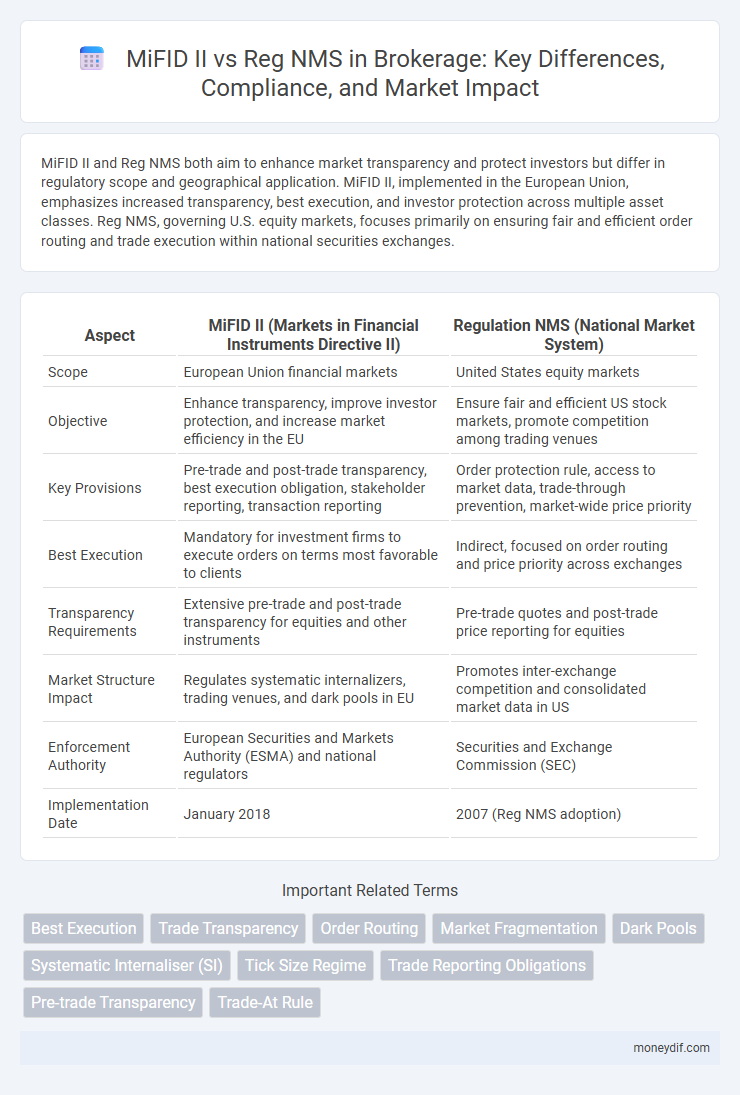
MiFID II and Reg NMS both aim to enhance market transparency and protect investors but differ in regulatory scope and geographical application. MiFID II, implemented in the European Union, emphasizes increased transparency, best execution, and investor protection across multiple asset classes. Reg NMS, governing U.S. equity markets, focuses primarily on ensuring fair and efficient order routing and trade execution within national securities exchanges.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | MiFID II (Markets in Financial Instruments Directive II) | Regulation NMS (National Market System) |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | European Union financial markets | United States equity markets |
| Objective | Enhance transparency, improve investor protection, and increase market efficiency in the EU | Ensure fair and efficient US stock markets, promote competition among trading venues |
| Key Provisions | Pre-trade and post-trade transparency, best execution obligation, stakeholder reporting, transaction reporting | Order protection rule, access to market data, trade-through prevention, market-wide price priority |
| Best Execution | Mandatory for investment firms to execute orders on terms most favorable to clients | Indirect, focused on order routing and price priority across exchanges |
| Transparency Requirements | Extensive pre-trade and post-trade transparency for equities and other instruments | Pre-trade quotes and post-trade price reporting for equities |
| Market Structure Impact | Regulates systematic internalizers, trading venues, and dark pools in EU | Promotes inter-exchange competition and consolidated market data in US |
| Enforcement Authority | European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA) and national regulators | Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) |
| Implementation Date | January 2018 | 2007 (Reg NMS adoption) |
Introduction to MiFID II and Reg NMS
MiFID II (Markets in Financial Instruments Directive II) is a comprehensive European Union regulatory framework implemented to enhance transparency, investor protection, and market efficiency in financial markets. Reg NMS (Regulation National Market System) is a U.S. regulatory initiative aimed at improving the fairness and competitiveness of the national equity market by promoting the best execution of trades across competing exchanges. Both MiFID II and Reg NMS establish rules governing trade execution, order handling, and market transparency but differ in geographic scope, regulatory focus, and specific compliance requirements.
Historical Background of MiFID II and Reg NMS
MiFID II, implemented in 2018, stems from the European Union's efforts to enhance transparency and investor protection following the 2007-2008 financial crisis. Reg NMS, introduced by the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission in 2007, aims to modernize and strengthen the National Market System for equity trading. Both regulations reflect critical historical responses to market fragmentation and technological advances impacting brokerage and trading environments globally.
Core Objectives: MiFID II vs Reg NMS
MiFID II aims to enhance transparency, investor protection, and market efficiency across European financial markets by imposing stringent pre- and post-trade transparency requirements and promoting fair competition. Reg NMS focuses on ensuring best execution and protecting US investors by enforcing rules that promote market competition and prevent trade fragmentation within the US equity markets. Both regulations seek to improve market integrity and investor confidence but differ in geographic scope and specific mechanisms for achieving fair and efficient trading environments.
Scope and Market Coverage Comparison
MiFID II governs European financial markets with a comprehensive scope covering equities, bonds, derivatives, and ETFs across all trading venues, emphasizing investor protection and market transparency. Regulation National Market System (Reg NMS) primarily focuses on U.S. equity markets, enforcing rules to promote fair and efficient trading across national exchanges and alternative trading systems. MiFID II's broader market coverage contrasts with Reg NMS's targeted approach to enhance price transparency and best execution within U.S. equities only.
Key Regulatory Requirements
MiFID II mandates enhanced transparency through pre- and post-trade reporting, strict best execution policies, and comprehensive market data access across EU venues. Reg NMS enforces robust order protection rules, real-time market data dissemination, and access to multiple trading venues, ensuring fair and efficient US equity markets. Both regulations aim to promote investor protection and market integrity but differ in scope and implementation frameworks specific to their jurisdictions.
Impact on Brokerages and Trading Venues
MiFID II enhances transparency and investor protection by imposing stringent pre- and post-trade reporting requirements on European brokerages and trading venues, resulting in increased operational costs but greater market integrity. Reg NMS, primarily affecting U.S. brokerages, focuses on promoting fair and efficient markets through rules like the Order Protection Rule, which mandates routing orders to the best price across trading venues, fostering competition but raising compliance complexity. Brokerages operating transatlantically face challenges reconciling MiFID II's comprehensive data disclosure demands with Reg NMS's emphasis on order execution quality, significantly impacting technology infrastructure and trading strategies.
Transparency and Reporting Standards
MiFID II enforces comprehensive transparency and reporting standards across EU brokerage activities, requiring pre- and post-trade transparency along with detailed transaction reporting to regulators and clients. In contrast, Reg NMS, applicable in the U.S., emphasizes market-wide trade reporting and order execution quality, promoting fairness through consolidated data feeds and the National Market System Plan. The stringent regulatory frameworks of MiFID II surpass Reg NMS in scope by mandating extensive disclosure of execution quality and enhanced post-trade transparency to protect investors.
Investor Protection Measures
MiFID II enforces stringent investor protection measures by enhancing transparency standards, imposing stricter rules on best execution, and mandating comprehensive product governance to mitigate conflicts of interest. Reg NMS, while focused primarily on market structure and facilitating fair and efficient price formation, incorporates investor protection through rules like order protection and access to multiple trading venues. The robust regulatory framework of MiFID II offers a more holistic approach to safeguarding investors compared to Reg NMS, emphasizing transparency, investor disclosures, and accountability in brokerage operations.
Challenges and Compliance Costs
MiFID II imposes extensive transparency and reporting requirements across European Union financial markets, significantly increasing compliance costs for brokerage firms due to the need for advanced monitoring and data management systems. In contrast, Reg NMS focuses primarily on ensuring fair access and order execution quality within U.S. equities markets, presenting challenges related to maintaining best execution and managing fragmented market venues. Brokerage firms face the dual challenge of aligning with MiFID II's comprehensive regulatory framework while navigating the operational complexities and compliance expenses associated with the fragmented U.S. market structure under Reg NMS.
Future Trends in Securities Regulation
Future trends in securities regulation emphasize harmonization between frameworks like MiFID II and Reg NMS to enhance market transparency and investor protection. MiFID II continues to drive stringent pre- and post-trade transparency requirements across European markets, influencing global standards. Reg NMS, focusing on US equities market structure, is increasingly integrating technology-driven solutions such as AI for best execution and real-time data dissemination.
Important Terms
Best Execution
Best Execution under MiFID II mandates investment firms to take all sufficient steps to obtain the best possible result for clients by considering factors like price, costs, speed, and likelihood of execution across multiple trading venues within the EU. In contrast, the U.S. Reg NMS primarily focuses on protecting price priority through the National Best Bid and Offer (NBBO), emphasizing transparent, efficient, and fair execution venues without the same comprehensive qualitative criteria mandated by MiFID II.
Trade Transparency
Trade transparency under MiFID II mandates comprehensive pre- and post-trade reporting requirements for European financial markets, enhancing investor protection and market integrity through detailed disclosures. In contrast, Reg NMS in the U.S. focuses primarily on ensuring price transparency and fair access to quotations across national exchanges, emphasizing order routing and best execution obligations without the extensive reporting framework found in MiFID II.
Order Routing
Order routing under MiFID II enforces transparent best execution standards across EU markets, while Reg NMS mandates fair and efficient order routing to protect US investors by ensuring access to the best available prices within national market systems.
Market Fragmentation
Market fragmentation under MiFID II increased competition by mandating multiple trading venues across the EU to promote transparency and investor protection, contrasting with Reg NMS in the US which standardizes trade execution across fewer national exchanges to ensure best execution. MiFID II's emphasis on transparency and equal access led to a proliferation of dark pools and alternative trading systems, while Reg NMS focuses on the National Best Bid and Offer (NBBO) to prevent trade-throughs and preserve market integrity.
Dark Pools
Dark pools, regulated under MiFID II in Europe with enhanced transparency and pre-trade transparency requirements, contrast with the U.S. Reg NMS framework that emphasizes fair access and order protection to limit off-exchange trading fragmentation.
Systematic Internaliser (SI)
Systematic Internalisers (SIs) under MiFID II operate as regulated entities conducting frequent, systematic, and substantial trading of equities, contrasting with Reg NMS in the U.S., which governs order protection and transparency on national exchanges without mandating internalisation.
Tick Size Regime
The Tick Size Regime under MiFID II establishes minimum price increments for equity trading in EU markets, contrasting with the Reg NMS framework in the US that focuses on order protection and routing without prescribing tick sizes.
Trade Reporting Obligations
MiFID II enforces comprehensive trade reporting obligations across EU financial markets to enhance transparency and reduce market abuse, whereas Reg NMS focuses on trade reporting and market data dissemination primarily within US equity markets to ensure best execution and market fairness.
Pre-trade Transparency
MiFID II mandates comprehensive pre-trade transparency for equity and bond markets across the EU, imposing strict publication of bid-ask quotes and order book depth, whereas Reg NMS in the US focuses primarily on pre-trade transparency for equities through the National Best Bid and Offer (NBBO) system, ensuring investors see the best available prices across exchanges.
Trade-At Rule
The Trade-At Rule under Reg NMS prioritizes executing orders at the national best bid or offer, while MiFID II emphasizes best execution across multiple European markets with increased transparency and investor protection.
MiFID II vs Reg NMS Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com