Envelope budgeting allocates fixed amounts of money to specific spending categories, helping control expenses by limiting funds within predetermined envelopes. Activity-based budgeting, by contrast, bases budget allocation on the costs of activities required to produce goods or services, offering a more detailed and accurate financial planning approach. This method improves resource allocation efficiency by linking expenses directly to business activities and performance outcomes.
Table of Comparison
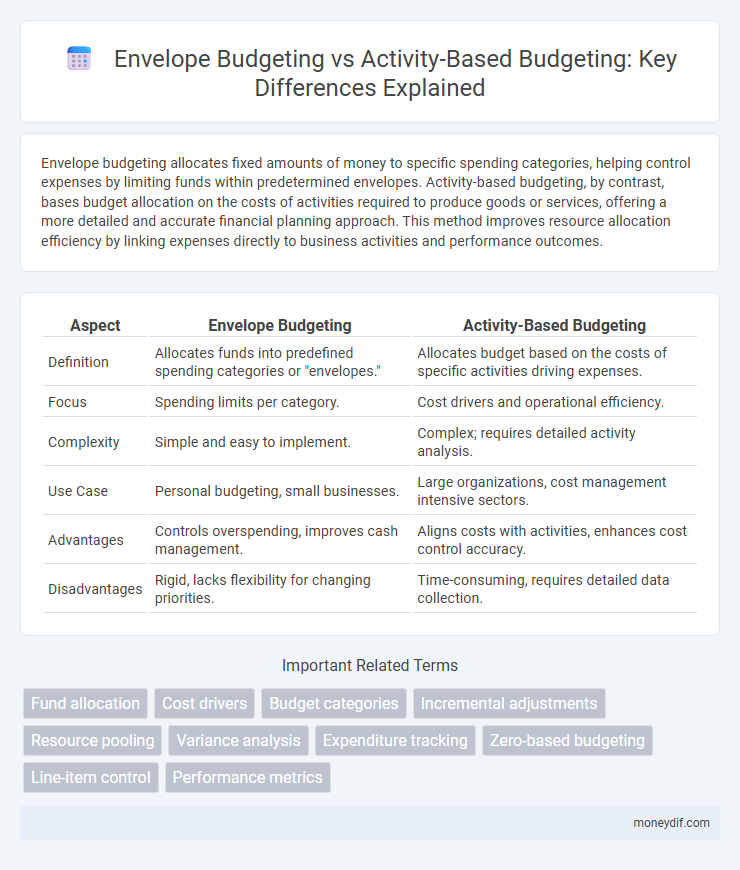
| Aspect | Envelope Budgeting | Activity-Based Budgeting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Allocates funds into predefined spending categories or "envelopes." | Allocates budget based on the costs of specific activities driving expenses. |
| Focus | Spending limits per category. | Cost drivers and operational efficiency. |
| Complexity | Simple and easy to implement. | Complex; requires detailed activity analysis. |
| Use Case | Personal budgeting, small businesses. | Large organizations, cost management intensive sectors. |
| Advantages | Controls overspending, improves cash management. | Aligns costs with activities, enhances cost control accuracy. |
| Disadvantages | Rigid, lacks flexibility for changing priorities. | Time-consuming, requires detailed data collection. |
Introduction to Envelope Budgeting and Activity-Based Budgeting
Envelope budgeting allocates funds into specific categories or "envelopes" to control spending and ensure financial discipline. Activity-based budgeting assigns costs to business activities based on resource consumption, providing a more accurate reflection of expenses tied to operational tasks. Both methods enhance budget management but differ in complexity and precision.
Core Principles of Envelope Budgeting
Envelope budgeting allocates fixed amounts of money to specific categories, helping individuals control spending by using only the allocated cash for each envelope. The core principle emphasizes strict budget limits per category, preventing overspending and promoting financial discipline. This method contrasts with activity-based budgeting, which focuses on the costs of activities driving expenses rather than fixed category allocations.
Key Concepts in Activity-Based Budgeting
Activity-Based Budgeting (ABB) centers on identifying cost drivers and allocating resources based on activities required to produce goods or services, contrasting with Envelope Budgeting's fixed allocation of funds to departments. ABB enhances cost accuracy by linking budgeting to operational activities, enabling more precise forecasting and efficiency improvements. Key concepts include activity analysis, cost driver determination, and budget formulation aligned with planned activity levels.
Comparing Envelope and Activity-Based Budgeting Methods
Envelope budgeting allocates fixed spending limits to specific categories, enhancing simplicity and control but lacking flexibility for dynamic business environments. Activity-based budgeting (ABB) links expenses to actual business activities, providing detailed insights into cost drivers and enabling more precise resource allocation. Comparing both, envelope budgeting suits straightforward financial planning, while ABB excels in complex operations requiring granular cost analysis and performance optimization.
Pros and Cons of Envelope Budgeting
Envelope budgeting offers a straightforward way to control spending by allocating fixed amounts to specific categories, which helps prevent overspending and encourages disciplined financial management. However, it lacks flexibility for unforeseen expenses and may not accurately reflect the dynamic nature of personal or organizational financial needs. The method's simplicity can lead to inefficiencies as it doesn't account for the varying costs and resource demands of different activities, unlike Activity-Based Budgeting which provides a more detailed and adaptable approach.
Advantages and Limitations of Activity-Based Budgeting
Activity-based budgeting (ABB) improves cost accuracy by aligning budget allocations with specific business activities, enabling more precise resource management compared to traditional envelope budgeting. ABB enhances decision-making through detailed analysis of activity costs but requires significant data collection and analysis efforts, which can increase complexity and administrative overhead. Limited applicability in organizations with less defined processes restricts ABB's effectiveness, making it less suitable for small businesses with simpler operations.
Suitability for Personal vs. Business Finance
Envelope budgeting is highly suitable for personal finance because it simplifies expense tracking by allocating cash into categorized envelopes, promoting disciplined spending. Activity-based budgeting is tailored for business finance, where it allocates costs based on activities and operational drivers, providing detailed insights for strategic planning. Personal finance benefits from the straightforward framework of envelope budgeting, while businesses require the analytical depth of activity-based budgeting to optimize resource allocation.
Implementation Steps for Each Budgeting Approach
Envelope budgeting implementation starts with allocating fixed spending limits to predefined categories, followed by tracking expenses strictly within these envelopes to control costs effectively. Activity-based budgeting requires identifying key activities and their cost drivers, estimating resource needs for each activity, and assigning budget amounts based on activity consumption patterns. Monitoring and adjusting budgets regularly ensures alignment with organizational goals in both approaches.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Envelope budgeting often faces challenges such as inflexibility and difficulty in adjusting funds to dynamic expenses, while activity-based budgeting struggles with complexity in accurately assigning costs to specific activities. Both methods require robust tracking systems and regular reviews to ensure alignment with financial goals and operational realities. Implementing integrated software solutions and consistent team training can mitigate these challenges by enhancing accuracy and adaptability in budget management.
Choosing the Right Budgeting Method for Your Needs
Envelope budgeting simplifies expense management by allocating fixed spending limits to categories, ideal for individuals prioritizing control and straightforward tracking. Activity-based budgeting allocates funds based on detailed analysis of business activities, enhancing precision for organizations seeking strategic cost management. Selecting the appropriate budgeting method depends on the complexity of financial goals and the need for either simplicity or detailed resource allocation.
Important Terms
Fund allocation
Envelope budgeting allocates funds into predefined spending categories to control expenses, while Activity-based budgeting assigns costs based on specific activities driving resource consumption for more precise financial management.
Cost drivers
Cost drivers in envelope budgeting focus on broad expenditure categories, while activity-based budgeting allocates costs based on specific activities driving resource consumption.
Budget categories
Envelope budgeting allocates fixed spending limits to predefined budget categories, while activity-based budgeting assigns costs based on specific business activities and resource usage.
Incremental adjustments
Incremental adjustments in envelope budgeting allocate fixed funds based on prior budgets, whereas activity-based budgeting adjusts resources according to detailed cost drivers and operational activities for more precise expenditure control.
Resource pooling
Resource pooling enhances cost control by consolidating shared expenses in envelope budgeting, whereas activity-based budgeting allocates resources more precisely based on specific activities and cost drivers.
Variance analysis
Variance analysis evaluates cost differences by comparing Envelope budgeting's fixed budget limits with Activity-based budgeting's detailed cost driver estimates for more accurate performance measurement.
Expenditure tracking
Expenditure tracking in envelope budgeting allocates fixed funds to specific categories for controlled spending, while activity-based budgeting tracks costs based on business activities to optimize resource allocation and efficiency.
Zero-based budgeting
Zero-based budgeting allocates funds by justifying every expense from scratch, contrasting with envelope budgeting's fixed spending limits and activity-based budgeting's focus on costs linked to specific activities.
Line-item control
Line-item control focuses on strict expenditure limits per budget category, often used in Envelope budgeting, whereas Activity-based budgeting allocates funds based on specific activities and their cost drivers for more precise resource management.
Performance metrics
Activity-based budgeting improves performance metrics by allocating costs based on actual activities, offering more accurate expense tracking compared to the broad estimates used in envelope budgeting.
Envelope budgeting vs Activity-based budgeting Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com