Baseline budget establishes a fixed financial plan based on initial assumptions and historical data, serving as a reference point for measuring performance. Forecast budget projects future financial outcomes by incorporating recent trends, market changes, and updated assumptions to provide a dynamic, adaptable estimate. Comparing baseline and forecast budgets enables organizations to identify variances, adjust strategies, and improve financial planning accuracy.
Table of Comparison
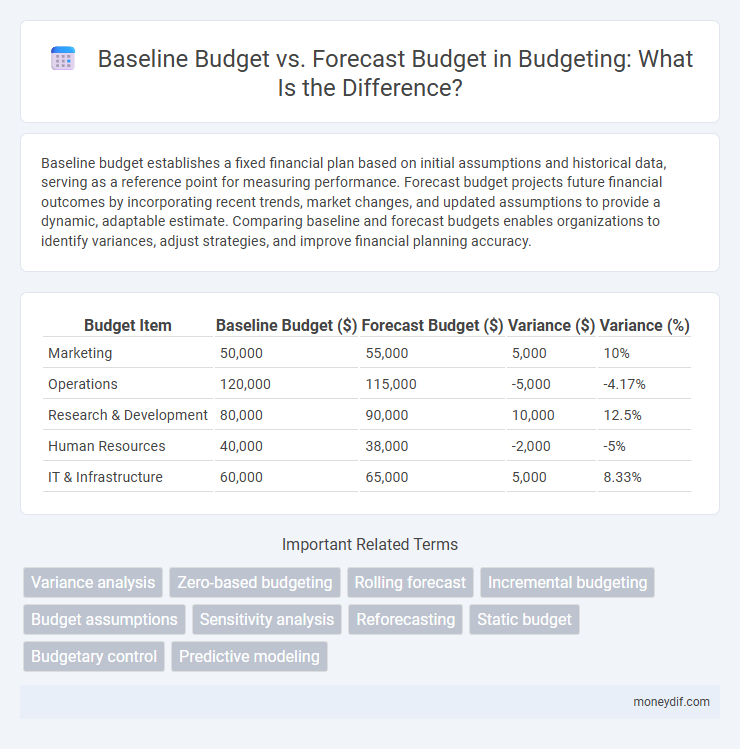
| Budget Item | Baseline Budget ($) | Forecast Budget ($) | Variance ($) | Variance (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marketing | 50,000 | 55,000 | 5,000 | 10% |
| Operations | 120,000 | 115,000 | -5,000 | -4.17% |
| Research & Development | 80,000 | 90,000 | 10,000 | 12.5% |
| Human Resources | 40,000 | 38,000 | -2,000 | -5% |
| IT & Infrastructure | 60,000 | 65,000 | 5,000 | 8.33% |
Defining Baseline Budget and Forecast Budget
The baseline budget represents the initial financial plan established at the start of a fiscal period, detailing expected revenues and expenditures based on historical data and strategic goals. The forecast budget is a revised projection that updates the baseline budget by incorporating actual performance metrics and adjusted assumptions to predict future financial outcomes. Accurate differentiation between these budgets is crucial for effective financial management and resource allocation.
Key Differences Between Baseline and Forecast Budgets
A baseline budget represents the original financial plan established at the start of a fiscal period, serving as a control against which actual performance is measured. In contrast, a forecast budget is a dynamic projection that adjusts anticipated revenues and expenses based on current trends and updated information. Key differences include the baseline budget's fixed nature for comparison and the forecast budget's flexibility to guide decision-making in response to changing conditions.
Purpose and Importance of Each Budget Type
Baseline budgets establish the initial financial plan based on historical data and set spending limits for a specific period, serving as a benchmark for performance evaluation. Forecast budgets predict future financial outcomes by incorporating current trends, market conditions, and expected changes, enabling proactive adjustments. Understanding the purpose and importance of each budget type enhances strategic decision-making and resource allocation accuracy.
Components of a Baseline Budget
The baseline budget consists of fixed costs such as rent, salaries, and utility expenses, forming a stable financial foundation. Variable costs, including materials and production expenses, are also included to reflect operational flexibility. This comprehensive structure enables effective comparison with forecast budgets that adjust for anticipated changes in market conditions and business goals.
Elements of a Forecast Budget
A forecast budget incorporates variable revenue projections and anticipated expenses based on market trends, seasonal fluctuations, and operational adjustments. It factors in elements like updated sales data, inflation rates, and cost of goods sold to provide a dynamic financial plan. Unlike the static baseline budget, the forecast budget adapts to real-time information, ensuring more accurate cash flow management and resource allocation.
When to Use Baseline vs Forecast Budgets
Baseline budgets are essential during the initial planning phase, providing a fixed reference point for expected revenues and expenses based on historical data and standard assumptions. Forecast budgets become critical when adjusting to changing market conditions, new business initiatives, or updated financial projections to reflect more dynamic and realistic financial outcomes. Using baseline budgets supports stability and performance measurement, while forecast budgets enable proactive decision-making and resource allocation in response to evolving business environments.
Impact on Project Management and Decision Making
Baseline budget establishes the original cost expectations and serves as a reference point for tracking project performance and identifying variances. Forecast budget reflects updated cost estimates based on current project progress and emerging risks, enabling proactive adjustments and resource reallocation. Accurate comparison between baseline and forecast budgets enhances decision-making, improves risk management, and supports timely corrective actions to ensure project success.
Common Challenges and Pitfalls
Baseline budgets often suffer from rigidity, failing to account for market fluctuations and unforeseen expenses, which leads to inaccuracies in financial planning. Forecast budgets face challenges in predicting future revenues and costs accurately due to volatile economic conditions and changing business environments. Both approaches risk misallocation of resources and can undermine strategic decision-making if they do not incorporate dynamic adjustments and continuous monitoring.
Best Practices for Effective Budgeting
Establishing a precise baseline budget is crucial for tracking financial performance against initial assumptions, enabling organizations to identify variances early. Regularly updating the forecast budget with real-time data improves accuracy by reflecting current market conditions and operational changes. Best practices include integrating baseline and forecast analyses into a continuous budgeting cycle to enhance decision-making and resource allocation efficiency.
Tools and Techniques for Budget Comparison
Baseline budget serves as the original plan against which financial performance is measured, while forecast budget projects future financial outcomes based on current trends. Tools and techniques for budget comparison include variance analysis, which identifies differences between baseline and forecast figures, and trend analysis, which evaluates historical data to predict future deviations. Software platforms like Microsoft Excel and specialized budgeting tools such as Adaptive Insights enable dynamic scenario modeling and real-time data visualization for effective budget comparison.
Important Terms
Variance analysis
Variance analysis quantifies the differences between the baseline budget and forecast budget, identifying deviations in revenue, expenses, and cash flow projections. It provides crucial insights into budget accuracy and financial performance, enabling organizations to adjust strategies and improve future forecasting.
Zero-based budgeting
Zero-based budgeting starts from a "zero base," requiring justification for all expenses, unlike baseline budgeting which adjusts previous budgets incrementally. Forecast budgeting utilizes historical data and trends to predict future financial needs, whereas zero-based budgeting demands a fresh evaluation of all cost drivers each period.
Rolling forecast
Rolling forecast continually updates financial projections by integrating actual performance data, providing a dynamic comparison against the static baseline budget. This approach enhances budget accuracy and agility, enabling businesses to adjust strategies based on evolving market conditions and operational changes.
Incremental budgeting
Incremental budgeting adjusts the baseline budget by applying changes based on new forecasts, emphasizing slight modifications rather than complete overhauls. This method simplifies budgeting by using the prior period's budget as a foundation and updating it with forecasted increases or decreases in costs and revenues.
Budget assumptions
Budget assumptions underpin the baseline budget by establishing expected revenues, costs, and economic conditions at the project's inception, serving as benchmarks for performance measurement. Forecast budgets adjust these assumptions dynamically based on real-time data and market trends, providing updated financial projections to guide decision-making and resource allocation.
Sensitivity analysis
Sensitivity analysis quantifies how changes in key variables impact the differences between baseline and forecast budgets, identifying financial risks and opportunities. By examining variations in revenue, costs, and assumptions, it enhances budget accuracy and supports informed decision-making.
Reforecasting
Reforecasting involves updating the forecast budget by incorporating actual performance data and changes in assumptions to ensure more accurate financial planning compared to the baseline budget. This process helps identify variances between the baseline budget and forecast budget, enabling organizations to adjust strategies and improve budgetary control.
Static budget
A static budget remains fixed based on the baseline budget, serving as a standard for evaluating actual performance without adjustments for changes in activity levels. In contrast, a forecast budget adjusts projections according to updated assumptions and anticipated operational changes, providing a dynamic comparison against actual results.
Budgetary control
Budgetary control involves monitoring actual expenditures against the baseline budget, which is a fixed financial plan established at the start of a fiscal period, ensuring adherence to initial cost limits. Forecast budgets, updated periodically based on current financial trends and performance data, allow for more dynamic adjustments and improved financial decision-making within the budgetary control process.
Predictive modeling
Predictive modeling in budget management harnesses historical data to generate accurate forecast budgets that serve as benchmarks against baseline budgets, enabling organizations to identify potential variances and optimize financial planning. Techniques such as regression analysis and machine learning algorithms enhance the precision of forecast budgets, improving resource allocation and risk management.
baseline budget vs forecast budget Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com