustainable projects, with green bonds funding environmental initiatives such as renewable energy and pollution reduction, while blue bonds specifically target ocean-related projects including marine conservation and sustainable fisheries. Issuance of green bonds reached over $500 billion in 2023, outpacing blue bonds, which totaled approximately $5 billion but are rapidly growing due to increased focus on ocean health and climate resilience.
Sustainability-linked bonds
Sustainability-linked bonds differ from green and blue bonds by tying financial incentives to the issuer's overall sustainability performance, rather than funding specific environmental projects; green bonds primarily finance renewable energy or clean transportation, while blue bonds target marine and water resource conservation. These instruments collectively drive capital towards environmental goals, with sustainability-linked bonds offering flexible use of proceeds linked to comprehensive ESG targets, contrasting the project-specific focus of green and blue bonds.
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG)
Green bonds are financial instruments specifically designed to fund projects that have positive environmental impacts, such as renewable energy, energy efficiency, and pollution reduction initiatives, aligning closely with Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria by prioritizing sustainability and climate action. Blue bonds, a subset within ESG investing, focus on marine and water-related projects, supporting ocean conservation, sustainable fisheries, and clean water infrastructure to address environmental challenges unique to aquatic ecosystems while promoting social and governance standards in coastal communities.
Impact investing
Impact investing focuses on generating measurable environmental benefits alongside financial returns, with green bonds funding projects like renewable energy and pollution reduction, while blue bonds specifically target ocean and marine ecosystem conservation. Both bond types attract investors aiming to support sustainable development, but blue bonds are uniquely tailored to marine-related climate resilience and biodiversity protection initiatives.
Marine conservation finance
Marine conservation finance leverages green bonds and blue bonds to fund sustainable ocean projects, with green bonds broadly supporting environmental initiatives and blue bonds specifically targeting marine and coastal ecosystem protection. Blue bonds provide targeted capital for fisheries management, pollution reduction, and habitat restoration, aligning investor interests with ocean health, while green bonds enable broader climate resilience efforts including marine conservation within a wider environmental context.
Renewable energy projects
Renewable energy projects financed through green bonds focus on clean energy sources like solar, wind, and bioenergy to reduce carbon emissions and promote sustainability. Blue bonds specifically target marine and water-related renewable initiatives, such as offshore wind farms and tidal energy, alongside ocean conservation efforts to protect aquatic ecosystems.
Ocean sustainability funding
Ocean sustainability funding increasingly leverages green bonds, which finance broad environmental projects including marine conservation, while blue bonds specifically target ocean and freshwater ecosystem restoration, fisheries management, and pollution reduction. Blue bonds provide a tailored financial instrument that addresses ocean-specific challenges, fostering sustainable maritime economies and enhancing marine biodiversity protection.
Green taxonomy
Green taxonomy classifies economic activities that contribute to environmental sustainability, guiding investments in green bonds dedicated to financing projects like renewable energy and clean transportation. Blue bonds fall under this taxonomy as specialized financial instruments targeting marine and freshwater conservation, supporting initiatives such as ocean protection and sustainable fisheries.
Carbon neutrality
Carbon neutrality focuses on balancing emitted and absorbed carbon dioxide, a goal supported by green bonds that finance renewable energy, energy efficiency, and sustainable infrastructure projects. Blue bonds specifically target marine and water-related environmental projects, contributing to carbon neutrality by protecting ocean ecosystems that act as significant carbon sinks.
SDG-aligned investment
SDG-aligned investment channels capital into sustainable development by prioritizing environmental and social impact, with green bonds focusing on climate change mitigation projects such as renewable energy and energy efficiency, while blue bonds specifically target marine and ocean conservation initiatives like sustainable fisheries and coastal ecosystem restoration. Both bonds contribute to achieving the Sustainable Development Goals by financing projects that promote sustainability, but blue bonds address the unique challenges of aquatic environments critical for biodiversity and livelihoods.
Green bond vs Blue bond Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com