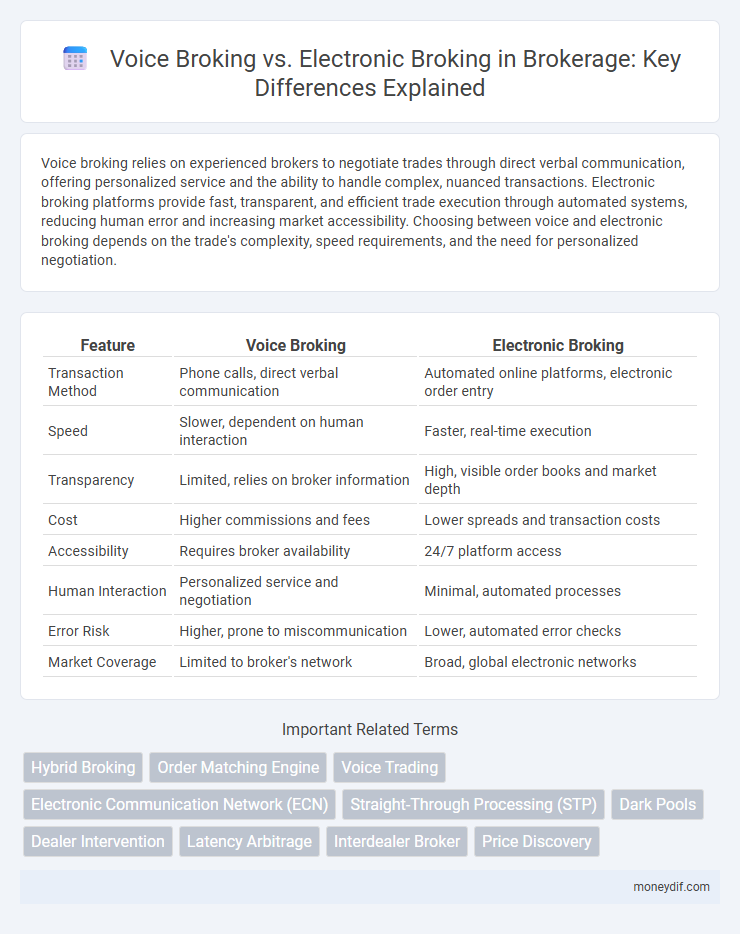
Voice broking relies on experienced brokers to negotiate trades through direct verbal communication, offering personalized service and the ability to handle complex, nuanced transactions. Electronic broking platforms provide fast, transparent, and efficient trade execution through automated systems, reducing human error and increasing market accessibility. Choosing between voice and electronic broking depends on the trade's complexity, speed requirements, and the need for personalized negotiation.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Voice Broking | Electronic Broking |
|---|---|---|
| Transaction Method | Phone calls, direct verbal communication | Automated online platforms, electronic order entry |
| Speed | Slower, dependent on human interaction | Faster, real-time execution |
| Transparency | Limited, relies on broker information | High, visible order books and market depth |
| Cost | Higher commissions and fees | Lower spreads and transaction costs |
| Accessibility | Requires broker availability | 24/7 platform access |
| Human Interaction | Personalized service and negotiation | Minimal, automated processes |
| Error Risk | Higher, prone to miscommunication | Lower, automated error checks |
| Market Coverage | Limited to broker's network | Broad, global electronic networks |
Introduction to Voice Broking and Electronic Broking
Voice broking involves traditional negotiation methods where brokers facilitate trades through direct verbal communication, emphasizing personal relationships and market expertise. Electronic broking utilizes digital platforms to execute trades rapidly, enhancing transparency and efficiency in financial markets. Both methods serve critical roles in brokerage, with voice broking catering to complex, high-value transactions and electronic broking supporting high-frequency, automated trading.
Key Differences Between Voice and Electronic Broking
Voice broking involves direct human interaction where brokers negotiate deals verbally, fostering relationship-based trading and flexible terms; electronic broking relies on automated platforms that offer speed, transparency, and standardized execution. Voice broking suits complex or bespoke transactions requiring discretion, while electronic broking excels in high-frequency, liquid markets by reducing errors and operational costs. The key differences lie in communication methods, execution speed, transparency level, and suitability for transaction complexity.
Evolution of Broking: From Voice to Electronic Platforms
The evolution of broking has witnessed a significant shift from traditional voice broking to advanced electronic broking platforms, revolutionizing trade execution speed and market transparency. Voice broking relied heavily on human interaction and phone communication, often resulting in slower transaction times and higher operational costs. Electronic broking platforms utilize sophisticated algorithms and real-time data processing, enabling immediate trade matching, reduced errors, and increased liquidity in global financial markets.
Advantages of Voice Broking in Financial Markets
Voice broking in financial markets offers personalized negotiation that allows brokers to leverage human judgment and market intuition, resulting in tailored trade executions. This method facilitates complex deal structuring and confidential exchanges, which are often challenging to replicate through electronic platforms. Voice broking also enables immediate feedback and relationship-building, enhancing trust and collaboration between market participants.
Benefits of Electronic Broking for Traders and Institutions
Electronic broking platforms offer traders and institutions enhanced speed and efficiency in executing orders, reducing transaction costs through automated processes. These platforms provide increased transparency and real-time market data, enabling more informed decision-making and improved price discovery. Access to a broader range of liquidity pools and advanced algorithmic trading tools further optimizes execution quality and market access.
Challenges Faced by Voice Broking in the Digital Era
Voice broking faces significant challenges in the digital era due to slower transaction speeds and higher operational costs compared to electronic broking platforms. The reliance on manual communication increases the risk of miscommunication and limits market transparency, making it difficult to meet the demands of speed and efficiency in modern trading. Furthermore, voice broking struggles to integrate advanced data analytics and automated risk management tools that are standard features in electronic broking systems.
Security and Compliance: Voice vs Electronic Broking
Voice broking involves direct human interaction, which increases the risk of miscommunication and potential regulatory breaches due to less standardized processes. Electronic broking platforms enforce automated compliance checks and encryption protocols, reducing errors and enhancing transaction security. Firms leveraging electronic broking benefit from audit trails and real-time monitoring, ensuring adherence to industry regulations and minimizing fraud exposure.
Impact of Technology on Broking Efficiency
Voice broking relies on telephone and verbal communication, limiting transaction speed and increasing human error risks, while electronic broking platforms streamline trade execution through automated algorithms and real-time data integration. The adoption of technology in electronic broking significantly enhances market transparency and reduces operational costs by minimizing manual intervention and increasing trade processing speed. Advanced algorithms in electronic broking also optimize price discovery and liquidity, transforming traditional brokerage models into more efficient and scalable systems.
Client Preferences: When to Choose Voice or Electronic Broking
Clients often prefer voice broking for complex, high-value transactions requiring personalized negotiation and real-time market insights. Electronic broking suits straightforward, high-frequency trades where speed, transparency, and automation reduce operational costs and enhance execution efficiency. Choosing between voice and electronic broking depends on the trade's complexity, urgency, and the client's need for tailored communication versus rapid, algorithm-driven execution.
Future Trends in the Broking Industry
Voice broking maintains a crucial role in handling complex negotiations and large, bespoke transactions where human judgment and relationship management are key. Electronic broking platforms, driven by AI and machine learning algorithms, continue to increase market efficiency by enabling faster trade execution, improved price transparency, and reduced operational costs. Future trends indicate a hybrid model where voice broking integrates advanced analytics and automation tools, enhancing decision-making while preserving personalized client interaction.
Important Terms
Hybrid Broking
Hybrid broking combines the personalized negotiation of voice broking with the speed and efficiency of electronic broking platforms, optimizing trade execution and market access for financial professionals.
Order Matching Engine
Order matching engines in voice broking rely on manual trader interactions to execute trades, whereas electronic broking platforms utilize automated algorithms to efficiently match orders with higher speed and accuracy.
Voice Trading
Voice trading leverages human brokers' expertise and negotiation skills, enabling personalized and complex financial transactions, whereas electronic broking platforms facilitate faster, automated trades with increased transparency and reduced operational costs. Financial institutions often combine voice and electronic broking to optimize liquidity access, mitigate counterparty risk, and enhance market efficiency in foreign exchange and fixed-income markets.
Electronic Communication Network (ECN)
Electronic Communication Networks (ECNs) enhance voice broking by automating trade matching and increasing transparency, while electronic broking systems eliminate voice interaction entirely, offering faster and more efficient trade execution in financial markets.
Straight-Through Processing (STP)
Straight-Through Processing (STP) enhances efficiency in electronic broking by automating transaction workflows, whereas voice broking relies on manual communication, increasing the risk of errors and processing delays.
Dark Pools
Dark pools facilitate large block trades with reduced market impact, where voice broking offers personalized negotiation while electronic broking provides faster, algorithm-driven execution.
Dealer Intervention
Dealer intervention in voice broking offers personalized negotiation flexibility, whereas electronic broking prioritizes speed and automated efficiency in trade execution.
Latency Arbitrage
Latency arbitrage exploits millisecond differences in market data transmission between voice broking and electronic broking platforms to gain trading advantages. Electronic broking's faster execution speeds and direct market access create opportunities for latency-sensitive traders to capitalize on slower voice broking communication delays.
Interdealer Broker
Interdealer brokers facilitate voice broking by offering personalized negotiation services, while electronic broking platforms enhance market transparency and speed through automated trade execution.
Price Discovery
Price discovery in voice broking relies on direct human interaction and negotiation, often resulting in flexible pricing, while electronic broking leverages algorithmic trading and real-time data to achieve faster, transparent, and more efficient market price formation.
Voice Broking vs Electronic Broking Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com