A custodian is a financial institution responsible for safeguarding a client's securities and assets, ensuring proper settlement and record-keeping. A depository, on the other hand, serves as a centralized electronic repository for holding and transferring securities, facilitating efficient clearing and settlement processes. Both play crucial roles in the brokerage ecosystem, but custodians focus on asset protection while depositories streamline transaction settlements.
Table of Comparison
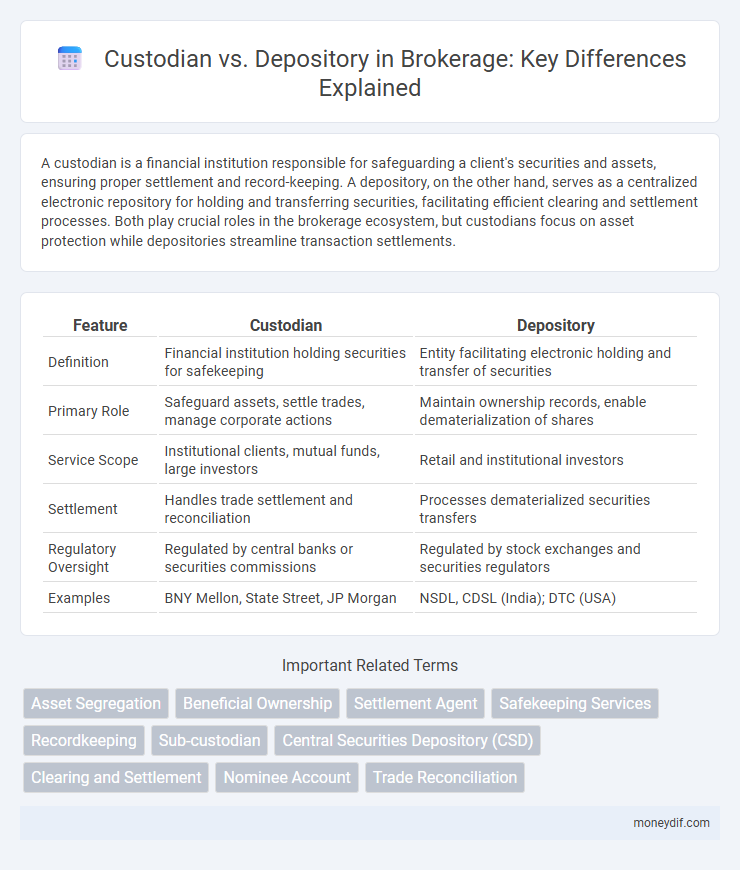
| Feature | Custodian | Depository |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Financial institution holding securities for safekeeping | Entity facilitating electronic holding and transfer of securities |
| Primary Role | Safeguard assets, settle trades, manage corporate actions | Maintain ownership records, enable dematerialization of shares |
| Service Scope | Institutional clients, mutual funds, large investors | Retail and institutional investors |
| Settlement | Handles trade settlement and reconciliation | Processes dematerialized securities transfers |
| Regulatory Oversight | Regulated by central banks or securities commissions | Regulated by stock exchanges and securities regulators |
| Examples | BNY Mellon, State Street, JP Morgan | NSDL, CDSL (India); DTC (USA) |
Introduction to Custodians and Depositories in Brokerage
Custodians in brokerage safeguard clients' securities, ensuring proper settlement and holding of assets to prevent loss or misuse. Depositories provide electronic storage and facilitate the transfer of securities, enabling seamless settlement and reducing the risks associated with physical certificates. Both entities play crucial roles in maintaining market integrity and investor confidence through secure and efficient asset management.
Definitions: What Is a Custodian?
A custodian is a financial institution responsible for safeguarding a client's securities and assets, ensuring their protection against theft or loss. Unlike a depository, which primarily holds securities in electronic form and facilitates their transfer, a custodian provides comprehensive services including settlement, reporting, and corporate actions management. Custodians play a crucial role in brokerage by maintaining asset security and enabling smooth transaction processing.
Definitions: What Is a Depository?
A depository is a financial institution that holds securities such as stocks, bonds, or mutual funds in electronic form, enabling secure and efficient transactions for investors. It acts as a central repository that facilitates the transfer, settlement, and safekeeping of financial assets, eliminating the need for physical certificates. Depositories play a critical role in modern brokerage operations by ensuring transparency, reducing risks associated with handling physical documents, and streamlining the settlement process.
Key Functions of Custodians in Brokerage
Custodians in brokerage primarily safeguard clients' securities and manage settlement processes, ensuring the safe transfer and holding of assets. They provide essential services such as asset servicing, including dividend collection, corporate actions processing, and reporting, enhancing transparency and operational efficiency. Custodians also play a critical role in regulatory compliance and risk management, protecting investors against fraud and operational errors.
Core Roles of Depositories in Financial Markets
Depositories play a crucial role in financial markets by holding securities in electronic form, ensuring secure and efficient transfer of ownership while minimizing the risks associated with physical certificates. They facilitate seamless settlement of trades by providing a centralized platform for dematerialization, rematerialization, and maintenance of securities accounts. Custodians, in contrast, primarily manage the safekeeping of assets and provide administrative services, whereas depositories specialize in the electronic handling and transfer of securities to streamline market operations.
Custodian vs Depository: Main Differences
Custodians safeguard financial assets on behalf of clients, providing personalized services such as settlement, reporting, and compliance management, while depositories primarily focus on holding securities electronically to facilitate easy transfer and settlement. Custodians often serve institutional investors with tailored asset protection and administrative support, whereas depositories act as central repositories ensuring security and efficiency in securities holding and clearing. The main differences lie in the scope of services, client focus, and regulatory frameworks governing each entity within the brokerage ecosystem.
Advantages of Using a Custodian
Custodians provide enhanced security for clients' assets by safeguarding securities in segregated accounts, reducing the risk of loss or theft compared to depositories. They offer comprehensive record-keeping and reporting services, enabling easier tracking of investment portfolios and facilitating regulatory compliance. Custodians also streamline settlement processes and provide value-added services such as income collection, tax support, and proxy voting, improving overall operational efficiency.
Benefits of Depositories for Investors
Depositories offer investors enhanced security by electronically holding securities, eliminating the risks associated with physical certificates such as loss, theft, or damage. They facilitate faster and more efficient transactions, allowing instant settlement and transfer of ownership, which increases liquidity and reduces settlement risks. Depositories also provide seamless access to corporate actions, dividend payments, and portfolio management services, significantly improving the overall investor experience.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Custodian and Depository
When choosing between a custodian and a depository, prioritize factors such as the level of asset protection, regulatory compliance, and transaction efficiency. Custodians typically offer personalized asset management and secure holding services, while depositories provide centralized clearing and settlement systems with faster trade processing. Consider the cost structure, technological integration, and the specific needs of your portfolio to ensure optimal risk management and operational convenience.
Conclusion: Which Is Better for Your Brokerage Needs?
Choosing between a custodian and a depository depends on your brokerage needs, as custodians offer personalized asset safekeeping and management, while depositories specialize in secure and efficient transaction settlements. Custodians provide tailored services such as asset servicing, compliance support, and risk management, making them ideal for individualized portfolio handling. Depositories excel in centralized record-keeping and streamlined securities transfer, benefiting brokerages prioritizing operational efficiency and regulatory adherence.
Important Terms
Asset Segregation
Asset segregation ensures client funds are separately maintained by custodians instead of being pooled with depository holdings, enhancing security and regulatory compliance.
Beneficial Ownership
Beneficial ownership refers to the true owner of securities held indirectly through a custodian or depository, where the custodian safeguards assets on behalf of clients while the depository records and facilitates the transfer of securities ownership.
Settlement Agent
A settlement agent ensures the transfer of securities by coordinating between custodians, who safeguard assets, and depositories, which hold and record securities transactions.
Safekeeping Services
Safekeeping services involve custodians who manage securities on behalf of clients with ownership rights, whereas depositories provide electronic record-keeping and facilitate the transfer of securities without holding ownership.
Recordkeeping
Custodians safeguard securities and maintain detailed transaction records on behalf of investors, ensuring precise recordkeeping and compliance with regulatory standards. Depositories, meanwhile, centralize the holding of securities in electronic form, streamlining recordkeeping by facilitating efficient transfer and settlement processes across financial markets.
Sub-custodian
A sub-custodian is a third-party financial institution appointed by a custodian bank to safeguard assets in foreign markets that the custodian cannot directly access, contrasting with depositories that hold securities directly for investors.
Central Securities Depository (CSD)
A Central Securities Depository (CSD) primarily facilitates the safekeeping and electronic settlement of securities, whereas a Custodian provides asset safekeeping, settlement, and value-added services on behalf of clients, highlighting their distinct roles in securities management.
Clearing and Settlement
Custodians safeguard and manage clients' securities while depositories facilitate electronic settlement and transfer of those securities within the clearing and settlement infrastructure.
Nominee Account
A nominee account held by a custodian enables investors to maintain beneficial ownership of securities while the depository facilitates electronic recording and transfer of these securities on the investor's behalf.
Trade Reconciliation
Trade reconciliation between custodians and depositories ensures accurate alignment of transaction records, mitigating settlement risks and enhancing operational efficiency in securities processing.
Custodian vs Depository Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com