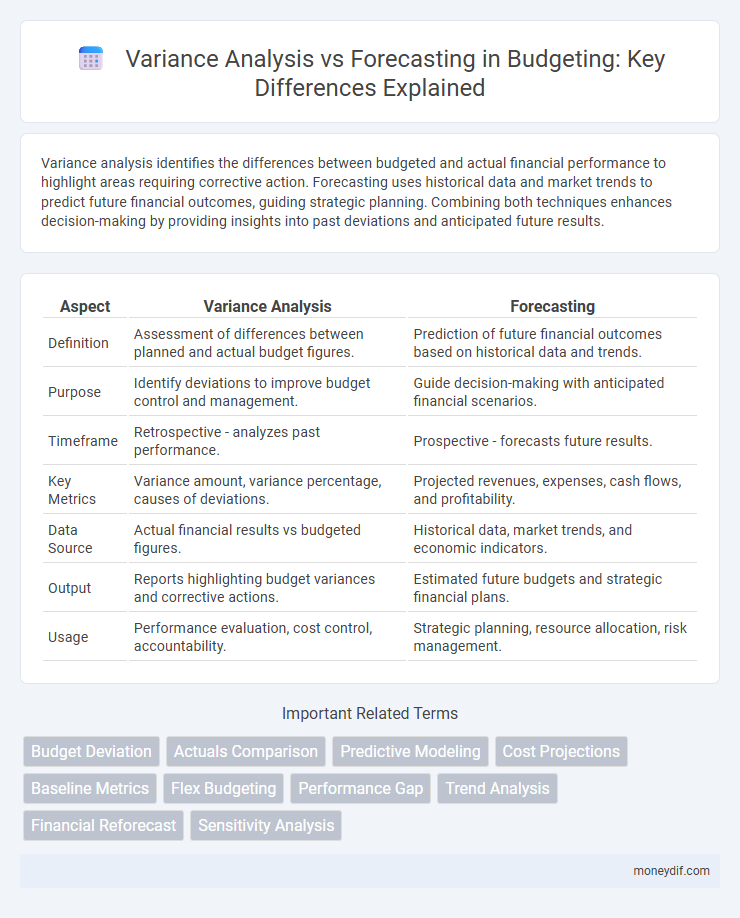
Variance analysis identifies the differences between budgeted and actual financial performance to highlight areas requiring corrective action. Forecasting uses historical data and market trends to predict future financial outcomes, guiding strategic planning. Combining both techniques enhances decision-making by providing insights into past deviations and anticipated future results.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Variance Analysis | Forecasting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Assessment of differences between planned and actual budget figures. | Prediction of future financial outcomes based on historical data and trends. |
| Purpose | Identify deviations to improve budget control and management. | Guide decision-making with anticipated financial scenarios. |
| Timeframe | Retrospective - analyzes past performance. | Prospective - forecasts future results. |
| Key Metrics | Variance amount, variance percentage, causes of deviations. | Projected revenues, expenses, cash flows, and profitability. |
| Data Source | Actual financial results vs budgeted figures. | Historical data, market trends, and economic indicators. |
| Output | Reports highlighting budget variances and corrective actions. | Estimated future budgets and strategic financial plans. |
| Usage | Performance evaluation, cost control, accountability. | Strategic planning, resource allocation, risk management. |
Understanding Variance Analysis in Budgeting
Variance analysis in budgeting involves comparing actual financial performance against budgeted figures to identify discrepancies and their causes. This process helps organizations pinpoint areas where spending deviates from plans, enabling corrective actions to control costs and improve financial accuracy. Understanding variance analysis is essential for effective budget management, ensuring resources are allocated efficiently and financial goals are met.
What is Forecasting in Financial Planning?
Forecasting in financial planning involves predicting future financial outcomes based on historical data, market trends, and economic indicators to guide budgeting and strategic decisions. It enables organizations to anticipate revenues, expenses, and cash flows, facilitating more accurate resource allocation and risk management. Effective forecasting supports proactive financial management by aligning business goals with expected financial performance.
Key Differences Between Variance Analysis and Forecasting
Variance analysis evaluates past financial performance by comparing actual results to budgeted figures, identifying deviations and their causes. Forecasting involves predicting future financial outcomes based on historical data, market trends, and planned activities to guide strategic decision-making. Key differences lie in their temporal focus--variance analysis is retrospective, while forecasting is prospective--and their primary purpose of performance evaluation versus future planning.
Purpose and Objectives of Variance Analysis
Variance analysis serves to identify and quantify deviations between budgeted and actual financial performance, enabling organizations to pinpoint areas of over or underperformance. Its primary objective is to provide actionable insights that facilitate corrective measures and enhance financial control. This process supports management in aligning operations with strategic financial goals by highlighting inefficiencies and cost overruns.
The Role of Forecasting in Budget Management
Forecasting plays a crucial role in budget management by predicting future financial outcomes based on historical data and market trends, enabling organizations to allocate resources efficiently. It supports variance analysis by providing baseline expectations against which actual performance is measured, helping identify deviations and underlying causes. Accurate forecasting enhances decision-making, risk management, and strategic planning to achieve financial goals.
Data Requirements for Variance Analysis vs Forecasting
Variance analysis requires detailed historical financial data, actual performance figures, and budgeted amounts to identify deviations and analyze causes of differences. Forecasting depends on current and historical data trends, external market indicators, and predictive models to project future financial outcomes. Accurate variance analysis demands granular transaction-level data, while forecasting benefits from broader datasets including macroeconomic variables and industry benchmarks.
Benefits of Variance Analysis for Organizations
Variance analysis provides organizations with critical insights into financial performance by comparing actual results with budgeted figures. It enables timely identification of deviations, facilitating corrective actions to control costs and improve resource allocation. Enhanced decision-making and operational efficiency stem from understanding the causes of variances, leading to better financial planning and strategic management.
How Forecasting Improves Budget Accuracy
Forecasting improves budget accuracy by using historical data and predictive analytics to estimate future financial performance more precisely, reducing the likelihood of variances between actual and planned expenses. Advanced forecasting models incorporate real-time market trends and economic indicators, enabling organizations to adjust budgets proactively and allocate resources more effectively. Continuous forecasting updates narrow the gap between expected and actual budget outcomes, facilitating better financial decision-making and operational efficiency.
Integrating Variance Analysis with Forecasting Techniques
Integrating variance analysis with forecasting techniques enhances budget accuracy by identifying discrepancies between projected and actual financial performance, enabling timely adjustments. Leveraging historical variance data improves predictive models, refining future budget forecasts and allowing more responsive financial planning. This synergy supports proactive decision-making, optimizing resource allocation and minimizing budgetary risks.
Best Practices for Effective Budget Control
Effective budget control hinges on combining variance analysis and forecasting to identify discrepancies and predict future financial outcomes accurately. Best practices include regularly monitoring budget variances to pinpoint areas of overspending or inefficiency, while updating forecasts based on real-time data to adjust resource allocation proactively. Leveraging integrated financial software and fostering cross-departmental collaboration enhances accuracy and responsiveness in maintaining budget adherence.
Important Terms
Budget Deviation
Budget deviation quantifies the difference between actual expenses and budgeted amounts, serving as a key metric in variance analysis. Forecasting enhances budgeting accuracy by predicting future financial trends, enabling proactive identification and management of potential budget deviations.
Actuals Comparison
Actuals Comparison in Variance Analysis involves evaluating real financial or operational results against Forecasting data to identify deviations and performance gaps. This process helps organizations pinpoint areas where actual outcomes differ from projected estimates, enabling targeted corrective actions and improved future forecasting accuracy.
Predictive Modeling
Predictive modeling integrates variance analysis by identifying deviations between actual and expected outcomes to enhance forecasting accuracy. Leveraging historical data patterns and variance trends allows predictive models to generate more precise future projections for decision-making.
Cost Projections
Cost projections integrate variance analysis by identifying deviations between actual and budgeted expenses to refine forecasting accuracy. Forecasting models leverage these variances to adjust cost estimates, enhancing financial planning and resource allocation.
Baseline Metrics
Baseline metrics provide a reference point for evaluating variance analysis by measuring actual performance against initial assumptions or historical averages. Forecasting relies on these baseline metrics to adjust predictions and minimize discrepancies between expected and real outcomes through continuous variance assessment.
Flex Budgeting
Flex budgeting enhances variance analysis by adjusting budgeted costs based on actual activity levels, providing a more accurate measure of performance deviations compared to static budgets. Unlike forecasting, which predicts future financial outcomes using historical data and trends, flex budgeting dynamically recalibrates budgets to reflect real-time operational changes, improving decision-making precision.
Performance Gap
Performance Gap represents the difference between actual results and forecasted outcomes, critical for identifying variances in financial or operational metrics. Variance Analysis quantifies this gap by comparing observed performance against projections, enabling more accurate forecasting and strategic adjustments.
Trend Analysis
Trend analysis identifies patterns in historical data to predict future outcomes, serving as a foundational input for variance analysis by highlighting deviations between actual performance and expected trends. Forecasting builds on trend analysis by using statistical models to project future values, while variance analysis evaluates the differences between these forecasts and actual results to inform decision-making and improve accuracy.
Financial Reforecast
Financial reforecast integrates variance analysis by comparing actual financial outcomes against original forecasts to identify discrepancies and adjust projections accordingly. This process enhances accuracy in budgeting and strategic planning by continuously refining future forecasts based on real-time financial performance data.
Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity analysis evaluates how changes in input variables affect model outcomes, providing insights into the robustness of forecasting models by highlighting which variables contribute most to output variability. Variance analysis complements this by quantifying the deviation between forecasted and actual results, enabling more accurate adjustments and improved predictive accuracy in financial and operational planning.
Variance Analysis vs Forecasting Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com