Straight-through processing (STP) enhances brokerage efficiency by automating trade execution from order placement to settlement, minimizing human error and reducing processing time. Manual processing relies heavily on human intervention, which can increase operational risks and delay transaction completion. Implementing STP streamlines workflows and improves accuracy in trade management compared to traditional manual methods.
Table of Comparison
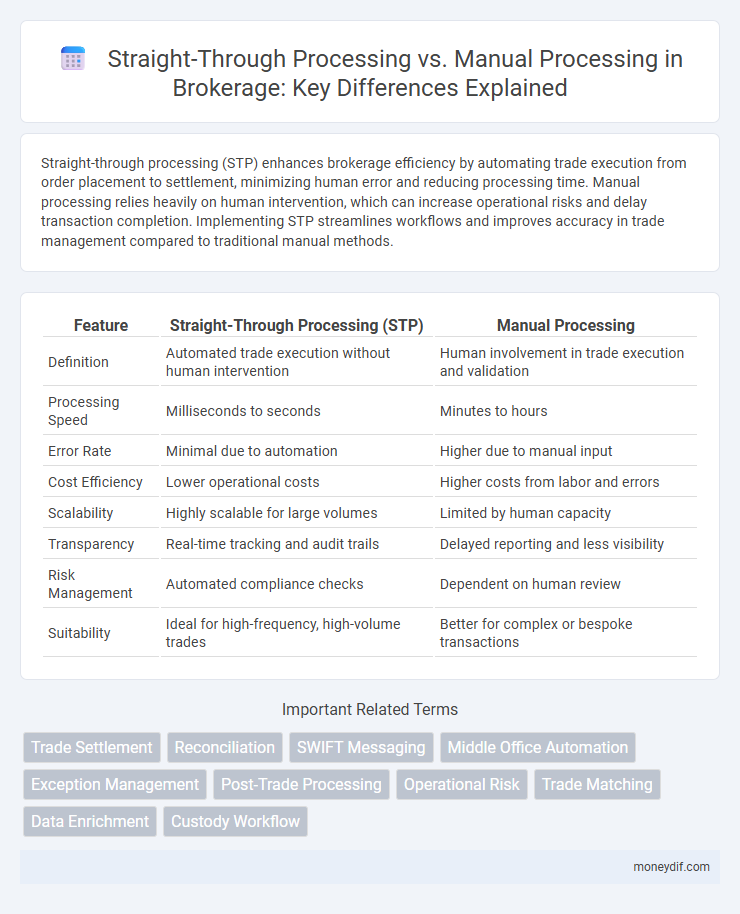
| Feature | Straight-Through Processing (STP) | Manual Processing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated trade execution without human intervention | Human involvement in trade execution and validation |
| Processing Speed | Milliseconds to seconds | Minutes to hours |
| Error Rate | Minimal due to automation | Higher due to manual input |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower operational costs | Higher costs from labor and errors |
| Scalability | Highly scalable for large volumes | Limited by human capacity |
| Transparency | Real-time tracking and audit trails | Delayed reporting and less visibility |
| Risk Management | Automated compliance checks | Dependent on human review |
| Suitability | Ideal for high-frequency, high-volume trades | Better for complex or bespoke transactions |
Introduction to Straight-Through Processing (STP) in Brokerage
Straight-Through Processing (STP) in brokerage enables automated trade execution by directly linking order placement, confirmation, and settlement systems, significantly reducing errors and processing time. This seamless integration improves operational efficiency, lowers costs, and enhances client satisfaction by minimizing manual intervention and the risk of human error during transaction processing. STP technology supports real-time data exchange, ensuring faster trade lifecycle completion compared to traditional manual processing methods.
Understanding Manual Processing in Brokerage Operations
Manual processing in brokerage operations involves human intervention for order entry, trade confirmation, and settlement tasks, which increases the risk of errors and delays. This process requires extensive input from brokers and back-office staff to verify trade details, handle exceptions, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. Compared to straight-through processing, manual workflows typically result in higher operational costs, slower transaction times, and reduced scalability in handling large volumes of trades.
Key Differences Between STP and Manual Processing
Straight-through processing (STP) automates trade execution by electronically routing orders without manual intervention, significantly reducing processing time and errors. Manual processing involves human input at multiple stages, increasing the risk of delays, data entry mistakes, and operational costs. Key differences include STP's integration with trading platforms for seamless workflow versus manual processing's reliance on paper-based or isolated system entries, impacting efficiency and scalability in brokerage operations.
Efficiency and Speed: STP vs Manual Processing
Straight-through processing (STP) significantly enhances efficiency and speed by automating transaction workflows, reducing human intervention, and minimizing errors, which leads to faster trade execution and settlement times. Manual processing, in contrast, relies on human input that increases processing time, introduces potential errors, and slows down the overall brokerage operations. STP's automated data validation and seamless integration with trading platforms enable brokers to handle higher volumes of trades rapidly compared to the slower, labor-intensive manual methods.
Error Reduction: How STP Outperforms Manual Methods
Straight-through processing (STP) significantly reduces errors by automating transaction workflows, eliminating manual data entry and minimizing human mistakes common in manual processing. STP systems validate and match trade details instantly, ensuring accuracy and compliance, which leads to faster settlement times and fewer failed trades. This automation enhances operational efficiency in brokerages by decreasing reconciliation efforts and mitigating financial risks associated with processing errors.
Cost Implications: Automated vs Manual Brokerage Processes
Straight-through processing (STP) in brokerage significantly reduces operational costs by minimizing manual intervention, lowering labor expenses, and decreasing error rates associated with manual processing. Automated brokerage workflows streamline transaction handling, resulting in faster settlement times and improved resource allocation compared to traditional manual methods. While initial investment in STP technology can be substantial, the long-term cost savings through increased efficiency and reduced risks make automated processes more cost-effective than manual brokerage operations.
Impact on Compliance and Regulatory Reporting
Straight-through processing (STP) significantly enhances compliance and regulatory reporting by automating data validation and reducing manual errors, ensuring accurate and timely submissions to regulatory bodies. In contrast, manual processing increases the risk of non-compliance due to human error, delays, and inconsistent data entries, which can result in fines and reputational damage. Leveraging STP optimizes audit trails and real-time reporting capabilities, critical for meeting stringent regulatory requirements in brokerage operations.
Client Experience: STP Versus Manual Processing
Straight-through processing (STP) enhances client experience by minimizing errors and accelerating transaction times, ensuring seamless trade execution without human intervention. Manual processing introduces delays and higher risks of mistakes due to multiple touchpoints, negatively impacting client satisfaction. Brokerages leveraging STP provide more transparent, efficient, and reliable services, fostering stronger client trust and retention.
Challenges in Implementing Straight-Through Processing
Implementing straight-through processing (STP) in brokerage faces challenges such as integrating disparate legacy systems and ensuring real-time data accuracy across multiple platforms. Manual intervention often becomes necessary to address exceptions and complex transactions that automated workflows cannot reliably handle. Compliance with evolving regulatory requirements further complicates the automation process, demanding robust validation and audit trails within STP frameworks.
Future Trends: The Evolution of Processing in Brokerage
Straight-through processing (STP) in brokerage enables seamless, automated trade execution that reduces errors and enhances efficiency, while manual processing relies heavily on human intervention, increasing operational risks and costs. Future trends indicate a shift toward fully integrated STP systems powered by artificial intelligence and blockchain technology, facilitating real-time data validation and settlement with minimal human involvement. This evolution promises improved accuracy, faster transaction times, and greater transparency in brokerage operations.
Important Terms
Trade Settlement
Trade settlement efficiency improves significantly with straight-through processing by automating transaction workflows, reducing errors and settlement time compared to manual processing.
Reconciliation
Reconciliation accuracy improves significantly with straight-through processing by automating transaction matching and reducing errors inherent in manual processing.
SWIFT Messaging
SWIFT messaging enables efficient straight-through processing by automating financial transaction communications and significantly reducing errors compared to manual processing.
Middle Office Automation
Middle Office Automation enhances straight-through processing (STP) by minimizing manual intervention, reducing errors, and accelerating trade settlements. Automating middle office workflows ensures seamless data validation, reconciliation, and risk management, optimizing operational efficiency compared to traditional manual processing methods.
Exception Management
Exception management in straight-through processing focuses on identifying and resolving discrepancies automatically to maintain seamless transaction flows, whereas manual processing relies on human intervention to handle exceptions, increasing processing time and risk of errors. Efficient exception management minimizes operational costs and enhances accuracy by reducing the frequency and impact of manual exceptions in automated workflows.
Post-Trade Processing
Post-trade processing benefits from straight-through processing (STP) by automating transaction workflows, reducing errors and settlement times compared to manual processing, which relies on human intervention and carries higher operational risks. STP enhances efficiency by seamlessly integrating trade confirmation, clearing, and settlement, while manual processing often leads to delays, increased costs, and regulatory compliance challenges.
Operational Risk
Operational risk in straight-through processing (STP) is significantly reduced due to automation minimizing human errors and processing delays, whereas manual processing increases exposure to risks such as input errors, process inconsistencies, and longer transaction times. Financial institutions leveraging STP benefit from enhanced efficiency and compliance, lowering operational losses compared to manual workflows prone to higher error rates and reconciliation issues.
Trade Matching
Trade matching automates the reconciliation of trade details between counterparties, significantly enhancing straight-through processing (STP) by reducing errors and settlement delays compared to manual processing. Manual processing introduces risks of mismatches and operational inefficiencies, whereas STP leverages real-time data validation and automated workflows to streamline post-trade operations.
Data Enrichment
Data enrichment enhances straight-through processing (STP) by automatically integrating accurate, comprehensive data sets, reducing errors and accelerating transaction times compared to manual processing, where human intervention often causes delays and inconsistencies. Leveraging enriched data in STP improves operational efficiency, customer experience, and compliance by enabling seamless, real-time decision-making without manual bottlenecks.
Custody Workflow
Custody workflow benefits significantly from straight-through processing (STP) by automating trade settlement, reducing operational risks and enhancing settlement speed compared to manual processing, which relies on human intervention prone to errors and delays. Implementing STP in custody operations improves data accuracy, streamlines reconciliation, and lowers processing costs, whereas manual workflows increase the likelihood of bottlenecks and compliance issues.
straight-through processing vs manual processing Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com