Encumbered funds represent budgeted amounts reserved for specific obligations or contracts yet to be paid, ensuring financial commitment without immediate cash outflow. Expended funds refer to actual disbursements made against the budget for goods or services received. Monitoring the distinction between encumbered and expended funds is critical for accurate budget management and cash flow forecasting.
Table of Comparison
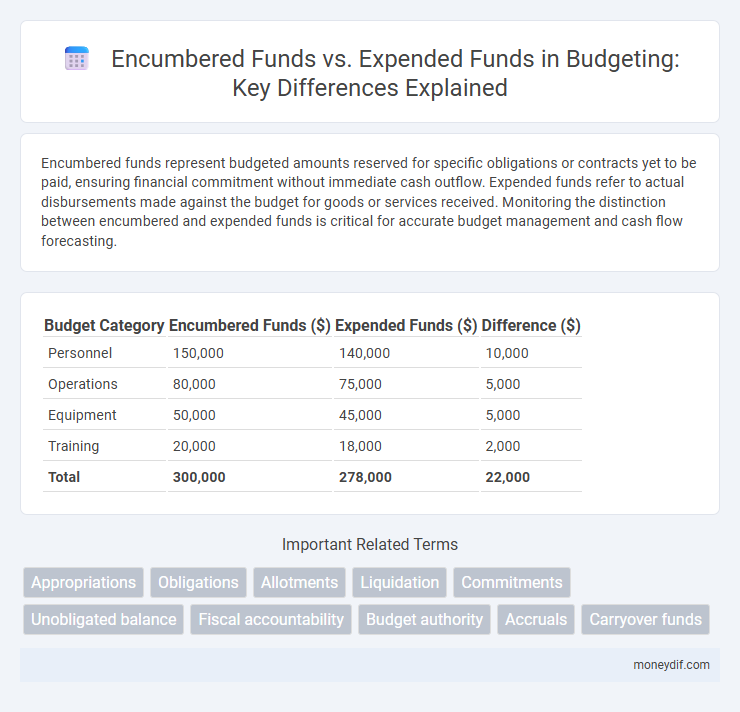
| Budget Category | Encumbered Funds ($) | Expended Funds ($) | Difference ($) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Personnel | 150,000 | 140,000 | 10,000 |
| Operations | 80,000 | 75,000 | 5,000 |
| Equipment | 50,000 | 45,000 | 5,000 |
| Training | 20,000 | 18,000 | 2,000 |
| Total | 300,000 | 278,000 | 22,000 |
Understanding Encumbered Funds in Budgeting
Encumbered funds represent money set aside in a budget to cover future expenses, ensuring that committed resources are reserved but not yet spent. These funds differ from expended funds, which reflect actual payments made and recorded in financial reports. Understanding encumbered funds is crucial for accurate budget management, as it helps organizations prevent overspending by distinguishing between committed obligations and liquidated costs.
What Are Expended Funds?
Expended funds refer to the actual amount of money spent or disbursed from a budget to pay for goods, services, or obligations during a specific period. These funds indicate completed financial transactions and reflect the real outflow of resources, unlike encumbered funds, which represent committed but not yet spent amounts. Tracking expended funds helps organizations monitor cash flow, ensure budget compliance, and evaluate financial performance accurately.
Key Differences: Encumbered vs Expended Funds
Encumbered funds represent budgeted amounts reserved for specific future expenses, ensuring obligations are accounted for before actual payment. Expended funds indicate the portion of the budget that has been spent or paid out, reflecting finalized financial transactions. Understanding the distinction between encumbered and expended funds is crucial for accurate budget tracking and fiscal management.
The Role of Encumbered Funds in Financial Planning
Encumbered funds represent committed financial resources allocated for specific expenses but not yet expended, playing a crucial role in accurate budget forecasting and cash flow management. Tracking encumbrances ensures organizations do not overcommit resources, maintaining fiscal discipline and providing a clearer picture of available funds versus actual expenditures. Proper management of encumbered funds supports strategic planning by aligning committed obligations with anticipated cash outflows, enhancing overall financial stability.
Tracking Expended Funds in Your Budget
Tracking expended funds in your budget ensures accurate financial management by monitoring actual cash outflows against planned allocations. This process enables timely identification of overspending or underspending, facilitating effective adjustments to maintain fiscal discipline. Employing real-time budget tracking software enhances transparency and supports strategic decision-making in managing organizational resources.
How to Manage Encumbered Funds Effectively
Managing encumbered funds effectively requires accurate tracking to ensure obligations align with available budget and prevent overspending. Implementing robust financial software can provide real-time visibility into encumbrances versus actual expenditures, facilitating timely adjustments. Regular reconciliation between encumbered and expended funds helps maintain budget integrity and supports informed decision-making.
Common Mistakes with Encumbered and Expended Funds
Common mistakes with encumbered and expended funds include failing to accurately differentiate obligations from actual expenditures, leading to distorted budget reports. Misclassifying funds as expended when they remain encumbered can cause overspending and cash flow issues. Consistently monitoring and reconciling encumbrances with actual expenses prevents errors in financial statements and ensures compliance with fiscal policies.
Reporting Requirements: Encumbered vs Expended Funds
Reporting requirements for encumbered funds mandate the documentation of commitments made through purchase orders or contracts, reflecting obligations that reduce available budget but do not yet represent cash outflows. Expended funds reporting focuses on actual disbursements, providing transparency on cash outflows and financial performance during the fiscal period. Accurate distinction between encumbered and expended funds ensures compliance with accounting standards and enables effective budgetary control and fiscal accountability.
Impact of Encumbrances on Year-End Budgets
Encumbered funds represent committed expenses that reduce the available budget but are not yet spent, while expended funds reflect actual cash outflows during the fiscal year. The impact of encumbrances on year-end budgets is significant because they restrict the remaining budget balance, potentially limiting new spending authority despite unspent appropriations. Accurately tracking and managing encumbrances ensures precise financial reporting and prevents overspending in subsequent periods.
Best Practices for Monitoring Encumbered and Expended Funds
Effective monitoring of encumbered and expended funds involves maintaining accurate, real-time tracking systems that clearly distinguish commitments from actual expenditures. Implementing routine reconciliations between budgeted amounts, encumbrances, and disbursements ensures transparency and prevents overspending. Leveraging financial management software with automated alerts supports proactive decision-making and compliance with budgetary constraints.
Important Terms
Appropriations
Appropriations represent the total budget authorized for specific government expenditures, while encumbered funds refer to the portion of these appropriations reserved for outstanding purchase orders or contracts, guaranteeing their availability upon settlement. Expended funds are the actual amounts spent or disbursed, reducing both the encumbered funds and overall appropriations accordingly.
Obligations
Obligations represent committed funds legally reserved for specific purposes, thereby reducing available budgetary resources, while expended funds refer to actual disbursements made to fulfill those commitments. Monitoring obligations versus expenditures is essential for accurate financial reporting and ensuring compliance with fiscal regulations on encumbered funds.
Allotments
Allotments represent the maximum amount of funds allocated for specific purposes, serving as a control mechanism to prevent overspending. Encumbered funds are portions of the allotments reserved for committed obligations, while expended funds reflect the actual disbursements made from these allotments.
Liquidation
Liquidation involves the conversion of encumbered funds, which are legally obligated but not yet spent, into expended funds representing actual disbursements or payments made. Monitoring the difference between encumbered and expended funds is crucial for accurate financial reporting and budget compliance.
Commitments
Commitments represent funds obligated for future expenses, often categorized as encumbered funds, which are reserved but not yet spent, ensuring budget control and financial planning accuracy. Expended funds refer to actual disbursements made, reducing available budget and reflecting finalized transactions in accounting records.
Unobligated balance
Unobligated balance represents the portion of budgetary funds not yet committed through encumbrances or expenditures, reflecting available resources for future obligations. Encumbered funds indicate commitments made but not yet paid, while expended funds are those fully disbursed, highlighting distinct stages in financial management and budget execution.
Fiscal accountability
Fiscal accountability ensures that encumbered funds, which are legally reserved for specific future expenses, are accurately tracked and distinguished from expended funds that have been fully disbursed. Proper management and reporting of these financial commitments prevent budget overruns and maintain transparency in government or organizational financial operations.
Budget authority
Budget authority represents the legal permission granted to incur financial obligations, distinguishing encumbered funds as amounts reserved for specific commitments, whereas expended funds reflect actual payments made. Monitoring the difference between encumbered and expended funds ensures accurate tracking of available budget resources and financial obligations within fiscal management.
Accruals
Accruals represent expenses recognized before cash payment, impacting the distinction between encumbered and expended funds by reflecting obligations incurred but not yet paid. Encumbered funds denote committed budget amounts reserved for future expenses, while expended funds indicate actual cash outflows, with accrual accounting bridging the timing gap between these financial statuses.
Carryover funds
Carryover funds refer to unspent budget allocations that remain available for use in subsequent fiscal periods, often encompassing encumbered funds, which are committed but not yet expended. Expended funds represent the actual money spent, differentiating them from encumbered funds that are reserved for future obligations within the carryover balance.
encumbered funds vs expended funds Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com